People with immune deficiencies or lowered immunity such as people undergoing cancer chemotherapy or organ transplants or those infected with HIV-AIDS are at high risk for contracting this fungal infection. Cryptococcus gattii Formerly a variant of C.

Cryptococcus neoformans is a ubiquitous environmental fungus that can cause life-threatening meningitis and fungemia often in the presence of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS liver cirrhosis diabetes mellitus or other medical conditions.
Cryptococcus neoformans causes what disease. Neoformans infection in the lungs can cause a pneumonia-like illness. The symptoms are often similar to those of many other illnesses and can include. In the brain cryptococcal meningitis.
Cryptococcosis is caused by the fungus Cyptococcus neoformans. It is spread by contact with pigeon droppings unwashed raw fruit or by infected individuals. People with immune deficiencies or lowered immunity such as people undergoing cancer chemotherapy or organ transplants or those infected with HIV-AIDS are at high risk for contracting this fungal infection.
C neoformans and C gattii are the fungi that cause this disease. Infection with C neoformans is seen worldwide. Infection with C gattii has mainly been seen in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States British Columbia in Canada Southeast Asia and Australia.
Cryptococcus is the most common fungus that causes serious infection worldwide. Life-threatening infections caused by the encapsulated fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans have been increasing steadily over the past 10 years because of the onset of AIDS and the expanded use of immunosuppressive drugs. Intricate host-organism interactions make the full understanding of pathogenicity and virulence of C.
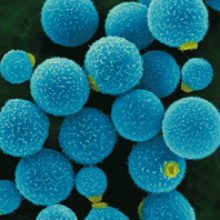
Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated fungal organism Figure 1 that can cause disease in apparently immunocompetent as well as immunocompromised hosts 1 2. Most susceptible to infection are patients with T-cell deficiencies 1 2. What Are the Signs and Symptoms Cryptococcosis.
Pleuritic chest pain sharp pain that occurs over the area of inflammation and increases with breathing movements Cough usually nonproductive. Hemoptysis bloody or blood tinged sputum Headache. Vision changes blurry or.
Two types of fungus can cause cryptococcal meningitis CM. They are called Cryptococcus neoformans C. Neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii C.
This disease is rare in healthy people. Cryptococcus neoformans is an encapsulated yeast that causes disease mainly in immunosuppressed hosts. It is considered a facultative intracellular pathogen because of its capacity to survive and replicate inside phagocytes especially macrophages.
Cryptococcus neoformans is a ubiquitous environmental fungus that can cause life-threatening meningitis and fungemia often in the presence of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS liver cirrhosis diabetes mellitus or other medical conditions. Cryptococcosis is a pulmonary or disseminated infection acquired by inhalation of soil contaminated with the encapsulated yeasts Cryptococcus neoformans or C. Symptoms are those of pneumonia meningitis or involvement of skin bones or viscera.
Diagnosis is clinical and microscopic confirmed by culture or fixed-tissue staining. Cryptococcosis is disease due to a species of the fungus Cryptococcus. Neoformans typically infects immunocompromised persons.
Most people in the United States who develop cryptococcal infections are HIV -positive. However occasionally persons with no apparent immune system problems develop cryptococcosis. Understanding the cause and progression of cryptococcosis in non-HIV cases will enable researchers to offer more effective treatments for this debilitating disease.
The fungus Cryptococcus neoformans can cause brain inflammation or meningitis. HIV infection is the most common risk factor for cryptococcosis due to C. Gattii infection with CNS involvement is frequently found in otherwise healthy individuals exposed to plant propagules found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Cryptococcusis believed to enter the body through the lung causing pulmonary disease but because of its neurotropic nature the central nervous system is a major target organ. The major risk factors include HIV and organ transplantation. Cryptococcus neoformans The best known and medically most relevant Cryptococcus species.
It is a major animal and human pathogen best known for causing severe forms of meningitis and meningoencephalitis. Cryptococcus gattii Formerly a variant of C. Neoformans it has recently been separated into a distinct species.
Cryptococcal disease is a very rare disease that can affect the lungs pneumonia and nervous system causing meningitis and focal brain lesions called cryptococcomas in humans. The main complication of lung infection is respiratory failure. Cryptococcus neoformans is the causative agent of cryptococcosis.
The most common clinical form of cryptococcosis is meningoencephalitis and the most common development motivator of cryptococcosis is AIDS. Meningitis is caused by C. Neoformans especially as a secondary infection for AIDS patients and is normally sub acute or chronic.