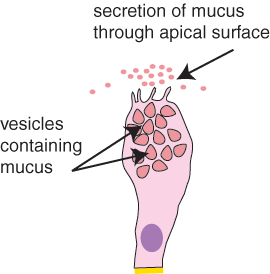
The remainder of the cell is filled with membrane-bound secretory granules filled with mucus. Location of Goblet Cells.

Intestinal metaplasia is said to occur when goblet cells grow in a place where it is not normal for them to do so.
What does a goblet cell do. Functions of Goblet Cells. Apart from comprising the epithelial lining of various organs production of large glycoproteins and carbohydrates the most important function of goblet cells is the secretion of mucus. This mucus is a gel-like substance that is composed mainly of mucins glycoproteins and carbohydrates.
Definition Goblet cells secrete mucus mucous glands Their product is packed in vesicles inside the cell and released by exocytosis merocrine glands They release their product on the surface of epithelium rather than in blood exocrine glands. Goblet cells are a type of intestinal mucosal epithelial cell which serves as the primary site for nutrient digestion and mucosal absorption. The primary function of goblet cells is to synthesize and secrete mucus.
Goblet Cells Definition. Goblet cells are a specialized type of epithelial cell that secrete mucins which are significant components. Structure of Goblet Cells.
Goblet cells get their name from their cup-like appearance. They are around a quarter as wide. Location of Goblet Cells.
Goblet cells are a specialized type of epithelial cell that secrete mucins which are significant components of mucus. They are most often found in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts where they make up part of the surface epithelium. The secretion of mucus in these tracts lubricates and protects the lining of the organs.
Goblet Cells The talent of goblet cells is to secrete mucus a viscous fluid composed primarily of highly glycosylated proteins called mucins suspended in a solution of electrolytes. Mucus serves many functions including protection against shear stress and chemical damage and especially in the respiratory tree trapping and elimination of particulate matter and microorganisms. Goblet cells are long slender cells found in most human organs that are almost entirely responsible for the production of mucus.
They occur most predominantly in the respiratory tract and they play an important role when it comes to helping the immune system flush out foreign bodies like pollen and smoke as well as viruses like that responsible for the common cold. Goblet cells are found in the intestines and respiratory system of mammals and the epidermis of fish. The main role of goblet cells is to secrete mucus in order to protect the mucous membrane where they are found.
Goblet cells accomplish this by s. Most of the esophagus is lined by squamous mucosa. Goblet cells normally line the intestines not the esophagus.
When goblet cells are found in a place where they are not supposed to be like the lining of the esophagus it is called intestinal metaplasia. Intestinal metaplasia can develop any place where squamous mucosa is normally found. The main role of goblet cells is to secrete mucus in order to protect the mucous membranes where they are found.
Goblet cells accomplish this by secreting mucins large glycoproteins formed mostly by carbohydrates. Why are goblet cells necessary for GI tract function. Of tall columnar cells called goblet cells because of their rough resemblance to empty goblets after they have discharged their contents.
Goblet cells are found scattered among the surface epithelial cells covering the villi and are a source of mucin the chief constituent of mucus. Regardless of fixation goblet cells have a distinctly polarized morphology. Their nucleus is at the base of the cell along with organelles such as mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi.
The remainder of the cell is filled with membrane-bound secretory granules filled with mucus. Goblet Cells - Science topic A glandular epithelial cell or a unicellular gland. Goblet cells secrete MUCUS.
They are scattered in the epithelial linings of many organs especially the SMALL. Goblet cells are a secretory epithelial cell lineage found in both the small and the large intestines. A major function of goblet cells is the production of mucus which forms a protective gel-like layer over the surface epithelium and protects against bacterial invasion Johansson et.
Epithelium is the tissue that forms the surfaces and linings of the body including the intestines. In the digestive tract this type of tissue is arranged to form a series of finger-like projections called villi that increase the surface area. It contains specialized goblet cells tiny glands that each contain a reservoir of mucus.
The density of the well developed goblet cell is a function of nuclear and cytoplasmic compression by the mass of mucigen. The fine structure of the resting goblet cell is indistinguishable from that of the principal columnar absorbing cells. It is characterized by the presence of goblet cellsand the absence of microvacuolated columnar cells.
Colorectal Goblet Cell Rich Hyperplastic Polyp NCI Thesaurus This group includes goblet cellrich mucin poor and microvesicular hyperplastic polyps. Colon Hyperplastic Polyp NCI Thesaurus. Gŏb lĭt Any of the specialized epithelial cells such as those found in the mucous membrane of the stomach intestines and respiratory passages that secrete mucus.
The goblet cells distend with mucin before secretion and collapse to a goblet. Goblet cells are normal in the gut but not in the esophagus. Intestinal metaplasia is said to occur when goblet cells grow in a place where it is not normal for them to do so.
In this case the esophagus. Barretts esophagus occurs when the mucosa of the esophagus changes its composition from squamous to goblet cells Ibarra 2012.