Quite obvious when ever there is blood loss it will also result in water loss and blood is nothing but water containing many cells and other constituents. Quite obvious when ever there is blood loss it will also result in water loss and blood is nothing but water containing many cells and other constituents.
Volumes of real losses that are significantly higher than what is economically justifiable indicate that action needs to be taken if the water supplier is to be viewed as water-efficient.
What are examples of water loss from humans. Some water is lost with feces too and a lot is lost in case of diarrhea. Water loss via bleeding. Quite obvious when ever there is blood loss it will also result in water loss and blood is nothing but water containing many cells and other constituents.
Some examples of a category 1 water loss. Broken water supply lines. Sink or tub overflows with no contaminants.
Melting ice or snow and falling rainwater. Broken toilet tanks and toilet bowls that do not contain contaminants or additives. Clean Water is water that comes from a source that does not pose substantial harm to humans.
Some examples of clean water damage are broken water supply lines sprinkler systems tub or sink overflows with no contaminants melting ice or snow falling rainwater and broken toilet tanks. Apart from the losses taking place as urine some of the other methods of losing water from the body include sweating through feces and through evaporation. The amount of water loss that takes place through feces is around 6 of the total fluid loss and the amount of fluid loss that take place through sweating is almost the same.
Acute water loss is the type that occurs within a short period of time and is primarily due to vomiting and diarrhea associated with illness overexertion through exercise or other uncommon situations that cause fluid deprivation or fluid loss. As a result some 11 billion people worldwide lack access to water and a total of 27 billion find water scarce for at least one month of the year. Inadequate sanitation is also a problem for 24 billion peoplethey are exposed to diseases such as cholera and typhoid fever and other water-borne illnesses.
Excess free water or hypotonic water can leave the body in two ways sensible loss such as osmotic diuresis sweating vomiting and diarrhea and insensible water loss occurring mainly through the skin and respiratory tract. In humans dehydration can be caused by a wide range of diseases and states that impair water homeostasis in the body. Water is required to replace losses which normally consist of insensible losses from the skin and respiratory tract urine sweating and faecal loss.
An obligatory urine loss occurs because of the need to remove various solutes from the body. Other losses eg sweating and faecal losses are quite small under normal conditions. Reducing urban water loss in Chittagong Bangladesh As the local water utility for Chittagong water network CWASA is required to deliver an equitable water supply for the entire population in its area.
However it was estimated that the water loss was approximately 60. The quantity of real losses in a given water systems is a good indicator of how efficient a water supplier is in managing its assets the distribution network and the product it delivers to its customers. Volumes of real losses that are significantly higher than what is economically justifiable indicate that action needs to be taken if the water supplier is to be viewed as water-efficient.
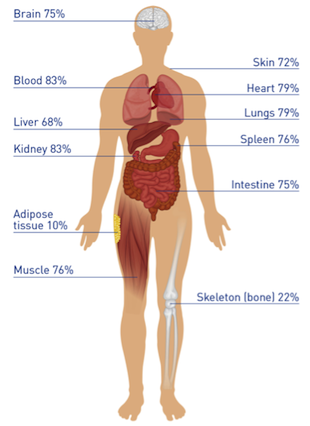
The organs of excretion in humans include the skin lungs and kidneys. Water is lost from the body as. Sweat from the skin.
Water vapour from the. Increased use of water by human beings leaves less water behind for aquatic ecosystems. Shortages of fresh clean water caused by wasting of these resources result in dehydration sickness and tension among people especially in developing nations.
Water losses via skin both insensible perspiration and sweating can range from 03 Lh in sedentary conditions to 20 Lh in high activity in the heat and intake requirements range from 25 to just over 3 Ld in adults under normal conditions and can reach 6 Ld with high extremes of heat and activity. 27 28 Evaporation of sweat from the body results in cooling of the skin. Lets begin by reviewing the two categories of water loss commonly cited within the water sector.
Real losses are physical water losses resulting from a leak a burst or overflow. Real losses can be an indicator of inefficiency on a distribution network or in under-invested aging infrastructure. A certain amount of water may be lost by evaporation from the lower layer also through cracks in the soil.
In temperate regions 25 to 50 per cent of the water received by soil in the form of rain is lost by evaporation. In arid and semi-arid regions the loss is as high as 70 to 80 per cent of the annual rainfall. Qatar the most at risk from water scarcity depends heavily on seawater desalination systems to supply drinking water to people and industries.
First pollution increases water treatment prices. This is due to the additional energy costs and chemicals to filter and clean the water. For example the Great Lakes in Minnesota suffer from enormous algae blooms.
This has increased water treatment costs by almost 400 per 1000 gallons according to the EPA.