
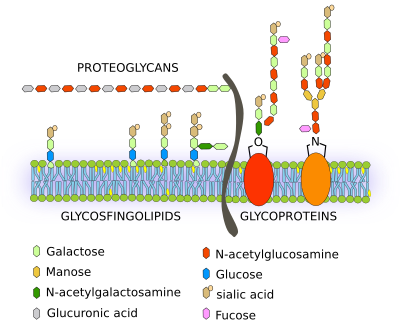
In comparison glycoproteins are protein molecules attached to the short chains of carbohydrates. Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic covalent bond.
Proteins covalently attached to carbohydrates glycans are called.
Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers. Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers source of energy for cell. Proteins with carbohydrate chains that can serve as cell recognition markers and can help neighboring cells interact or stick to each other. Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers.
Long protein chains that help the cell hold its shape. Organelles and other large molecules can travel along these chains like super highways of the cell. Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers source of energy for cell.
Proteins with carbohydrate chains that can serve as cell recognition markers and can help neighboring cells interact or stick to each other. Transport or channel proteins. Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic covalent bond.
Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Proteins with carbohydrate chains that can serve as cell recognition markers and can help neighboring cells interact or stick to each other. Transport or channel proteins.
Proteins that help carry substances across the membrane or allow molecules to pass through a channel. Lipids with carbohydrate chains that serve as cell recognition markers. Proteins with carbohydrate chains that can serve as cell recognition markers and can help neighboring cells interact or stick to each other.
A glycolipid is a lipid that has an attached carbohydrate. Its function is to contribute energy and act as a marker for cellular recognition. Glycolipids appear where carbohydrate chains have a connection to phospholipids that appear on the cell membranes exoplasmic surface.
The carbohydrates appear on the exterior surface of the cell membrane for. Glycolipids are carbohydrate-attached lipids which are associated with cell membranes. They play important roles in providing energy and serve as markers for cellular recognition.
Often covalently bonded to proteins and lipids on cell surfaces and act as recognition signals. Human blood groups get specificity from oligosaccharide chains. Glycosidic bonds to form polysaccharides including starch chitin and cellulose.
Carbohydrates are used as an energy source as a source for carbon and can be attached to other macromolecules including lipids and proteins to serve as recognition markers for the cell. Proteins covalently attached to carbohydrates glycans are called. Polysaccharides are storage forms of sugars and form structural components of the cell.
In addition polysaccharides and shorter polymers of sugars act as markers for a variety of cell recognition processes including the adhesion of cells to their neighbors and the transport of proteins to appropriate intracellular destinations. Extrinsic Recognition is when the cell of one organism recognizes a cell from another organism like when a mammalian cell detects a microorganism in the body. The molecules that complete this binding consist of proteins carbohydrates and lipids resulting in a variety of glycoproteins lipoproteins and glycolipoproteins.
Glycolipid is a lipid molecule with attached short chains of carbohydrates. Glycolipids mainly occur on the cell membrane. Their main function is to involve in cell recognition.
In comparison glycoproteins are protein molecules attached to the short chains of carbohydrates. They occur on the cell membrane as well as in the blood. SURFACE CARBOHYDRATES on a cell serve as points of attachment for other cells infectious bacteria viruses.
Bohydrate side chains on proteins may serve as markers for identifying which. Other forms of carbohydrate-mediated cell recognition. To cause disease viruses bacteria.
Lectins or proteins that bind carbohydrates can recognize specific oligosaccharides and provide useful information for cell recognition based on oligosaccharide binding. Citation needed An important example of oligosaccharide cell recognition is the role of glycolipids in determining blood types. Complex carbohydrates are better for your health than simple carbohydrates.
Oligosaccharides form glycoproteins while polysaccharides are found in cell membranes and used to move proteins around within cells. Both types of complex carbohydrates serve as cell recognition markers. Starches how plant cells store carbohydrates glycogen.
Their function is to serve as markers for the cell so it can be recognized by other cells molecules etc. Sterols are characterized by a tetra-ring base. Cholesterol left a common sterol in membranes is distinguished by this specific base hydrophopic additions and a hydrophilic hydroxy group.
Phosphatidylserine lipids are known to be involved in signaling for the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells or pieces of cells. They accomplish this by being exposed to the extracellular face of the cell membrane after the inactivation of flippases which place them exclusively on the cytosolic side and the activation of scramblases which scramble the orientation of the phospholipids.