
For a median follow-up of 20 months interquartile range 7-60 months 29 patients 174 reached the primary end point 19 patients with MVA and 10 patients with end-stage heart failure. January 1 20XX through December 31 20XX.
And move to.
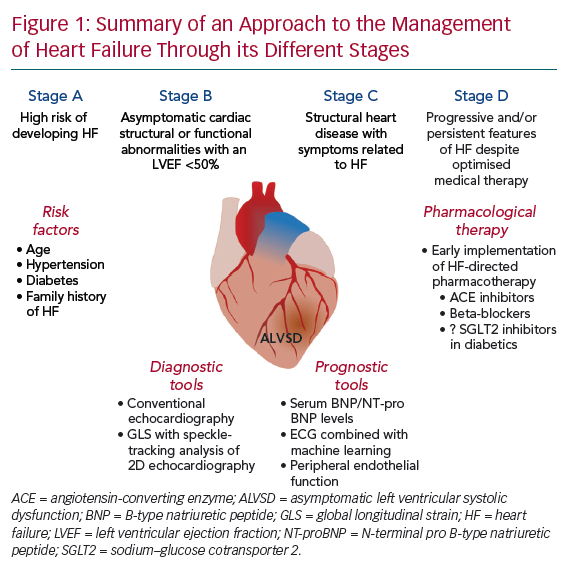
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction lvsd. The term end stage has been used to describe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM with left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD defined as occurring when left ventricular ejection fraction is. The prognosis of HCM-LVSD has reportedly been poor but because of its relative rarity the natural history remains incompletely characterized. The Management of Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction LVSD Class I - No symptoms and no limitation in ordinary physical activity eg.
Shortness of breath when walking climbing. Class II - Mild symptoms mild shortness of breath andor angina and slight limitation during ordinary activity. NT-proBNP is elevated in a wide spectrum of cardiac diseases other than left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
We believe that NT-proBNP is a useful rule-out test for the diagnosis of LVSD in the primary care setting whose usefulness and potential cost effectiveness would be further enhanced by setting appropriate local cut-off levels. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD decreases global cerebral blood flow and predisposes to hypoperfusion. We evaluated the relationship between LVSD as measured by LV ejection fraction LVEF and clinical outcomes in patients with anterior cerebral circulation LVO who underwent ET.
Methods This multicenter retrospective cohort study. THE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF LEFT VENTRICULAR SYSTOLIC DYSFUNCTION LVSD DIAGNOSIS The basis for a historical diagnosis of heart failure should be reviewed and only patients who have confirmed LV systolic dysfunction on echo should be managed in accordance with this guideline. For a suspected new diagnosis use the heart failure diagnostic pathway.
For a median follow-up of 20 months interquartile range 7-60 months 29 patients 174 reached the primary end point 19 patients with MVA and 10 patients with end-stage heart failure. Eight 44 arrhythmic events occurred among individuals with baseline mild to moderate left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD LVEF 36-49. Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction LVSD Patient confirmed to have symptomatic LVSD Loop diuretic should be initiated to reduce symptoms due to fluid overload.
How to adjust the loop diuretic dose as directed by symptoms morning weight Commence. And move to. And up-titrate Still symptomatic of heart failure Sinus rhythm QRS duration 130ms Sinus.
Patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD following myocardial infarction MI are at high risk of developing heart failure. The addition of neprilysin inhibition to renin angiotensin system RAS inhibition may result in greater attenuation of adverse LV remodeling due to increased levels of substrates for neprilysin with vasodilatory anti-hypertrophic anti. Beta-Blocker Therapy for Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction LVSD eCQM Identifier Measure Authoring Tool 144.
January 1 20XX through December 31 20XX. American Heart Association-American. Left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD is a common and serious complication of myocardial infarction MI that leads to greatly increased risks of sudden death and of heart failure.
Left ventricular dysfunction LVD with subsequent congestive heart failure CHF constitutes the final common pathway for a host of cardiac disorders. Coronary artery narrowing or ischaemic heart disease is the dominant cause of heart failure and is often associated with acute or prior myocardial infarction. The remaining aetiologies include cardiomyopathy hypertension and a variety.
Heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD are increasingly common disorders with outcomes worse than many cancers. Evidence-based therapies such as ACE inhibitors and beta-blockers improve prognosis and symptoms and reduce healthcare expenditure. However despite the high prevalence and malignant prognosis few studies have reported the impact.
The term end stage has been used to describe hypertrophic cardiomyopathy HCM with left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD defined as occurring when left ventricular ejection fraction is. The prognosis of HCM-LVSD has reportedly been poor but because of its relative rarity the natural history remains incompletely characterized. Patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD following myocardial infarction MI are at high risk of developing heart failure.
The addition of neprilysin inhibition to renin angiotensin system RAS inhibition may result in greater attenuation of adverse LV remodeli. Type 2 diabetes mellitus T2D is associated with the development of left ventricular systolic dysfunction LVSD and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction HFrEF.