Trauma patients are at increased risk for hypothermia which in turn increases their mortality risk. Uncontrollable hemorrhage often compounded by coagulopathy is the most frequent cause of early death in these patients.

In this retrospective study of 173 patients early post-traumatic hypothermia was found to correlate with physiologic indicators of volume deficit independently of the amount of intravenous fluid received.
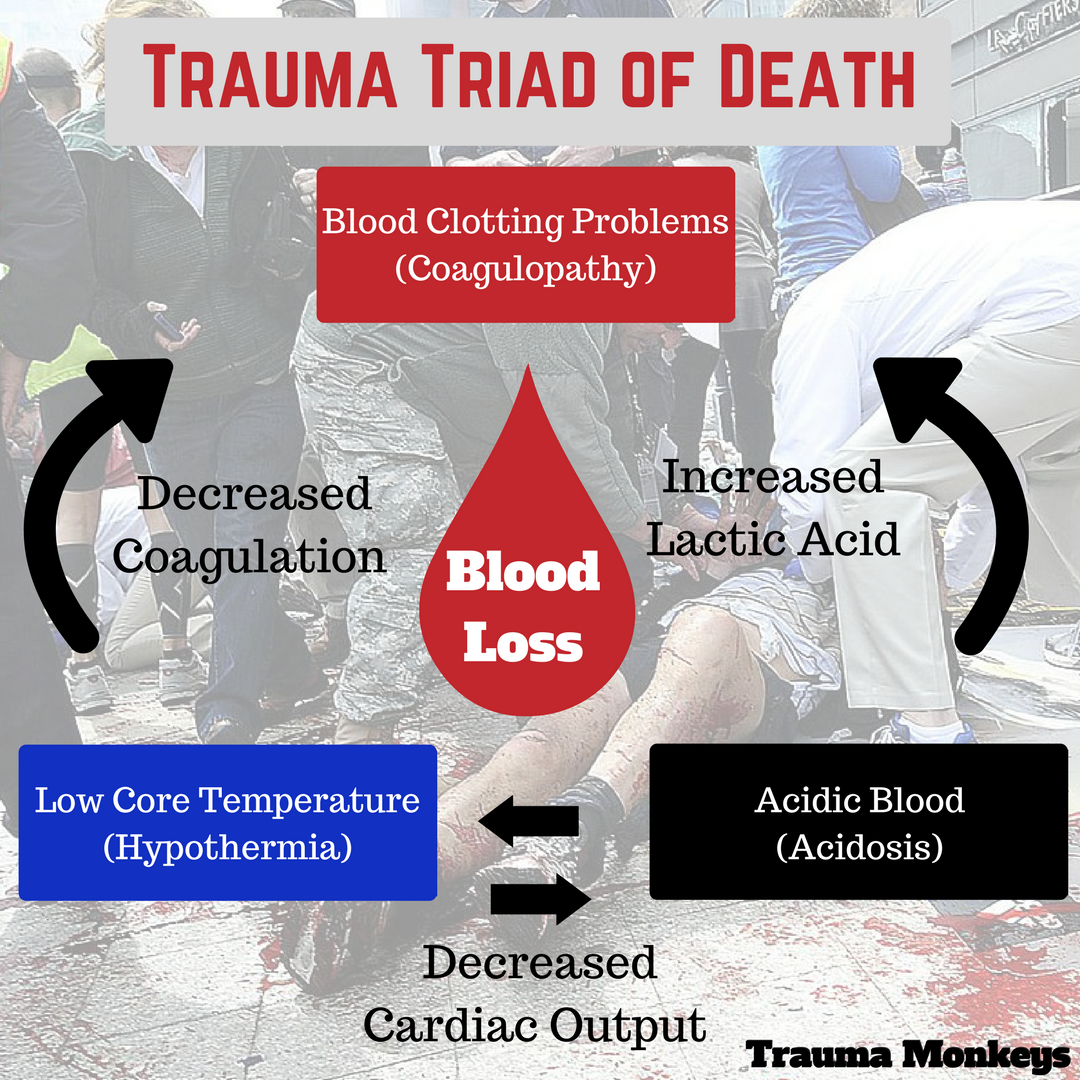
Hypothermia in trauma patients. Hypothermia is a common finding in severely injured patients. Historically described as a consequence of wartime casualties where cold exposure was common this topic has resurfaced in the trauma literature because of the increasing recognition of the morbidity and mortality associated with hypothermia. Hypothermia along with acidosis and coagulopathy has been identified as a component.
Hypothermia is a disorder that causes catastrophic dysfunction in the bodys regulation of homeostasis. Trauma patients are at increased risk of hypothermia from both intrinsic and iatrogenic causes. Rapid recognition and aggressive intervention is necessary to prevent organ failure and death.
Passive external active external active core and extracorporeal rewarming have all been. This report will focus on the role of hypothermia a third of the lethal triad in trauma examining literature to assess how prehospital temperature control can impact on the trauma patient. Spontaneous hypothermia following trauma has severely deleterious consequences for the trauma victim.
However both active warming of patients and clinically induced hypothermia can produce. Hypothermia in trauma patients. 9847699 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types.
Hypothermiatherapy Multiple Traumatherapy Prognosis. Trauma patients are often hypothermic temperature 35 C upon arrival at the hospital. Hypothermia is with hypotension and hypoxia perfectly known to be directly responsible for complications.
Hypothermia is responsible with acidosis and coagulopathy of the lethal triad of trauma. Perhaps the most serious effect of hypothermia in the trauma victim is its effect on coagulation. Uncontrollable hemorrhage often compounded by coagulopathy is the most frequent cause of early death in these patients.
Dilutional thrombocytopenia is usually cited as the primary cause of coagulopathic bleeding when trauma victims undergo massive. Hypothermia is common after severe injury and has been associated with an increased mortality rate in patients stratified by anatomic indices of injury severity. In this retrospective study of 173 patients early post-traumatic hypothermia was found to correlate with physiologic indicators of volume deficit independently of the amount of intravenous fluid received.
There was no correlation found between. The chilling effect of hypothermia on trauma patients Hypothermia pathophysiology. In trauma hypothermia begins when the bodys core temperature dips below 36 C 968 F.
Steps to reduce hypothermia. If the patient begins to shiver it means that hypothermia. Hypothermia in trauma patients is caused by a multitude of factors.
Hemorrhagic shock traumatic brain injuries and alcohol intoxication impair the bodys ability to regulate its core. Hypothermia is common in trauma victims. In several studies on severe trauma injury hypothermia has been reported as occurring in up to two third of the patients 1.
Hypothermia is associated with aggravated injury and increased mortality 2 3. Hypothermia is a common finding in the trauma patient and contributes to increased morbidity and mortality in this group of critically ill patients. Although initial temperatures may be normal decreases in core temperatures during the course of initial evaluation and resuscitation are common.
Hypothermia contributes to alterations in physiologic functions and through alterations of the normal. Physicians commonly ignore hypothermia an often-underappreciated event associated with mortality in trauma patients in general due to its prevalence and belief that it is secondary to the injury itself secondary hypothermia. One major criticism of many of the studies reporting the effects of hypothermia on mortality in trauma patients is that patients who develop hypothermia are often more severely injured than.
The effects of hypothermia on coagulation may represent a two-edged sword in patients with acute brain injury who are treated with therapeutic cooling. On the one hand inhibition of coagulation can have positive effects such as improvements in the microcirculation and inhibition of the formation of harmful microthrombi in the brain. On the other hand this could lead to increased bleeding risk and.
Hypothermia is uncommon and not lethal. 66 of Trauma patients become hypothermic and almost all patients suffer a drop in core temperature. Mortality was twice as high 53 in patients with a Core Body Temperature.
Hypothermia in the patient with trauma must be hypothermia may alter immune response mechanisms differentiated from accidental or exposure such as chemotaxis granulocyte phagocytosis hypothermia and that induced for therapeutic macrophage motility and the production of purposes. Hypothermia may increase the anticonvulsants. Trauma patients are at increased risk for hypothermia which in turn increases their mortality risk.
Nurses caring for these patients must be well-informed about hypothermia so.