Head and neck cancers account for approximately 4 of all cancers in the United States 28. Its estimated annual incidence is 53260 and HNSCC was responsible for 10750 deaths in 2020.
In agreement with other meta-.
Hpv head and neck cancer statistics. The incidence of HPV-positive versus negative non-OPSCC of the head and neck was 062 95 CI 058-066 versus 138 95 CI 132-144. White race 547 and male sex 800 had the highest incidences of HPV-positive OPSCC with a unimodal age incidence distribution peaking at ages 60 to 64 years 2723. HPV positivity was associated with lower cancer-specific mortality than HPV-negative.
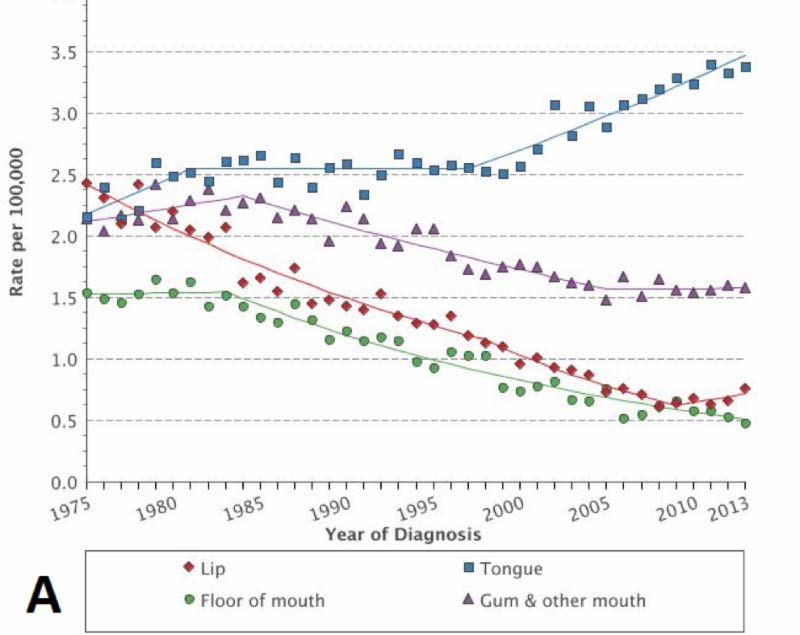
Rate of cancers attributable to human papillomavirus HPV among HNCs is highly depending on world region and tobacco use prevalence. It increases in high-income countries. In the US population the number of HPV-attributable oropharyngeal cancers now exceeds the number of cervix cancers.
HPV vaccination for boys is recommended in an increasing number of countries. Head and neck cancer is the 8th most common cancer in the UK accounting for 3 of all new cancer cases 2017. In females in the UK head and neck cancer is the 13th most common cancer with around 3800 new cases in 2017.
In males in the UK head and neck cancer is the 4th most common cancer with around 8500 new cases in 2017. We review published studies of association of HPV with anatomical site-specific Head Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma HNSCC in these populations and attempt a meta-analysis. From MEDLINEPubMedWEB-of SCIENCEEMBASEScopus databases we found 67 relevant studies with a total of 7280 cases.
15 case-control studies met our inclusion criteria for meta-analysis totaling 1106 cases 638 controls. Head and neck cancer accounts for about 4 of all cancers in the United States. This year an estimated 66630 people 48740 men and 17890 women will develop head and neck cancer.
It is estimated that 14620 deaths 10640 men and 3980 women from head and neck cancer. Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 30 to 40 percent of all head and neck cancers. Oncologists are seeing cases of this cancer due to HPV infection in mostly non-smokers non-drinkers and younger Caucasian males in higher socioeconomic brackets according to.
HPV infection is associated with most oropharyngeal cancers 70 and a small minority of cancers at other anatomical sites in the head and neck 1 2. As described below HPV-positive HNSCC. It is estimated that there are around 2300 more cases of head and neck cancer each year in England than there would be if every deprivation quintile had the same age-specific crude incidence rates as the least deprived quintile.
Around 520 of these cases are in. Head and neck cancers account for approximately 4 of all cancers in the United States 28. These cancers are more than twice as common among men as they are among women 29.
Head and neck cancers are also diagnosed more often among people over age 50 than they are among younger people. Approximately 87 of HPV DNApositive patients whereas dual testing for oral cavity and larynx sites was rarely performed. With regard to HPV type distribution HPV16 prevalence accounted for 822 of all HPV DNApositive cases and was higher for OPC 90 than for other cancer types.
In agreement with other meta-. HPV is thought to cause 70 of oropharyngeal cancers in the United States. It usually takes years after being infected with HPV for cancer to develop.
It is unclear if having HPV alone is enough to cause oropharyngeal cancers or if other factors such as smoking or chewing tobacco interact with HPV to cause these cancers. About 60 of oropharyngeal squamous cell cancers in the USA are positive for HPV 16. HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma seems to be a distinct clinical entity and this malignant disease has a better prognosis than HPV-negative tumours due in part to increased sensitivity of cancers to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Here we show that human papillomavirus HPV-specific B cell responses are detectable in samples from patients with HPV-positive head and neck cancers with active production of HPV. In the United States head and neck squamous cell carcinoma HNSCC accounts for 4 of all malignancies. Its estimated annual incidence is 53260 and HNSCC was responsible for 10750 deaths in 2020.
1 In addition to the traditional risk factors of alcohol and tobacco use human papillomavirus HPV has been implicated in the pathogenesis of HNSCC. In 2015 head and neck cancers globally affected more than 55 million people 24 million mouth 17 million throat and 14 million larynx cancer and they caused over 379000 deaths 146000 mouth 127400 throat 105900 larynx cancer. Together they are the seventh most-frequent cancer and the ninth most-frequent cause of death from cancer.
Squamous Cell Head and Neck Cancer and the Human Papillomavirus was convened. On November 910 2008 almost 80 investigators largely drawn from the NCI Head and Neck Steering Committee and Task Forces met in Washington DC. To focus on the epidemiology natural history and diagnosis of HPV-associ-ated squamous cell head and neck cancers.
The total number of deaths from head and neck cancers in 2011 was 944 accounting for 22 of all deaths from cancer 43221. In 20062010 5year relative survival was 682 for all.
