
Calculating MAP Mean Arterial Pressure - YouTube. Arterial blood pressure can be described by systolic blood pressure SBP diastolic blood pressure DBP or mean arterial pressure MAP.
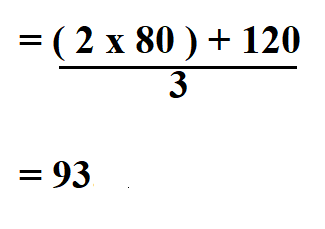
MAP SBP 2 DBP 3.
How to calculate map pressure. This however is not very practical and as it turns out the MAP can be calculated simply by knowing the systolic blood pressure and the diastolic blood pressure. Machines that determine an individuals blood pressure reading will often also show the MAP. The equation with which the MAP can be calculated is the this.
MAP DBP 13SBP-DBP where the DBP is the diastolic blood pressure and the SBP is the systolic blood. Another way to calculate the MAP is to first calculate the pulse pressure subtract the DBP from the SBP and divide that by 3 then add the DBP. MAP 13 SBP DBP DBP.
MAP 13 83-50 50. MAP 13 33 50. MAP 11 50.
MAP 61 mm Hg. There are several clinical situations in which it is especially important to monitor mean arterial pressure. Arterial blood pressure can be described by systolic blood pressure SBP diastolic blood pressure DBP or mean arterial pressure MAP.
Mean arterial pressure is an indication of global perfusion pressure necessary for organ perfusion and oxygen delivery. The normal MAP is 70100 mm Hg and a MAP of at least 60 mm Hg is necessary for adequate cerebral perfusion. Note that MAP is based largely on DBP because most of the cardiac cycle is spent in diastole.
MAP SBP 2. To calculate the MAP you need two values - you systolic and diastolic blood pressure. They are usually given in the form XXYY where XX is the systolic pressure and YY - the diastolic.
For example a person with blood pressure 12080 has SBP 120 mmHg and DBP 80 mmHg. In the next paragraph we will teach you how to measure blood pressure. The following formula is used to calculate the mean arterial blood pressure.
MAP 13 SBP 23 DBP. Where MAP is mean arterial pressure. SBP is systolic blood pressure.
DBP is diastolic blood pressure. As can be seen from the formula the relationship is not a 11 ratio of SBP to DBP. The blood pressures are all measure in units of mmHG.
Mean arterial pressure MAP is a function of systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The easiest way to calculate MAP is to get the pulse pressure Systolic BP Diastolic BP then multiply the result with 13. The answer you get add it to diastolic pressure and the result is the MAP.
13SBP-DBPDBP MAP Explanation. The Mean Arterial Pressure MAP calculates mean arterial pressure from measured systolic and diastolic blood pressure values. This is an unprecedented time.
It is the dedication of healthcare workers that will lead us through this crisis. Equation and Example for calculating Mean Arterial PressureMean Arterial Pressure Systolic-Diastolic Blood Pressure 3 Diastolic Blood PressureExampl. MPAP Chemla formula 061 x SP PA 2 mmHg MPAP 4 x PR peak velocity 2 right atrial pressure RAP MPAP 90 062 x RVOT acceleration time.
Calculated MAP MAWP and Test Pressures Defenition. This pressure is based on calculation for every element of the vessel using the nominal thickness exclusive of corrossion allowance. It is the basis for establishing the set pressure of any pressure.
To calculate the MAP. You need to know the patients blood pressure and this formula. MAP SBP 2 DBP 3.
Systolic blood pressure PLUS diastolic blood pressure which is multiplied by 2 and then DIVIDED by 3. Lets work a problem. Mean Arterial Pressure MAP STUDY.
Terms in this set 8 MAP. Driving force for blood flow. How do you calculate MAP.
Diastolic 13 systolic pressure - diastolic pressure Low Blood Pressure hypotension -decline in pressure gradient -can impair blood flow. At normal resting heart rates MAP can be estimated through SBP and DBP with any of the following formulas. MAP DBP 13 PP where PP SBP DBP therefore MAP DBP 13 SBP DBP.
MAP 280 3 MAP 93. The reference range for MAP in a healthy individual is 70-110 meaning that the patient above is A-OK. You want to be sure to keep your patients MAP 65 to ensure adequate organ perfusion.
Yes I know that most cardiac monitors with non-invasive blood pressure NIBP monitoring capability will automatically calculate. Formula to calculate MAP. To calculate mean arterial pressure we begin by doubling the diastolic blood pressure Then add the systolic blood pressure And then divide the result by 3.
Calculating MAP Mean Arterial Pressure - YouTube. A patients mean arterial pressure is a mathematical calculation of the patients average blood pressureMy websitehttpwww. While MAP can only be measured directly by invasive monitoring it can be approximately estimated using a formula in which the lower diastolic blood pressure is doubled and added to the higher systolic blood pressure and that composite sum then is divided by 3 to estimate MAP.