
The detected antibodies stem from contact with undiscovered non-pathogenic filoviruses that are endemic in Africa and that are closely related to Ebola virus. The virus first spreads to people through direct contact with the blood body fluids and tissues of animals.
The virus spread by close contact with infected persons.
How is ebola virus infection detected. Ebola virus can be detected in blood after onset of symptoms. It may take up to three days after symptoms start for the virus to reach detectable levels. Polymerase chain reaction PCR is one of the most commonly used diagnostic methods because of its ability to detect low levels of Ebola virus.
Confirmation that symptoms are caused by Ebola virus infection are made using the following diagnostic methods. Antibody-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA antigen-capture detection tests. Another test for Ebola looks for antibodies produced by the bodys immune system in response to the virus.
Known as the antigen-capture enzyme. Hepatic or liver dysfunction can occur in Ebola virus infections. Signs of liver damage may be seen in elevated levels of serum aspartate aminotransferase AST and alanine aminotransferase ALT transaminase enzymes within cells assessed via a.
Scientists do not know where Ebola virus comes from. Based on similar viruses they believe EVD is animal-borne with bats or nonhuman primates being the most likely source. Infected animals carrying the virus can transmit it to other animals like apes monkeys duikers and humans.
The virus first spreads to people through direct contact with the blood body fluids and tissues of animals. A person infected with Ebola virus will typically develop. A high temperature a headache joint and muscle pain a sore throat severe muscle weakness.
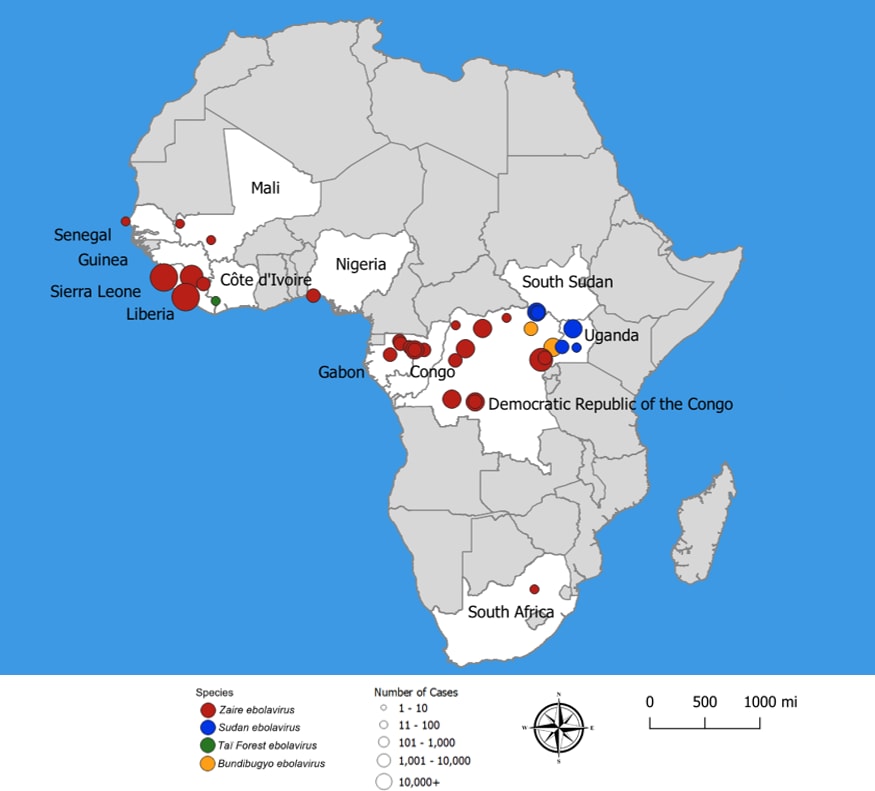
Outbreak occurred in Booué in the fall. Index patient was a hunter living in a logging camp. The virus spread by close contact with infected persons.
There were reports of several dead chimpanzees in the area. Testing of a skin sample obtained from one of the chimpanzees confirmed the animal was infected with Ebola virus. Plausible explanations for these discrepant serosurvey results are.
The serosurveys are artifacts due to cross-reaction of Ebola virus antigens with non-anti-Ebola virus antibodies. The detected antibodies stem from contact with undiscovered non-pathogenic filoviruses that are endemic in Africa and that are closely related to Ebola virus. Or Ebola virus causes widespread subclinical infection in.
PCR is one of the most widely used diagnostic tests for detecting pathogens including viruses that cause diseases such as Ebola African swine fever and foot-and-mouth disease. Since the COVID-19 virus only contains RNA real time or conventional RTPCR is used to detect it. Ebola also known as Ebola virus disease EVD or Ebola hemorrhagic fever EHF is a viral hemorrhagic fever of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses.
Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus with a. Ebola is a rare but deadly virus that causes fever body ache diarrhoea etc. When it enters the body it kills cells and also makes some of them to explode.
It affects the immune system causes. Using cellular biology and genetic approaches the researchers demonstrated for the first time how the Ebola virus can attach to enter and infect T. Though these methods have high levels of specificity the detection of virus material in the bloodthe standard approach for diseases such as Ebola virus disease EVD and Marburg virus disease MVD diagnosislimits the overall ability of this assay to detect infection as these viruses do not undergo significant early replication in the.
The virus which is thought to have originated in fruit bats was first detected in 1976 in an outbreak near the Ebola River in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo. How is the disease. Unfortunately when the outbreak started no gear specifically designed to protect against Ebola virus infection existed and this problem raised some uncertainties throughout the year.
In a new role for WHO the Organization supervised and funded the construction of treatment centres as requested by ministries of health and developed floor. Ebola virus infections can be diagnosed definitively in a laboratory through several types of tests including. Antigen-capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA testing.
How deadly is Ebola. The Ebola strain in the current outbreak is the most lethal of the five known strains of the virus. It is called Ebola Zaire and usually kills up to 9 out of 10 infected.