Asthma is an incurable disease. Asthma is an incurable disease.
The longer you smoke the higher your risk of greater loss of age-related brain volume.
How asthma affects the nervous system. By drcase 11 Mar 2014 Health. A properly functioning nervous system should be the first priority in solving asthma since it is the nervous system which controls all of our bodily functions. The nervous system works by sending and receiving messages or impulses to all parts of the body.
Airway inflammation associated with asthma may affect neuronal activity at several points along the neural reflex pathway including the function of the primary afferent sensory nerves integration within the central nervous system synaptic transmission within autonomic ganglia and transmission at the level of the postganglionic neuroeffector junction. Current asthma therapies treat asthma attacks as immune responses and focus on immune system suppression. However a study by Dimitri Trankner of Howard Hughes Medical Institute in Virginia and his.
The parasympathetic nerves of an asthmatic overstimulate the bronchial tubes and this makes the tubes constrict. An overactive parasympathetic nervous system could explain why such nonspecific stimuli such as smoke viruses and even sudden weather changes trigger wheezing in both allergic and nonallergic asthmatics. Asthma is often considered a disease of the immune system because immune cells go into overdrive when they sense a trigger and cause inflammation.
A new study implicates remodeling of nerves in the airways as a key contributor to heightened sensitivity and airway constriction in patients with asthma. According to Johns Hopkins University research indicates that asthma can affect your nervous system. A nerve growth factora nervous system proteinhas been found to increase sensitivity to irritants among people suffering from asthma and allergies.
Mayo research examines how asthma affects immune system increasing risk for nonrespiratory conditions. PD 99 focuses his research on determining how asthma affects the immune system specifically the extent to which asthma epidemiology affects the risk and severity of communicable and noncommunicable. The main parts of the nervous system are.
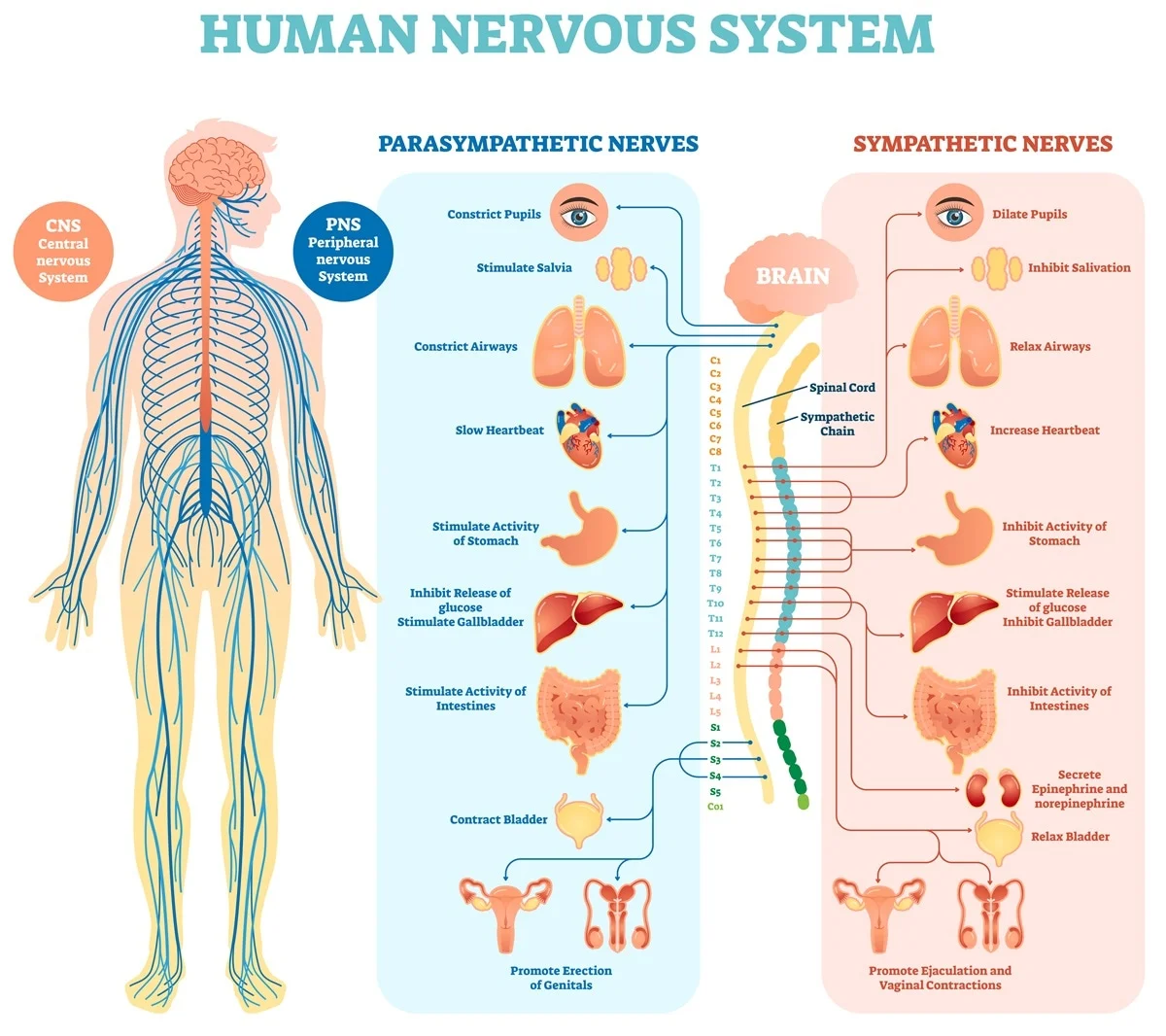
Central nervous system CNS. Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS. Your brain uses your nerves to send messages to the rest of your body.
Each nerve has a protective outer layer called myelin. Myelin insulates the nerve and helps the messages get through. According to Johns Hopkins University research indicates that asthma can affect your nervous system.
A nerve growth factor–a nervous system protein–has been found to increase sensitivity to irritants among people suffering from asthma and allergies. Asthma is an incurable disease. However it can be properly managed with medications.
Asthma is associated with autonomic nervous imbalance. An increased bronchial sensitivity to cholinergic constrictors and possibly a decreased sensitivity to beta2-adrenergic dilators have been reported in this disease. Also non-adrenergic and non-cholinergic NANC mediators have a.
Smoking may increase your risk of developing dementia and stroke and it may also cause personality changes. If you smoke you may experience faster cognitive decline than non-smokers. The longer you smoke the higher your risk of greater loss of age-related brain volume.
Increased blood pressure or hypertension. It is important to know that asthma is not caused by emotional factorsas was commonly believed years ago. Emotional anxiety and nervous stress can cause fatigue which may affect the immune system and increase asthma symptoms or aggravate an attack.
However these reactions are considered to be more of an effect than a cause. Specifically Kenkel is interested in understanding how different birth experiences including vaginal delivery emergency C-section and scheduled C-section affect the developing nervous system. The somatic nervous system transmits sensory communications.
It is responsible for voluntary movement and action. It is composed of sensory afferent neurons. The autonomic nervous system.
This is the part of the peripheral nervous system that is not generally considered to be under voluntary control. This system is further divided into two subdivisions. The sympathetic nervous system which typically stimulates or speeds up functions in the body and the parasympathetic nervous system which.
