
It is made by immunising sheep against the venom of the box jellyfish and then collecting that part of the sheeps blood which neutralises this poison. Mechanism of Antivenom.
Antivenom often spelled antivenin is an antibody product that can disable a particular venoms toxins.
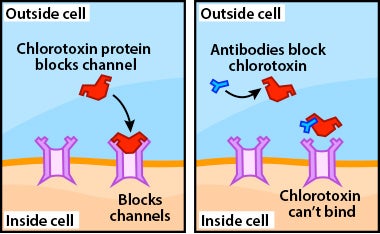
How antivenom works in the body. Antivenom then usually includes many different molecules to stop the effects of different toxins in the body. To understand how antivenom works lets first take a moment to review what venom does to your cells using deathstalker scorpion venom as an example. This kind of venom contains a protein called chlorotoxin which blocks channels on the cells surface.
Antivenom often spelled antivenin is an antibody product that can disable a particular venoms toxins. If injected quickly after a bite or sting the antibodies in antivenom neutralize the venom potentially saving the victims life or limb. Mechanism of Antivenom.
Antivenom acts to neutralize the poisonous venom of the cobra and causesthe venom to be released from the receptor site. Thus the receptor sitesthat were previously blocked by venom are now free to interact with theacetylcholine molecule and. Antivenoms work by boosting our immune response after a snakebite.
They are made by immunizing donor animals such as horses or sheep with snake venoms. These animals have robust immune systems and produce powerful antibodies that can bind to snake venom components enabling our own immune defences to eliminate these toxins. Antivenom often spelled antivenin is an antibody product that can disable a particular venoms toxins.
If injected quickly after a bite or sting the antibodies in antivenom neutralize the venom potentially saving the victims life or limb. Making antivenom is a painstaking resource-intensive time-consuming process. Have a large body mass get along with each other and are forgiving.
Goats and sheep can work well too. An antivenom is a biological product used to treat venomous bites or stings. Its made by milking the relevant animal spider snake or whatever for venom.
Small amounts of venom are injected into an animal commonly a horse goats sheep or rabbits may also be used so that over time the animal produces antibodies. Author summary Snakebite is an important medical problem in tropical regions including in Nepal where tens of thousands of people are bitten every year. Snakebite can result in life-threatening envenoming and correct identification of the biting species is crucial for doctors to choose appropriate treatment and anticipate complications.
This paper compares two different doses of antivenom for. The African antivenom is especially useful because it can treat bites from ten different venomous snakes found in Africa. There are cheaper antivenom alternatives but they dont always work well and arent specific to different snake bites.
Theyre riskier as far as side effects are concerned. Snake antivenom is a medication made up of antibodies used to treat snake bites by venomous snakes. It is a type of antivenom.
It is a biological product that typically consists of venom neutralizing antibodies derived from a host animal such as a horse or sheep. The host animal is hyperimmunized to one or more snake venoms a process which creates an immunological response that produces large numbers of neutralizing antibodies against various components of the venom. Antibody a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance called an antigen.
Antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens in order to remove them from the body. Learn more about the function and structure of antibodies in this article. Box Jellyfish Antivenom is an injection designed to help neutralise the effect of the poison venom of the box jellyfish.
It is made by immunising sheep against the venom of the box jellyfish and then collecting that part of the sheeps blood which neutralises this poison. In human blood there are 13 different molecules that regulate clotting and one of the most affected by venom is fibrinogen. When the venom enters the blood toxins activate the clot formation process and fibrinogen among other clotting factors is exhausted in the process.
In the test tube this makes a solid clot. How antivenoms are made and tested Antivenoms used in Australia are usually made by injecting small sub-lethal doses of venom into horses. The immune systems of.
In human blood there are 13 different molecules that regulate clotting and one of the most affected by venom is fibrinogen. When the venom enters the blood toxins activate the clot formation process and fibrinogen among other clotting factors is exhausted in the process. In the test tube this makes a solid clot.
Antivenoms can prevent or reverse most of the snakebite envenomings effects and play a crucial role in minimizing mortality and morbidity. These preparations are included in the WHO List of Essential Medicines and should be part of any primary health care package where snakebites occur. Polyvalent Snake Antivenom is an injection designed to help neutralise the effect of the poison venom of most snakes that are encountered in Australia and in Papua New Guinea.