This can induce the antibody-mediated adverse drug effect of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia HIT. Four different patient populations were investigated.

This can induce the antibody-mediated adverse drug effect of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia HIT.
Heparin platelet factor 4 antibody. Platelet factor 4heparin antibodies are not always associated with thrombocytopenia. In 135 children who underwent cardiac surgery and were given unfractionated heparin 60 neonates undergoing first-time surgery and 75 older children undergoing re-operations platelet factor 4heparin antibodies were not detected preoperatively in either group 72 c. Antiplatelet factor 4–heparin antibodies in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies.
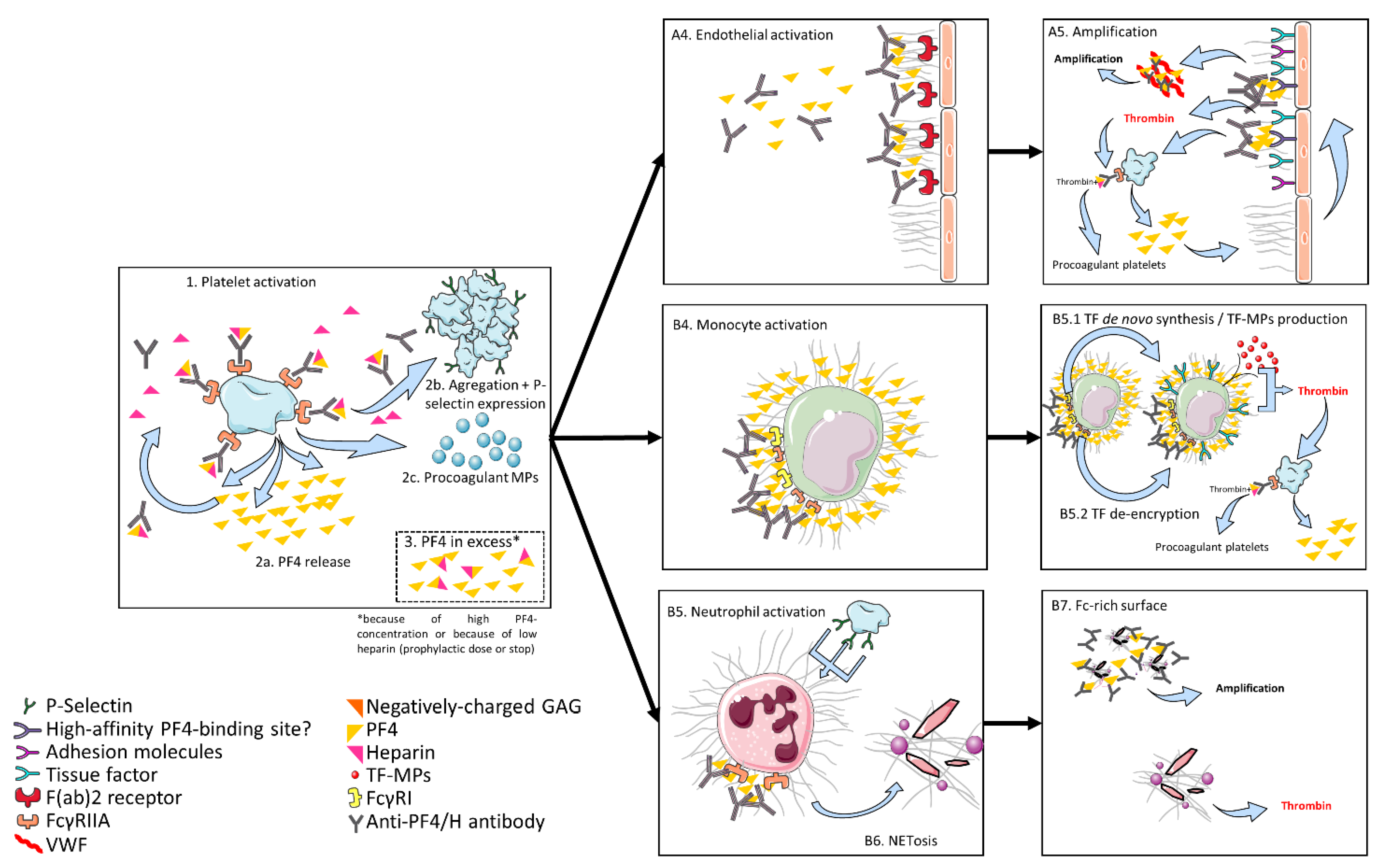
Antibodies directed against platelet factor 4-heparin are present in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia HIT. Additionally it has been suggested that heparin can be an antigenic target of antiphospholipid antibodies aPL. Platelet surface and leads to release of platelet factor 4 PF4.
If a critical stoichiometric ratio of heparin to PF4 is achieved the heparin-PF4 complex undergoes a conformational change that exposes novel epitopes leading to antibody Ab formation. The heparin-PF4 complexbound antibody then binds to platelets leading to activation and microparticle release. Platelet factor 4 PF4heparin antibody typically associated with heparin therapy is reported in some heparin-naive people.
Seroprevalence in the general population however remains unclear. We prospectively evaluated PF4heparin antibody in approximately 4000 blood bank donors using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for initial and then repeated confirmatory testing. Recent studies using immunological methods demonstrated that antibodies contained in plasma or in purified total immunoglobulin IgG from patients suffering HIT recognize as target antigen the complex heparinplatelet factor PF4.
In the present study the role of PF4 in in-vitro platelet aggregation induced by purified total IgG or platelet-poor plasma from patients suffering HIT was investigated. 25 Zeilen Antibodies against heparin-platelet factor 4 HPF4 represent an important component in. All 11 patients as well as another 17 for whom the researchers had blood samples tested positive for antibodies against platelet factor 4 PF4.
These antibodies are also observed in people who develop heparin induced thrombocytopenia. None of the patients had received heparin before their symptoms started however. Testing for antibodies to platelet factor 4 PF4 was positive in 22 patients with 1 equivocal result and negative in 1 patient.
On the basis of the pathophysiological features observed in. In those affected after being given heparin the immune system makes antibodies to a complex of heparin and a protein called platelet factor 4 triggering. Antibodies to the platelet factor 4heparin complex are linked to the pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia type II HIT II and the thrombotic complications associated with this syndrome.
7 Because the antibodies may induce thrombosis by activating the vascular endothelium as well as platelets 7 we postulated that the presence of these antibodies would. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia HIT is one of the most clinically important drug-induced complications in hospitalized patients. This paradoxical prothrombotic response to anticoagulant therapy is an immunologic con-dition in which antibodies to a complex of endogenous platelet factor 4 PF4 and exogenous heparin activate.
Four different patient populations were investigated. 32 patients with the immune type of HIT with thromboembolic complications 13 patients with HIT without thromboembolism 24 patients with heparinplatelet factor 4 PF4 antibodies without clinical symptoms of HIT and 20 heparintreated patients with thrombocytopenia caused by other reasons. In all patients the immunglobulin mixture of.
Platelet factor 4 PF4heparin antibody typically associated with heparin therapy is reported in some heparin-naive people. Seroprevalence in the general population however remains unclear. We prospectively evaluated PF4heparin antibody in approximately 4000 blood bank donors using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for initial and then repeated confirmatory testing.
Antibody was detected initially in 249 66. 95 confidence interval CI 58-74. Patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty can develop anti-PF4heparin antibodies without heparin exposure.
Dynamic mechanical prophylaxis is a heparin-independent risk factor for anti-PF4heparin antibody formation in this patient population. The chemokine platelet factor 4 PF4 undergoes conformational changes when complexing with polyanions. This can induce the antibody-mediated adverse drug effect of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia HIT.