However over the past several years with. JAK2V617F myeloproliferative neoplasms MPNs harboring the same mutation in hematopoietic stem cells HSCs display diverse phenotypes including polycythemia vera PV essential thrombocythemia ET and primary myelofibrosis PMF.
Depletion of an E3 ligase Hectd1 impairs ribosomal subunit joining and protein translation efficiency by promoting retention of its substrate ZNF622 in regenerating hematopoietic stem cells during stress.
Hematopoietic stem cell tree. The classical roadmap of hematopoietic hierarchy has been proposed for nearly 20 years and has become a dogma of stem cell research for most types of adult stem cells including hematopoietic stem cells HSCs. However with the development of new technologies such as omics approaches at single-cell resolution recent studies in vitro and in vivo have suggested that heterogeneity is a. A hematopoietic stem cell is a cell isolated from the blood or bone marrow that can renew itself can differentiate to a variety of specialized cells can mobilize out of the bone marrow into circulating blood and can undergo programmed cell death called apoptosisa process by which cells that are detrimental or unneeded self-destruct.
Ever since hematopoietic stem cells HSCs were first identified half a century ago their differentiation roadmap has been extensively studied. The classical model of hematopoiesis has long held as a dogma that HSCs reside at the top of a hierarchy in which HSCs possess self-renewal capacity and can progressively give rise to all blood lineage cells. However over the past several years with.
Hematopoietic stemprogenitor cells HSPCs isolated from bone marrow have been successfully employed for 50 years in hematological transplantations. Currently these cells are more frequently isolated from mobilized peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood. In this chapter we overview several topics related to these cells including their phenotype methods for isolation and in vitro and in.
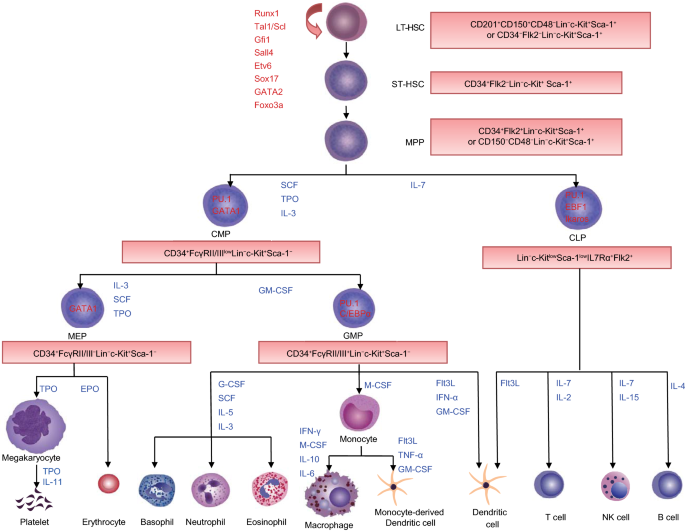
Hematopoietic stem cells HSCs are rare 1 per 10 5 bone-marrow cells small mononuclear cells that tend to be noncycling or to have long cell cycles. HSCs divide to form more HSC self-generation or to form cells committed either to lymphocyte formation common lymphoid progenitors CLPs or to the formation of myeloid cells common myeloid progenitors CMPs Figure 1. JAK2V617F myeloproliferative neoplasms MPNs harboring the same mutation in hematopoietic stem cells HSCs display diverse phenotypes including polycythemia vera PV essential thrombocythemia ET and primary myelofibrosis PMF.
These chronic malignant disorders are ideal models to analyze the pathological consequences of stem cell heterogeneity. Haematopoietic stem cells HSCs are able to give rise to the haematopoietic system 1 2 thereby serving as an invaluable source in regenerative medicine transplantation for. Lv et al.
Uncover a key role of ubiquitin-dependent regulation of ribosomal assembly and protein synthesis in hematopoietic stem cell regeneration. Depletion of an E3 ligase Hectd1 impairs ribosomal subunit joining and protein translation efficiency by promoting retention of its substrate ZNF622 in regenerating hematopoietic stem cells during stress. Flow cytometry and cell cycle analysis showed activation of the entire hematopoietic tree including myeloid progenitors.
The cycling fraction of the most upstream hematopoietic stem cells increased from 334019 to 732052 after tMCAO P. Drawing shows the steps a blood stem cell goes through to become a red blood cell platelet or white blood cell. Drawing shows a myeloid stem cell becoming a red blood cell platelet or myeloblast which then becomes a white blood cell.
Drawing also shows a lymphoid stem cell becoming a lymphoblast and then one of several different types of. Hematopoietic Tree Plasma Cell. Drawing shows the steps a blood stem cell goes through to become a red blood cell platelet or white blood cell.
A myeloid stem cell becomes a red blood cell a platelet or a myeloblast which then becomes a granulocyte the types of granulocytes are eosinophils basophils and neutrophils. A lymphoid stem cell becomes a. Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation HSCT is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells usually derived from bone marrow peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood.
It may be autologous the patients own stem cells are used allogeneic the stem cells come from a donor or syngeneic from an identical twin. It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers. As therapeutic alternative hematopoietic stem cells HSCs can be harnessed to overexpress transgenes in downstream hematopoietic lineages.
Flow cytometry and cell cycle analysis showed activation of the entire hematopoietic tree including myeloid progenitors. The cycling fraction of the most upstream hematopoietic stem cells increased from 334019 to 732052 after tMCAO P. Hematopoietic stem cells HSCs represent a heterogeneous population of primitive blood progenitor cells that fall into several different classes.
12 Within the human body they are mainly located in the bone marrow of adults but are also found in various fetal tissues such as umbilical cord blood placenta and fetal liver. HSCs are functionally defined by their self-renewal capacity and. Hematopoietic stem cells HSCs produce all blood cell types throughout adult life but their behavior in their native bone marrow niche is poorly understood.
Show that HSCs exhibit a dynamic morphology and complex motility patterns that involve serial interactions with stromal cells in the bone marrow.