The gut microbiota in IBD IBD-ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease-is emerging as a worldwide epidemic. A specific metabolite of the gut microbiota is also likely to be involved in the.

Nevertheless the gut microbiota plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of several disease processes including inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut microbiota and ibd. The gut microbiota in IBD IBD-ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease-is emerging as a worldwide epidemic. An association between the increased incidence of IBD and environmental factors linked to socioeconomic development has been persistently detected in different parts of the world. The lifestyle in developed countries mig.
Although the etiology of IBD is unknown gut microbiota alteration dysbiosis is considered a novel factor involved in the pathogenesis of IBD. The gut microbiota acts as a metabolic organ and contributes to human health by performing various physiological functions. Deviation in the gut flora composition is involved in various disease pathologies including IBD.
This review aims to. This review focused on the clinical evidence available that considers the impact of some nutrients on IBD onset and the role of different diets in the management of IBD and their effects on the gut microbiota composition. The effects of the Specific Carbohydrate Diet low fermentable oligosaccharides disaccharides monosaccharides and polyols FODMAP diet gluten free diet anti-inflammatory diet and Mediterranean diet are investigated with regard to their impact on microbiota.
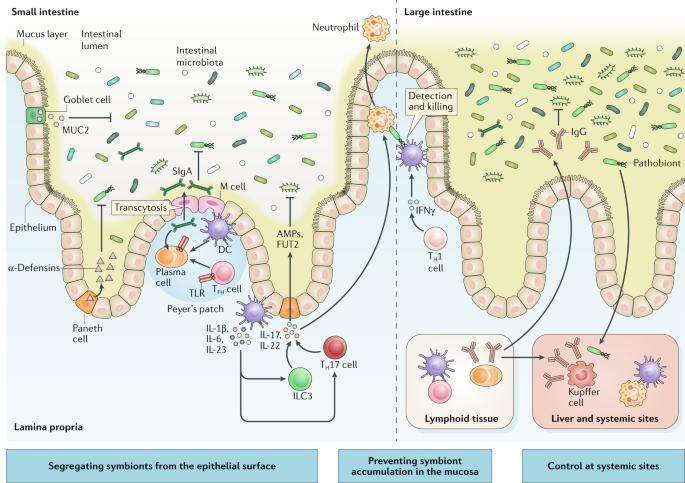
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD involves a dysregulated immune response to the gut microbiota in genetically predisposed hosts. Experimental animal models of colitis provide the best evidence that bacteria present in the bowel of the animals have an essential role in the pathogenesis of colitis since in most models germ-free animals do not develop disease. Various alterations of the gut microbiota have been report-ed in IBD patients Table 1.
Most studies have shown re-duced diversity of the gut microbiota in IBD patients 69. The most consistent observations of altered composition of the gut microbiota in IBD patients are a reduction in Firmicutes and an increase in Proteobacteria 6 7 1012. Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is a chronic and relapsing inflammatory disorder of the gut.
Although the precise cause of IBD remains unknown the most accepted hypothesis of IBD pathogenesis to. The gut microbiota and its mammalian host have co-evolved to live together in a mutualistic relationship where the host provides a unique niche for the growth of bacteria while the gut microbiota provides essential metabolic functions and helps to maintain immune homeostasis in the host. Nevertheless the gut microbiota plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of several disease processes including inflammatory bowel disease.
Despite the high number of gut microbiome studies and emerging evidence supporting the gut microbiomes involvement in disease pathogenesis no single microorganism has been identified as a pathogenic agent in IBD. Retrospective studies and meta-analyses on antibiotic use in ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease and long-term outcomes are conflicting. What is the link between our microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease IBD.
The role gut health and our microbiome plays in IBD is an area being researched more and more. It is becoming increasingly accepted that intestinal dysbiosis an imbalance of the gut microbiota is found in people with IBD 678. However it is not yet understood if this is a cause or a consequence of IBD and more.
In the gut microbiota of IBD metagenomic studies have identified significant shifts in oxidative stress pathways and reduced carbohydrate metabolism and amino acid biosynthesis 5556. However metagenomics is limited to revealing the functional potential not the functional activity of microorganisms. In this context metatranscriptomics enables one to measure actual gene expression.
A metagenomic analysis of the gut microbiota showed a decrease in genes responsible for carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism and an increase in those in the oxidative stress pathway in IBD patients raising the possibility that oxidative stress from the gut microbiota causes intestinal inflammation in IBD patients. A specific metabolite of the gut microbiota is also likely to be involved in the. A healthy gut microbiota has been established to date.
Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota has been associated with numerous adverse condi-tions such as Clostridioides difficile formerly designated Clostridium difficile infection CDI 1 metabolic syndrome 2 3 inflammatory bowel disease IBD. Download Citation On Mar 1 2017 Iain Dickson published Gut microbiota. Diagnosing IBD with the gut microbiome Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is a heterogenous set of inflammatory diseases mediated by the immune system which a ect the gastrointestinal tract. The two main IBD manifestations are Crohns Disease CD and ulcerative colitis UC. Changes in the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota have been linked to IBD but a direct causal association has yet to be established in humans.
This Review discusses the. Further evidence supporting the pivotal role of gut microbiome in the onset of IBD is that CD and UC patients often present a characteristic dysbiosis 202122232425. Fecal microbiota transplantation seems to induce remission in active UC.
The use of antibiotics and probiotics induce and maintain the remission of IBD 272829. Depletion of commensal microbes can result in impaired mucosal healing. Each individuals gut microbiome is a community of trillions of microbes including bacteria viruses and fungi that research indicates play an important role in numerous diseases including IBD.
IBD which affects more than 35 million people worldwide and is growing in prevalence is a chronic disease marked by periods of remission followed by flare-ups in which the disease becomes active.