12 rijen 1 Functional Anatomy of the Knee Joint. Any swelling that occurs in the joint is contained inside the capsule which is why injuries can cause the knee to balloon.
Eds Surgery and Arthroscopy of the Knee.
Functional anatomy of knee joint. Knee joint Articular surfaces. The tibiofemoral joint is an articulation between the lateral and medial condyles of the distal end. The joint capsule of the knee joint is one of a composite nature mainly formed by muscle tendons and.
12 rijen 1 Functional Anatomy of the Knee Joint. The knee joint articulatio genus is the largest. 1986 The functional anatomy of the knee joint - kinematics of the ligaments.
Trickey EL Hertel P. Eds Surgery and Arthroscopy of the Knee. Publisher Name Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
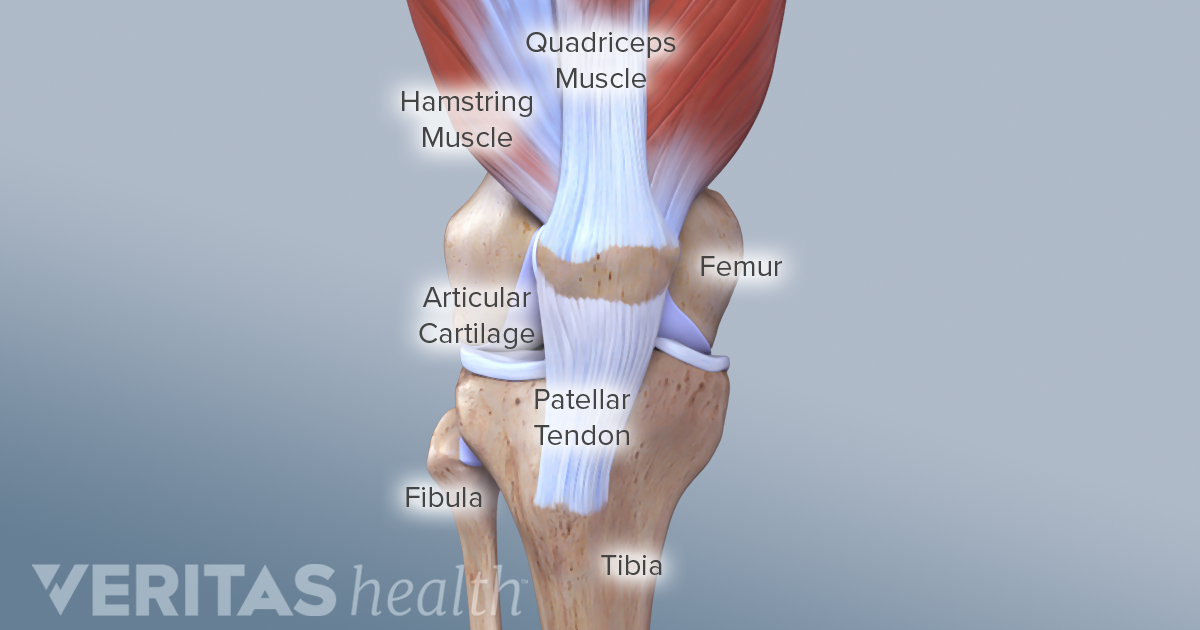
Knee Anatomy and Function The knee is the largest joint in the body and is central to nearly every routine activity. The knee joint is formed by the ends of 3 bones. The lower end of the thigh bone femur the upper end of the shin bone tibia and the kneecap patella.
Normal Anatomy and Biomechanics of the Knee Fred Flandry MD FACSw and Gabriel Hommel MD Abstract. Functionally the knee comprises 2 articulationsthe patellofemoral and tibiofemoral. Stability of the joint is governed by a combination of static ligaments dynamic muscular forces meniscocapsular aponeurosis bony topography and joint load.
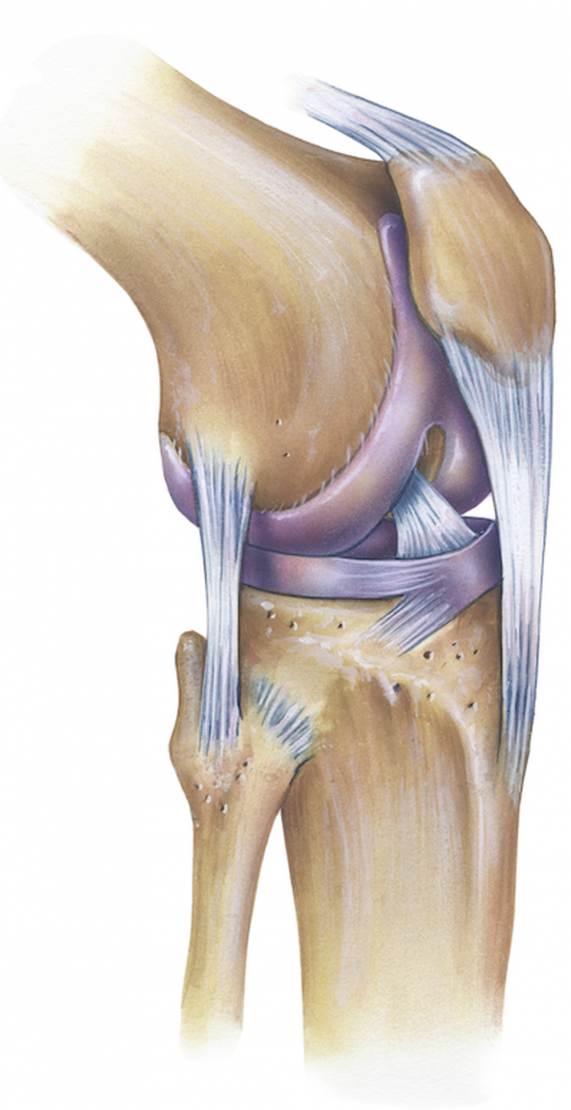
The knee joint is thus primarily a hinge with the wheel- shaped surfaces of the femoral condyles gliding and rolling in a twin set of concave curved gutters. The tibial and patellar surfaces. The anatomical and functional details of the cruciate ligamants of the knee were studied on 20 cadaver knees and 24 fresh knees.
Each anterior cruciate ligament was found to consist of 2 parts. A distinct anteromedial band AMB and a main posterolateral part. The exact geometry of the ligaments and.
The cruciate ligaments of the knee joint. As open anatomical knowledge is less present in our daily practice it is even more important to highlight this complex anatomy and function of the knee. It is the purpose of this review to perform a systematic review of knee anatomy highlight the complex function of the knee joint and present an overview about recent and current knowledge about knee function.
Knee consists predominantly of the quadriceps muscles namely the rectus femoris biarticular vastus lateralis monoarticular vastus medialis and vastus intermedius and the primary function of these muscles is to extend the knee joint. The posterior aspect of the knee consists of the biceps femoris biarticular semimembranosus. Another important part of knee anatomy is the joint capsule.
This is like a bag that surrounds the joint containing synovial fluid to nourish and lubricate the knee allowing it to move smoothly and freely. Any swelling that occurs in the joint is contained inside the capsule which is why injuries can cause the knee to balloon. The 3B Scientific Anatomy Video Knee Joint demonstrates the structure of the knee joint.
In addition to the bones involved in the knee joint the function. Profound knowledge in functional and clinical anatomy is a prerequisite for efficient diagnosis in medical practice. However anatomy teaching does not always consider functional and clinical aspects.
Here we introduce a new interprofessional approach to effectively teach the anatomy of the knee joint. Your account has been temporarily locked. Your account has been temporarily locked due to incorrect sign in attempts and will be automatically unlocked in 30 mins.
WebMDs Knee Anatomy Page provides a detailed image and definition of the knee and its parts including ligaments bones and muscles. The knee joint is a compound joint consisting of two different articulation points that combine to form the joint. It may also be referred to as a bicondylar joint as movement primarily occurs in one plane flexion extension.