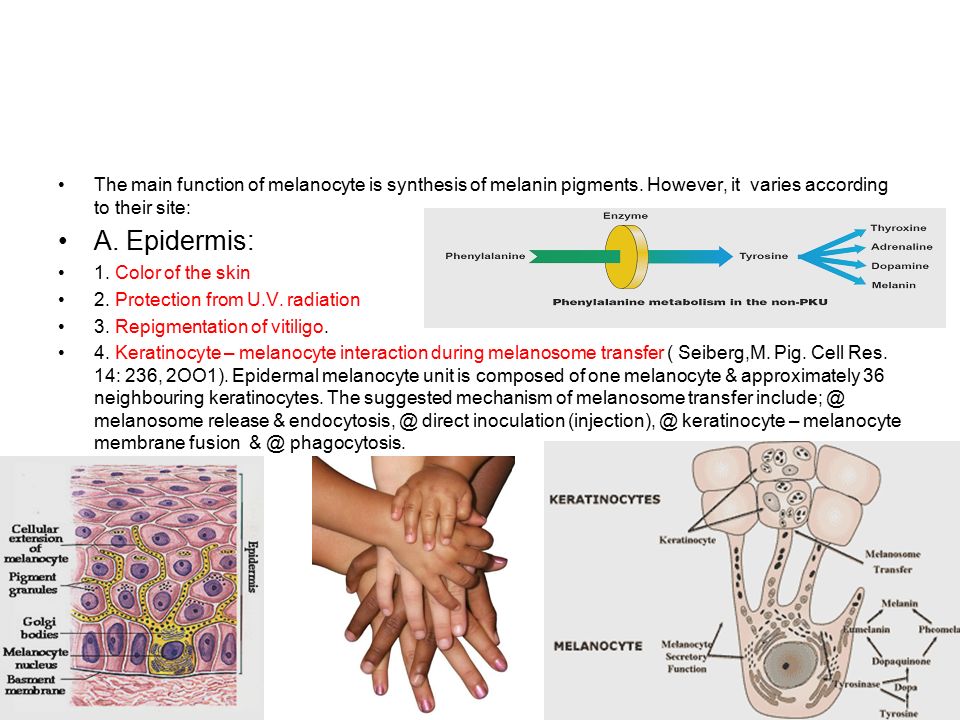
The biological pigment melanin is present in most of the biological systems. Melanin plays a delicate dual role in the body.

It manifests a host of biological and pharmacological properties.
Function of melanin in the human body. The Function of Melanin Melanins purpose has nothing to do with human vanity and everything to do with protecting the organism. UV radiation from the sun is a well-known carcinogen and in high enough exposures can lead to a number of related types of melanoma which are malignancies of the skin. Melanin plays a delicate dual role in the body.
It helps protect the body from the effects of ultraviolet UV light from the sun and sunlamps by producing a brownish pigment a tan. But melanin can also collect in concentrated forms that pose health risks. First of all you should know that melanin is a pigment the main function is to determine the color of your skin.
However a lack or excess of this component in our body can lead to skin problems and other issues related to the hair or eyes. 2 The melanocytes melanin are present in the bottom layer of our epidermis skin. Melanin is the central pigment in our skin but its role in the human body is about so much more than simply determining the skin color we see.
Melanin is the pigment responsible for your skin color and tone but did you know this fascinating biomolecule also converts light into heat and can transform other forms of radiation into metabolically useful forms of energy. From the Department of Dermatology The Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions Baltimore. An informal survey of my colleagues revealed that most dermatologists believe the primary function of melanin in humans is to act as a sunscreen to protect us from ultraviolet UV radiation in sunlight.
The leading textbooks of dermatology support this notion. The primary function of melanin is in skin pigmentation. Melanin has other important roles in the human body such as sunlight absorption and sun screening protection from ultraviolet radiation charge-transfer redox activity free radical scavenging antimicrobial immune defense immunomodulation and ion chelating.
Cells called melanocytes located just below the outer surface of the skin produce melanin which is in higher levels in people with darker skin. Melanins primary function is to protect the skin from sun damage but it carries additional benefits that are enjoyed mostly by those with darker skin. Melanin is a skin pigment.
It occurs humans and animals both and it makes hair skin and eyes appear darker. People with high amounts of melanin lead to having darker skin and people with less melanin have lighter skin. Melanin also helps to protect our skin from UV rays.
Melanin also helps to block processes in the body that lead to skin cancer. The biological pigment melanin is present in most of the biological systems. It manifests a host of biological and pharmacological properties.
Its role as a molecule with special properties and functions affecting general health including photoprotective and immunological action are. Melanin is the pigment that produces the wide variation seen in skin and hair color in humans. Melanin is synthesized by cells in the skin and hair follicles called melanocytes.
Two major classes of melanin are known. Eumelanin a brown-black pigment. And pheomelanin an orange-to-red pigment.
Functions of Human Skin Melanin Melanin is the brown black non-haemoglobin-derived pigment normally present in the hair skin choroid of the eye meninges and adrenal medulla. It is synthesized in the melanocytes and dendritic cells both of which are present in the basal cells of the epidermis. On exposure to sunlight for example the human epidermis undergoes gradual tanning as a result of an increase in melanin pigment.
2 It is a mechanism for the absorption of heat from sunlight a function that is especially important for cold-blooded animals. 3 It affords concealment to. First to protect the skin from the UV ultraviolet rays emitted from the sun the body produces the Melanocyte stimulating hormone to trigger the release of melanin the chemical in skin that causes people to have darker skin or when a person tans this is the buildup of melanin in the skin.
Melanin is an important component that in addition to determining the color of the skin hair and eyes if not present can cause great sensitivity in the skin as it acts as a protective layer to radiation. The darker your skin the lower the level of damage that solar radiation can cause in it. Melanin protects the skin by shielding it from the sun.
When the skin is exposed to the sun melanin production increases which is what produces a tan. Its the bodys natural defense mechanism against sunburn. Time in the Sun Comes With a Cost.