
This article will focus more on the follicular type of thyroid cancer discussing the etiology epidemiology histology evaluation. This article will focus more on the follicular type of thyroid cancer discussing the etiology epidemiology histology evaluation.
Follicular thyroid carcinoma FTC is the second most common thy-roid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma.
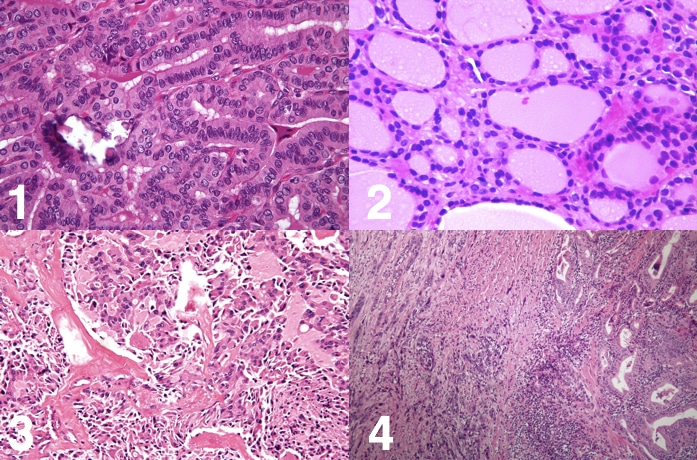
Follicular carcinoma thyroid histology. Follicular thyroid carcinoma FTC is the second most common thyroid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma. The authors studied the clinical course of 132 patients with FTC to determine whether there was a direct relation between the histologic degree of invasion tumor recurrence and patient survival. Thyroid carcinoma with follicular differentiation but no papillary nuclear features Hürthle cell oncocytic carcinoma is discussed separately Comprises 6 - 10 of thyroid carcinomas.
Insufficient dietary iodine is a risk factor. Usually solitary cold nodule on radionuclide scan. Follicular thyroid carcinoma FTC is the second most common thyroid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma.
The authors studied the clinical course of 132 patients with FTC to determine whether there was a direct relation between the histologic degree of invasion tumor recurrence and patient survival. Follicular thyroid carcinoma abbreviated FTC is an uncommon malignancy of the thyroid gland. It is also known as follicular carcinoma.
Follicular nodules are the most commonly encountered problems in the surgical pathology of the thyroid. These lesions can be classified along the full spectrum of thyroid pathology from hyperplastic nodules to benign follicular adenomas and malignant follicular carcinomas and follicular variant papillary carcinomas. Follicular thyroid carcinoma is diagnosed based on pathologic confirmation of follicular cells that do not have the nuclear atypia seen in papillary thyroid cancer including capsular and vascular invasion.
Therefore the basis of evaluation is mainly on the histologic findings of. Follicular thyroid cancer is a tumor of the follicular cells that are lined by cuboidal epithelial cells and have capsular and vascular invasive properties. Compared to follicular carcinoma follicular adenoma is benign and occurs more commonly with a ratio estimated to be 5 to 1.
This article will focus more on the follicular type of thyroid cancer discussing the etiology epidemiology histology evaluation. Thyroid nodules are very common findings and high-resolution sonography the preferred method for thyroid nodules 1 has drastically multiplied the number of incidentally spotted thyroid nodules. Follicular thyroid adenomas FTAs are very common thyroid nodules and follicular thyroid carcinomas FTCs represent 1022 of thyroid carcinomas second only to papillary thyroid.
Diagnostic from malignant disease thereby reducing the number and accuracy ¼ 888 Frozen section alone 908 Final histological diagnosis Table 6 Benign Papillary Follicular Others Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative frozen section diag- nodule carcinoma carcinoma 19 noses with intraoperative cytology intraoperative frozen. Follicular carcinoma is the second most common type of thyroid cancer in adults. The tumour may be described as a thyroid nodule on ultrasound imaging.
Most tumours are separated from the surrounding normal healthy thyroid gland by a thin barrier called a capsule. Anatomy and histology of the thyroid gland. The role of histology and staging systems in predicting survival.
Lo CY 1 Chan WF Lam KY Wan KY. 1Departments of Surgery University of Hong Kong Medical Centre Queen Mary Hospital Pokfulam Hong Kong China. To evaluate the risk factors including tumor histomorphology for survival specific to follicular thyroid carcinoma.
Code follicular and papillary carcinoma of the thyroid to papillary carcinoma follicular variant 8340. Use the comment to code the histology for the right lobectomy. Probable is an acceptable ambiguous term to use for coding histology.
See the Ambiguous Terms Used to Code Histology section of the General Instructions in the MPH manual. Visual survey of surgical pathology with 11226 high-quality images of benign and malignant neoplasms related entities. Follicular Carcinoma Focused Follicular Carcinoma with stained slides of pathology.
Histological appearance of a minimally invasive angioinvasive follicular thyroid carcinoma. A Microfollicularsolid pattern of growth of the neoplasia surrounded by a thick capsule HE 4. Follicular adenoma FA is defined as a benign encapsulated non-invasive thyroid tumour differentiating towards follicular epithelium and lacking the nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
By autopsy findings FAs have been reported in 35 of adults. Under microscopy the tumors contain neoplastic follicular cells which overall can have a solid trabecular or follicular growth pattern that usually produces microfollicles. Follicular thyroid carcinoma FTC is the second most common thy-roid malignancy after papillary thyroid carcinoma.
The authors studied the clinical course of 132 patients with FTC to determine whether there was a direct relation between the histologic degree of invasion tumor recurrence and.