In your brothers case hemorrhage is the most likely cause. Complication of the endoscopic sinus surgery.
Cerebral infarction and literally means softening of the brain as a result of liquefactive necrosis.
Focal area of encephalomalacia. This area of tissue undergoes contractions and eventually forms encephalomalacia within the brain Traumatic brain injury Blunt force trauma to the skull will lead to. Various diseases and health conditions can cause this decline in the brain. The disorder generally occurs due to a stroke or some serious head injury which can lead to bleeding or hemorrhage into the brain.
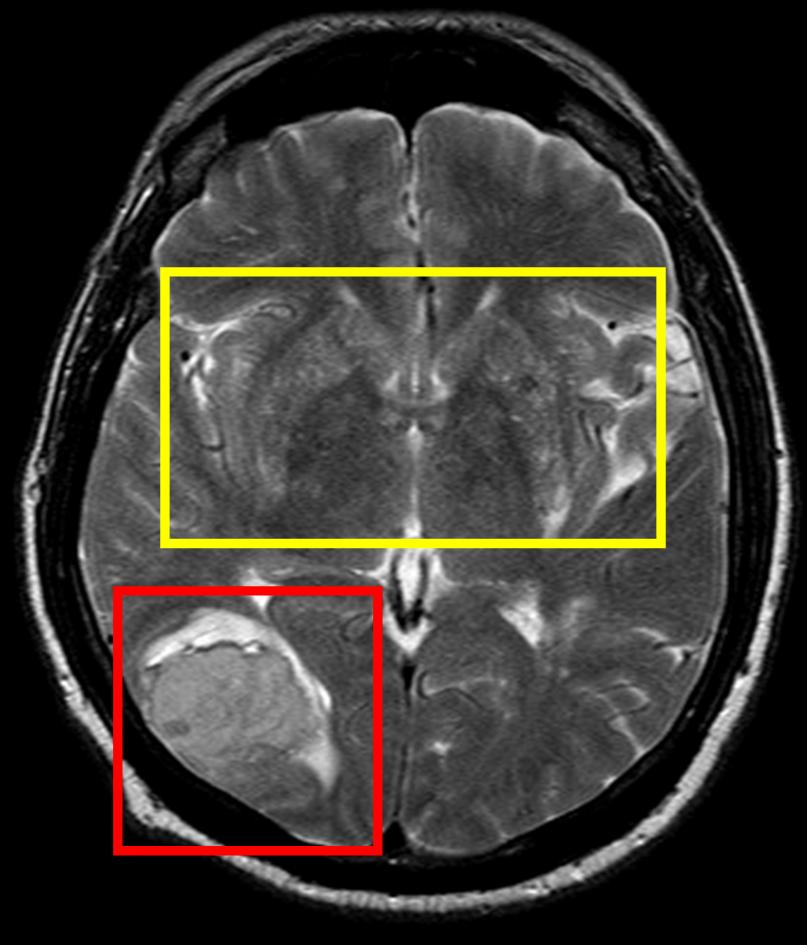
Cerebral Softening is most commonly seen in areas with an abnormal accumulation of blood. Encephalomalacia in the frontal lobe. Complication of the endoscopic sinus surgery.
Encephalomalacia is the softening or loss of brain tissue after cerebral infarction cerebral ischemia infection craniocerebral trauma or other injury. The term is usually used during gross pathologic inspection to describe blurred cortical margins and decreased consistency of brain tissue after. Encephalomalacia literally softening of the brain is a nonspecific term for the end result of liquefactive necrosis of brain parenchyma.
It can be focal or diffuse and can be seen in adults children and even in utero. Encephalomalacia can occur anywhere in the brain. After trauma characteristic locations are anteroinferior frontal and temporal lobes.
Encephalomalacia is an old term coined by pathologists to describe the macroscopic appearance of the brain following a variety of insults eg. Cerebral infarction and literally means softening of the brain as a result of liquefactive necrosis. English-speaking radiologists have however appropriated the term and use it perhaps more loosely to denote an area that has undergone liquefactive necrosis leaving.
The causes of encephalomalacia are different types of trauma to the brain a cerebral hemorrhage or a cerebral ischemia. Most times when we encounter encephalomalacia it was caused by some type of birth injury either during the labor and delivery of a child or the treatment shortly thereafter. Encephalomalacia may be caused by a brain injury.
A softening of the brain can occur in a specific area or can be widespread. A hemorrhage or bleed into the brain can cause encephalomalacia which is typically seen in a localized area where there is an abnormal collection of blood. Encephalomalacia in this part of the brain can cause damage to memory emotions speech sensory perception and muscle control.
This form damages the brains white matter or the area of the brain responsible for learning and brain function. It also carries nerve signals throughout the cerebrum and different parts of the brain. Encephalomalacia is an area of brain that has been previously injured either by physical trauma injury or by ischemia stroke.
It is essentially an area of brain that is dead. There is no way to treat it or make it better - it is permanent. Your symptoms will depend on which exact part of you brain has died.
Encephalomalacia can be localized or it can spread to adjacent brain tissue from a local focal area. Below are important conditions that can cause extensive softening of brain tissue. Cerebral infarction leading to stroke is the most common cause for encephalomalacia.
Encephalomalacia also named as cerebral softening is an area of focal brain damage that is most commonly seen in areas with insufficient blood supply. Occipital Hypometabolism on FDG PETCT Scan in a Child with Hodgkins Lymphoma. Encephalomalacia and gliosis refer to brain damage or loss of brain cells.
This condition can occur as a result of trauma hemorrhage or infections in the brain. In your brothers case hemorrhage is the most likely cause. Unfortunately there is no treatment currently available to reverse brain damage.
A softening of the brain can occur in a specific area or can be widespread. A hemorrhage or bleed into the brain can cause encephalomalacia which is typically seen in a localized area where there is an abnormal collection of blood. Though rare extensive softening of the brain can also be caused by degeneration or deterioration of the brain.