Hydrolysis of anandamide to arachidonic acid and ethanolamine results in the loss of its biological activities. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2.

2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2.
Endogenous ligand for cannabinoid receptors. In 1990 the gene encoding a cannabinoid receptor CB1 was cloned. This prompted the search for endogenous ligands. In 1992 N-arachidonoylethanolamine anandamide was isolated from pig brain as an endogenous ligand and in 1995 2-arachidonoylglycerol was isolated from rat brain and canine gut as another endogenous ligand.
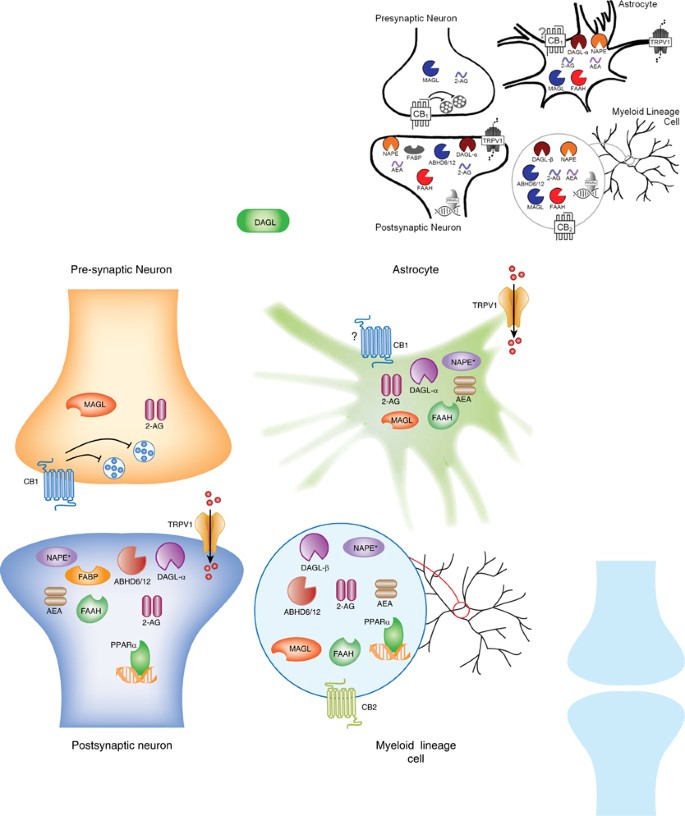
Both anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol exhibit various. The existence of an endogenous cannabinoid system was demonstrated conclusively with the discovery of endogenous brain constituents capable of activating the cannabinoid receptors functionally. These compounds are synthesized by neuronal cells and inactivated through re-uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis by both neurons and astrocytes.
In analogy with the endorphins they can be referred to as. Endocannabinoids and the endogenous cannabinoid system In 1992 the first endogenous ligand of CB 1 receptors was identified in porcine brain. This substance is the amide of arachidonic acid AA with ethanolamine and was named anandamide from the Sanskrit word ananda meaning bliss.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. Evidence is gradually accumulating which shows that 2-arachidonoylglycerol plays important physiological roles in several mammalian tissues and cells yet the details remain ambiguous. Anandamide an Endogenous Ligand of Cannabinoid Receptors Inhibits Human Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation Through a Lipid Rafts Mediated Mechanism Claudia Grimaldi and Maurizio Bifulco Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of Salerno 84084-Fisciano Italy.
2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. Previously we provided evidence that 2-arachidonoylglycerol but not anandamide N-arachidonoylethanolamine is the true natural ligand for the cannabinoid receptors. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2.
Evidence is gradually accumulating which shows that 2-arachidonoylglycerol plays important physiological roles in several mammalian tissues and cells yet the details remain ambiguous. In this study we first examined the effects of 2-arachidonoylglycerol on the motility of human natural killer cells. We found that 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
The endocannabinoid system was revealed following the understanding of the mechanism of action of marijuanas major psychotropic principle Δ 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and includes two G-protein-coupled receptors GPCRs. The cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors their endogenous ligands the endocannabinoids the best studied of which are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol 2-AG and the proteins that regulate the levels and activity of these receptors and ligands. Ligands for the cannabinoid receptor are often grouped for ease of division into plant-derived cannabinoids phytocannabinoids synthetic cannabinoids and endogenous cannabinoids endocannabinoids Mechoulam et al 2014.
Anandamide an endogenous eicosanoid derivative arachidonoylethanolamide binds to the cannabinoid receptor a member of the G protein-coupled superfamily. It also inhibits both adenylate cyclase and N-type calcium channel opening. The enzymatic synthesis of anandamide in bovine brain tissue was examined by incubating brain membranes with 14Cethanolamine and arachidonic acid.
The most studied endogenous ligands that bind cannabinoid receptors are AEA Devane et al 1992 and 2-arachidonoylglycerol 2-AG Mechoulam et al 1995. Sugiura et al 1995. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol 2-AG is a unique molecular species of monoacylglycerol isolated in 1995 from rat brain and canine gut as an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors.
2-AG is rapidly formed from arachidonic acid-containing phospholipids through increased phospholipid metabolism such as enhanced inositol phospholipid turnover in various tissues and cells upon stimulation. A simple and efficient synthesis of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol an endogenous agonist for cannabinoid receptors was achieved using Novozym 435 immobilized lipase from Candida Antarctica. Cannabinoid endogenous ligand 2-arachidonoylglycerol biocatalysis.
Anandamide arachidonoylethanolamide was discovered as an endogenous agonist for the cannabinoid receptors. Hydrolysis of anandamide to arachidonic acid and ethanolamine results in the loss of its biological activities. The enzyme responsible for this hydrolysis was solubilized partially purified from the microsomes of porcine brain and referred to as anandamide amidohydrolase.
In addition to the. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol is an endogenous ligand for the cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. Previously we provided evidence that 2-arachidonoylglycerol but not anandamide N -arachidonoylethanolamine is the true natural ligand for the cannabinoid receptors.
THC as well as the two major endogenous compounds identified so far that bind to the cannabinoid receptors anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol 2-AG produce most of their effects by binding to both the CB 1 and CB 2 cannabinoid receptors.