
Telomeres are crucial to the life of the cell. However this important function for telomeres in chromosome end protection can be lost as telomeres shorten with cell division in culture or in self-renewing tissues with advancing age.
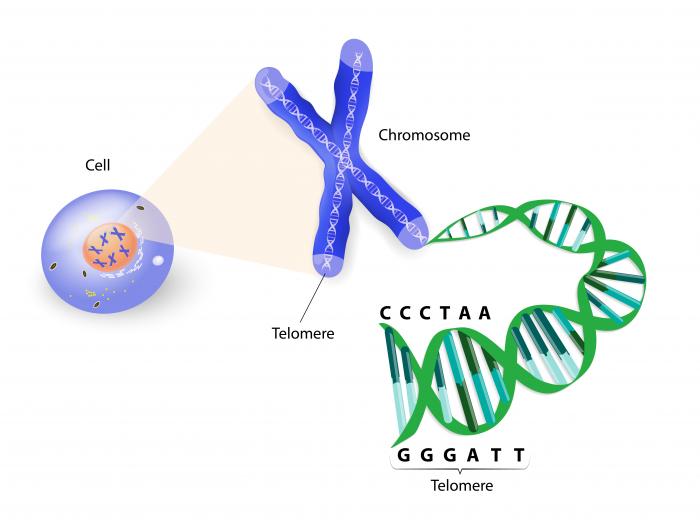
Telomeres are made of repetitive sequences of non-coding DNA that protect the chromosome from damage.
End of chromosomes telomeres. A telomere is the end of a chromosome. Telomeres are made of repetitive sequences of non-coding DNA that protect the chromosome from damage. Each time a cell divides the telomeres become shorter.
Eventually the telomeres become so short that the cell can no longer divide. Telomeres are essential factors located at the ends of chromosomes from the Greek. Telos meaning end and meros meaning part that are required for chromosome-end protection and genomic stability.
They are made up of short tandem repeats rich in GC base pairs that may differ in sequences across different species. Telomeres are specialised structures at the end of linear chromosomes. They consist of tandem repeats of the hexanucleotide sequence TTAGGG as well as a protein complex called shelterin.
Together they form a protective loop structure against chromosome fusion and degradation. Shortening or damage to telomeres and opening of the loop induce an uncapped state that triggers a DNA damage response resulting in senescence or apoptosisAverage telomere. Telomeres disguise the chromosome ends in eukaryotes The ends of linear eukaryotic chromosomes must not be perceived by the cell as broken DNA ends.
Protein-DNA complexes called telomeres disguise. At the ends of each of your chromosomes are stretches of DNA called telomeres. Telomeres help protect the ends of your chromosomes from damage or fusing with nearby chromosomes.
The ends of eukaryotic chromosomes are protected by specialized structures termed telomeres that serve in part to prevent the chromosome end from activating a DNA damage response. However this important function for telomeres in chromosome end protection can be lost as telomeres shorten with cell division in culture or in self-renewing tissues with advancing age. Impaired telomere function leads.
Telomeres protect the end of the chromosome from DNA damage or from fusion with neighbouring chromosomes. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster lacks telomerase but instead uses retrotransposons to maintain telomeres. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase enzyme that carries its own RNA molecule eg with the sequence 3-CCCAAUCCC-5 in Trypanosoma brucei which is.
Telomeres are the caps at the end of each chromosome that protect your DNA from unraveling or fraying. Generally longer telomeres are associated with health and longevity. But extremely long telomeres can make cancer cells immortal.
This video explains ehats is the telomeres the telomerase activity and the end replication problem. WITHOUT TELOMERES THE ENDS OF THE CHROMOSOMES WOULD BE REPAIRED LEADING TO CHROMOSOMES FUSION AND MASSIVE GENOMIC INSTABILITY. THEY PROTECT THE CHROMOSOMES.
THEY SEP A RATE ONE CHROMOSOME FROM ANOTHER IN THE DNA SEQUENCE. Scene 4 1m 39s TELOMERES FUNCTION. Telomeres are also thought to.
Included in the noncoding DNA are long stretches that make up the centromere and long stretches at the ends of the chromosome the telomeres. Telomeres are crucial to the life of the cell. They keep the ends of the various chromosomes in the cell from accidentally becoming attached to each other.
The telomeres of humans consist of as many as 2000 repeats of the sequence 5 GGTTAG 3. Telomeres are repetitive DNA sequences that protect the ends of each chromosome. Telomeres shorten with every cell division due to the end replication problem and with DNA damage.
Telomeres shorten with age and in disease Blackburn 2015. Long telomeres form a loop that prevents the DNA end from acting as broken DNA. Chromosomes were unstable and prone to rearrangements and fusion whereas the chromosome ends were protected from such events12.
The special nature of chromosomal ends was noted and they were named telomeres from the Greek words telos end and meros part by Muller. However the molecular nature of the telomeres was unknown. Telomeres as protective caps on the tips of eukaryotic chromosomes.
How telomerase extends telomeres. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Donate Login Sign up.
Search for courses skills. The function of telomeres is to protect chromosome ends from chromosome fusions and degradation during the process of cellular replication therefore ensuring the proper functionality and viability of cells. Cell division plays a critical role in normal growth maintenance and repair of.