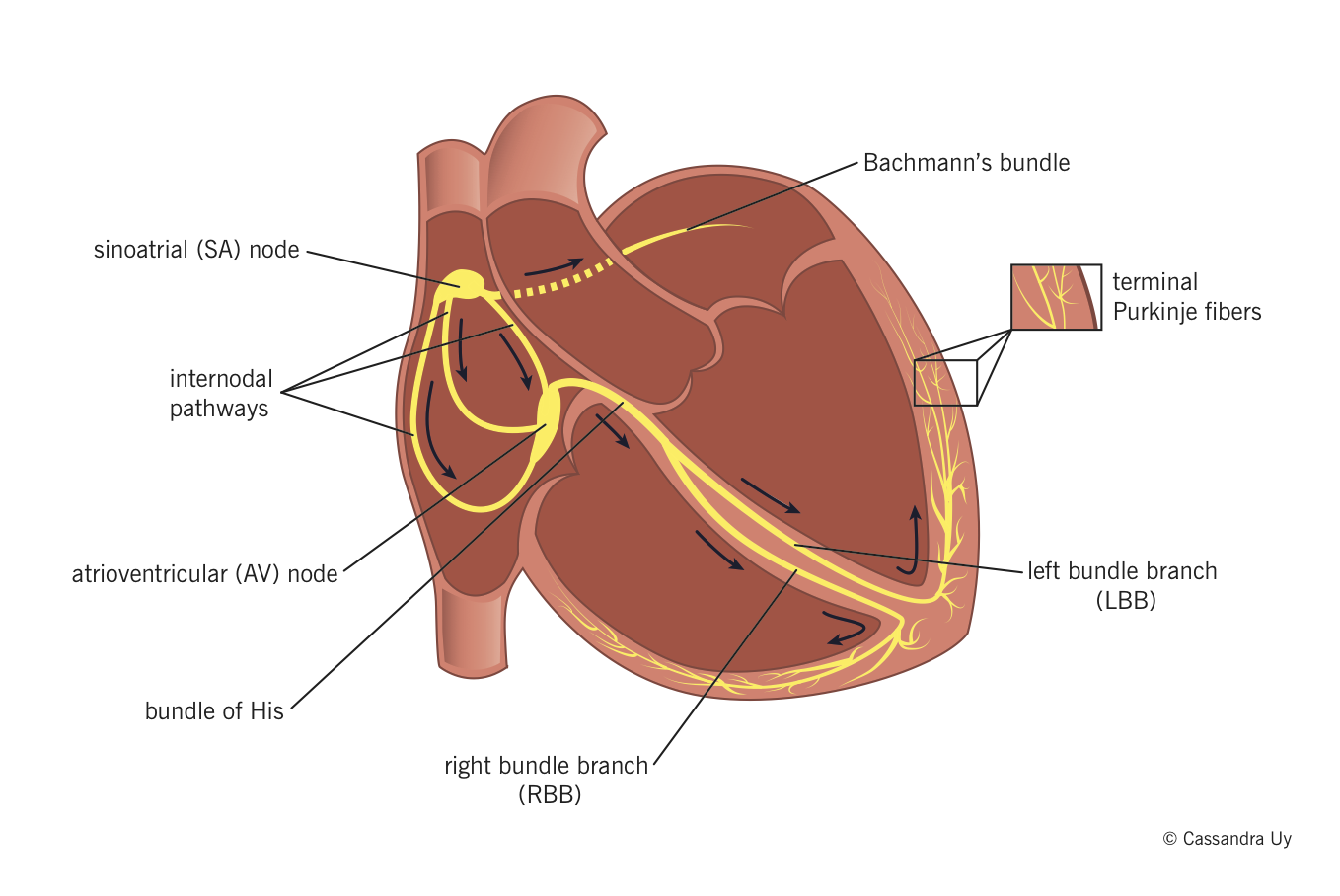
An electrical stimulus is generated by the sinus node also called the sinoatrial node or SA node. Your heart beats as a result of the generation and conduction of electrical impulses.

The heart made up of striated cardiac muscle is the pump that governs the flow of blood being an important player in maintaining body homeostasis.
Electrical firing mechanism of the heart. An electrical stimulus is generated by the sinus node also called the sinoatrial node or SA node. This is a small mass of specialized tissue located in the right upper chamber atria of the heart. The sinus node generates an electrical stimulus regularly 60 to 100 times per minute under normal conditions.
The atria are then activated. The electrical stimulus travels down through the conduction. By careful placement of surface electrodes on the body it is possible to record the complex compound electrical signal of the heart.
This tracing of the electrical signal is the electrocardiogram ECG also commonly abbreviated EKG K coming kardiology from the German term for cardiology. Careful analysis of the ECG reveals a detailed picture of both normal and abnormal heart function and is an. The electrical signal spreads through the chambers of the heart.
First the atria are activated. The electrical signal then travels down through the conduction pathways to the hearts ventricles. This causes them to contract and pump out blood.
The electrical signal then travels from the sinus node to the atrioventricular node AV node. There the signals slow down for a very short period. What is electrical firing mechanism of the heart.
Lnelson4420 07192019 Medicine College 10 pts. Answered What is electrical firing mechanism of the heart. 1 See answer.
Firing mechanism using a firing magneto battery or alternating-current power in circuit with an electric primer. One side of the line is connected by an insulated wire to the primer and the other side is grounded to the frame of the weapon. The hearts electrical system is responsible for making and conducting signals that trigger the heart to beat.
These signals cause the hearts muscle to contract. With each contraction blood is pumped throughout the body. The process begins in the upper chambers of the heart atria which pump blood into the lower chambers ventricles.
The ventricles then pump blood to the body and lungs. The regulation of electrical signals by the AV node ensures that electrical impulses do not move too rapidly which can result in atrial fibrillation. In atrial fibrillation atria beat irregularly and very rapidly at rates of between 300 to 600 times per minute.
Normal heart rate is between 60 to 80 beats per minute. Atrial fibrillation can result in adverse conditions such as blood clots or heart failure. Your hearts electrical system controls the timing of your heartbeat by regulating your.
Heart rate which is the number of times your heart beats per minute. Heart rhythm which is the synchronized pumping action of your four heart chambers. Your hearts electrical system should maintain.
A steady heart rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute at rest. The hearts electrical system also increases. First-degree heart block occurs when the electrical impulse moves through the hearts AV node more slowly than normal.
This usually results in a slower heart rate. The condition may cause dizziness or lightheadedness or it may cause no symptoms at all. Mechanism of blood flow will be discussed in the next paragraph.
The heart made up of striated cardiac muscle is the pump that governs the flow of blood being an important player in maintaining body homeostasis. The main purpose of the heart pumping blood throughout the body is to supply oxygen to and at the same time get rid of carbon dioxide waste from body tissues. Your heart beats as a result of the generation and conduction of electrical impulses.
Cardiac conduction is the rate at which the heart conducts electrical impulses. These impulses cause the heart to contract and then relax. The constant cycle of heart muscle contraction followed by relaxation causes blood to be pumped throughout the body.
The heart generates its own electrical signal also called an electrical impulse which can be recorded by placing electrodes on the chest. This is called an electrocardiogram ECG or EKG. The cardiac electrical signal controls the heartbeat in two ways.
However rather than being struck by a firing pin or by equivalent mechanical means an electric current serves to detonate the primer. After which the provided action delivers the thermal impulse necessary to ignite the propellant which then deflagrates producing pressure. Electrical activity that originates from the sinoatrial node is propagated via the His-Purkinje network the fastest conduction pathway within the heart.
The electrical signal travels from the sinoatrial node SAN which stimulates the atria to contract to the atrioventricular node AVN which slows down conduction of the action potential from the atria to the ventricles. This delay allows the ventricles to fully fill with. The hearts activity is dependent on the electrical impulses from the sinoatrial SA node and atrioventricular AV node which form the intrinsic conduction system of the heart.
The SA and AV nodes act as a pacemaker for the heart determining the rate at which it beats even without signals from the larger nervous system of the human body. The SA and AV nodes initiate the electrical impulses that cause contraction within the atria and ventricles of the heart. SA node is called the pacemaker of the heart.
Normally SA node is responsible for generating the cardiac electrical impulses that bring about the mechanical activity that is contraction of the heart. SA node has the fastest rate of autorhythmicity. Heart conduction system.
The electrical conduction system that controls the heart rate. This system generates electrical impulses and conducts them throughout the muscle of the heart stimulating the heart to contract and pump blood. Among the major elements in the cardiac conduction system are the sinus node atrioventricular node and the autonomic nervous system.
The sinus node is the heart. Heart matt ers a publication of the adult congenital heart association IfyourAVnodeisnotworkingwellyoumaydevelopa conditionknownasheartblockFirst-degreeheartblockis. How the heart functions electrically The hearts natural pacemaker the SA node sends out regular electrical impulses from the top chamber the atrium causing it to contract and pump blood into the bottom chamber the ventricle.
The electrical impulse is then conducted to the ventricles through a form of junction box called the AV node. The impulse spreads into the ventricles causing.