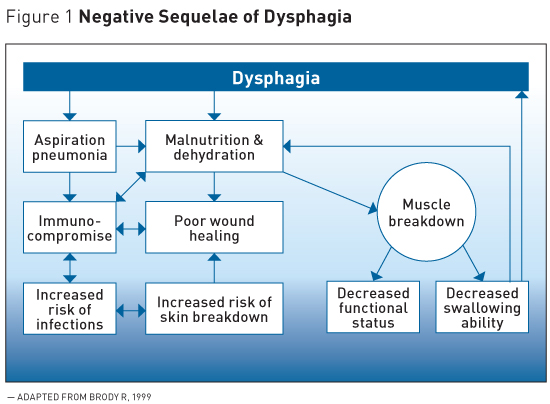
Swallowing problems can lead to aspiration. Dysphagia has a negative impact on the quality of life for those suffering from it.
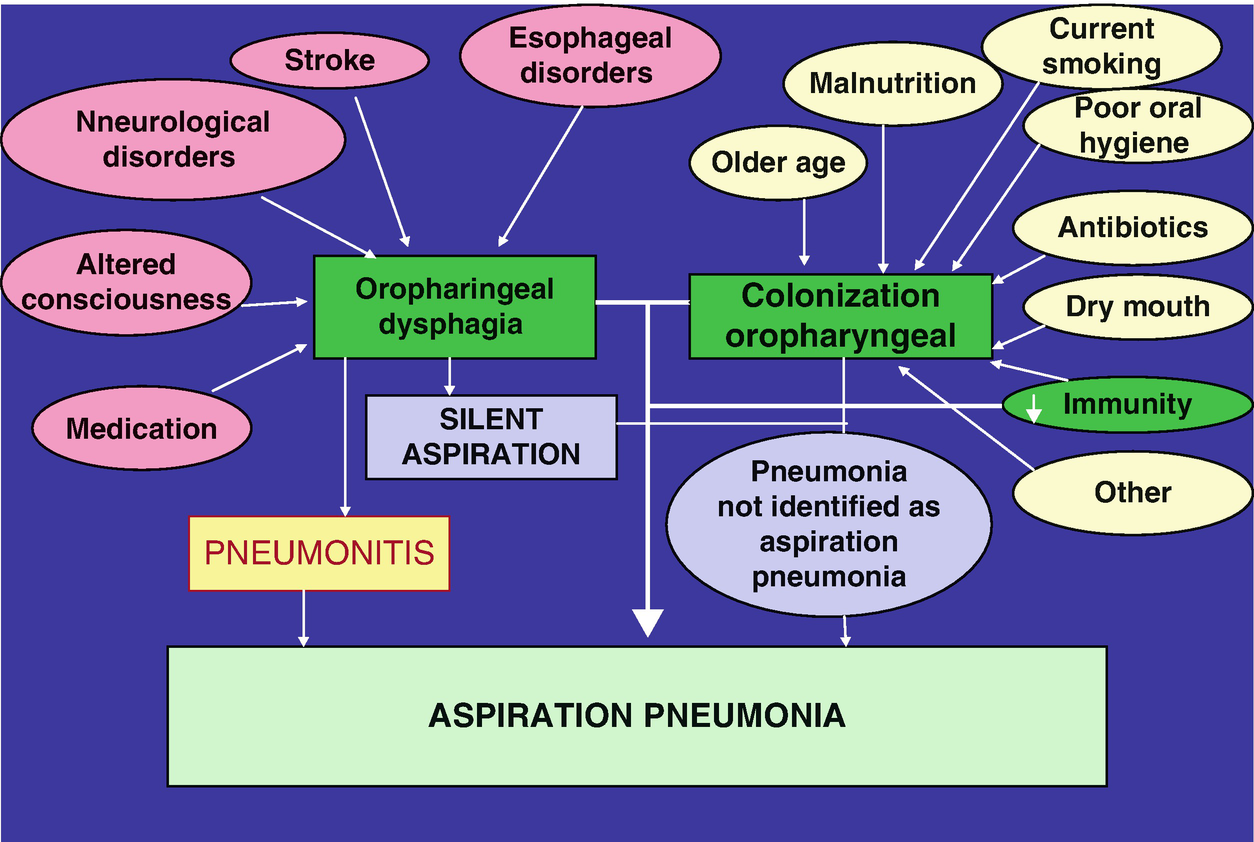
102169internalmedicine6576-20 Aspiration pneumonia continues to be a major cause of hospitalization and mortality in elderly.
Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia. Oropharyngeal aspiration is an important etiologic factor leading to pneumonia in the elderly. The incidence of cerebrovascular and degenerative neurologic diseases increase with aging and these disorders are associated with dysphagia and an impaired cough reflex with the increased likelihood of oropharyngeal aspiration. Elderly patients with clinical signs suggestive of dysphagia andor who.
Aspiration pneumonia is a common diagnosis in older adults and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Oropharyngeal and esophageal dysphagia often related to stroke dementia poor oral hygiene or multiple chronic illnesses increases the risk of aspiration. Nurse practitioners NPs need to be aware that frequent episodes of pneumonia may be caused by.
A 70-year-old male developed dysphagia and consequent aspiration pneumonia during recovery from severe COVID-19. He had altered sense of taste and absent gag reflex. Videoendoscopy videofluorography and high-resolution manometry revealed impaired pharyngolaryngeal sensation silent aspiration and mesopharyngeal contractile dysfunction.
These findings suggested that. Since aspiration pneumonia is fundamentally based on dysphagia we should shift the therapy for aspiration pneumonia from pathogen-oriented therapy to function-oriented therapy. Function-oriented therapy in aspiration pneumonia means therapy focusing on slowing or reversing the functional decline that occurs as part of the aging process such as dementia dysphagia.
Finally dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia risk factor were analyzed between these two groups. Number of previous cerebral infarction National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale NIHSS score masticatory muscle paralysis abolition of gag reflex were correlated with the deglutition difficulty in these patients. Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia are the 2 most serious medical conditions seen in late-stage Alzheimers disease AD patients.
Pseudobulbar dysphagia is associated with weight loss which is not always prevented by optimizing the management of the dysphagia. Failure of basic homeostatic mechanis. Dysphagia and aspiration pneumonia are the 2.
Dysphagia is the major pathophysiologic mechanism leading to aspiration pneumonia in the elderly. Dysphagia has a negative impact on the quality of life for those suffering from it. Awareness of dysphagia in the elderly the diagnostic procedures and treatment options available should be increased among the medical profession.
Microbiology of Aspiration Pneumonia Basically the pathogens that contaminate the nasopharynx and oropharynx are those responsible for AP 1. Strong correlation has been found between cul-tures of dental plaque samples and those of bronchoalveolar lavage in patients with nosocomial pneumonia associated with mechanical ventilation. Key points about aspiration from dysphagia Aspiration is when something enters the airway or lungs by accident.
It may be food liquid or some other material. This can cause serious health problems such as pneumonia. Aspiration can happen when a.
A Key Concept in Pneumonia Treatment Satoru Ebihara 1 Midori Miyagi Yuta Otsubo Hideki Sekiya2 and Takae Ebihara3 Key words. Swallowing function dysphagia multidisciplinary team Intern Med 60. 102169internalmedicine6576-20 Aspiration pneumonia continues to be a major cause of hospitalization and mortality in elderly.
Trouble with chewing and swallowing. Food and saliva may go into the lungs instead of the stomach Aspiration. Food goes into the airway but the person can still breathe.
Person may cough Silent aspiration no coughing Choking. Aspiration Pneumonia and Dysphagia in the Elderly Paul E. And Danielle Kaplan MA Community-acquired pneumonia CAP is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the elderly and the leading cause of death among residents of nursing homes.
Oropharyngeal aspiration is an important etiologic factor leading to pneumonia in the elderly. The incidence of cerebrovascular. DYSPHAGIA AND ASPIRATION A common problem for many of the people that we work with is dysphagia.
Dysphagia is a word that describes any problem a person may have with swallowing. Swallowing problems can lead to aspiration. Aspiration describes a condition when food or fluids that should go into the stomach go into the lungs instead.
Oropharyngeal aspiration is an important etiologic factor leading to pneumonia in the elderly. The incidence of cerebrovascular and degenerative neurologic diseases increase with aging and these disorders are associated with dysphagia and an impaired cough reflex with the increased likelihood of oropharyngeal aspiration. Elderly patients with clinical signs suggestive of dysphagia andor who have.
Aspiration pneumonia is the most serious problem for patients with dysphagia. Preventing aspiration pneumonia requires both the effort to minimize aspiration and the techniques to avoid pneumonia onset even if the patient experiences aspiration. To accomplish this body positions are 1.
Described in relation to the pathogenesis of aspiration pneumonia. Dysphagia was concluded to be an important risk for aspiration pneumonia but generally not suffi-cient to cause pneumonia unless other risk factors are present as well. A dependency upon others for feeding emerged as the dominant risk factor with an odds ratio.
While swallowing dysfunction is associated with aspiration pneumonia dysphagia may not be sufficient unless other risk factors are present. Neurologic conditions that can directly impact the nerves involved in the swallow mechanism include stroke Parkinsons disease and multiple sclerosis. Severe temporomandibular joint disorder TMD could induce dysphagia which could lead to aspiration pneumonia.
However no clinical study has reported that TMD-related dysphagia could result in aspiration pneumonia. Integrative Korean medicine KM is suggested to be an effective treatment for patients with severe TMD.