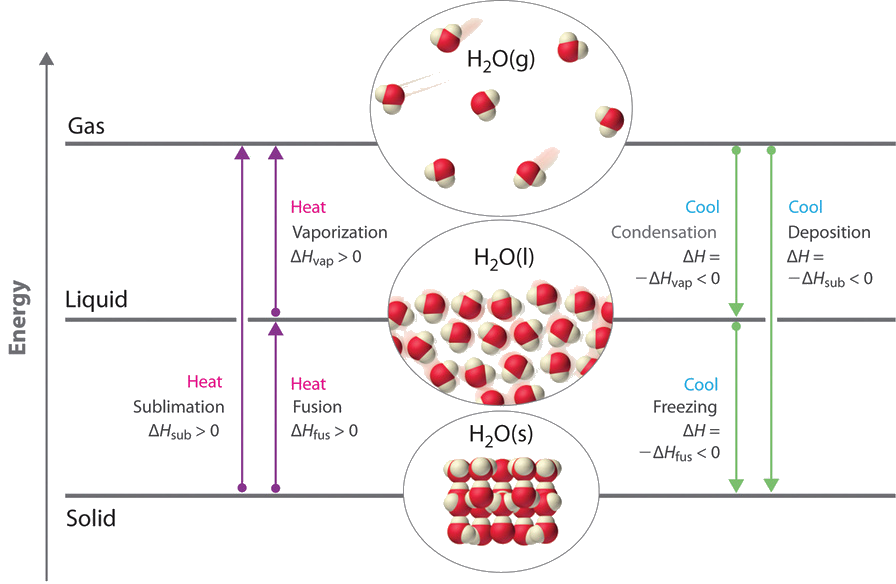
The mass of the substance does not change due to the conservation of mass. The energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the solid phase to the liquid phase or released when the substance changes from liquid to solid is known as the heat of fusion.
Stays the same B.
During a phase change mass. During a phase change. The mass of the substance does not change due to the conservation of mass. In a closed system the mass does not change no matter what phase change or chemical reaction takes.
During a phase change. The mass of the substance does not change due to the conservation of mass. In a closed system the mass does not change no matter what phase change or chemical reaction.
During a phase change mass 3 points stays the same increases decreases increases then decreases. 3 Show answers Another question on Chemistry. Kc 0040 for the system below at 450oc.
If a reaction is initiated with 040 mole of cl2 and 040 mole of pcl3 in a 20 liter container what is the equilibrium concentration of cl2 in the same system. During a phase change mass A. Stays the same B.
During a phase change mass 3 points stays the same increases decreases increases then decreases - 12859939. The energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the solid phase to the liquid phase or released when the substance changes from liquid to solid is known as the heat of fusion. The energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the liquid phase to the vapor phase is known as the heat of vaporization.
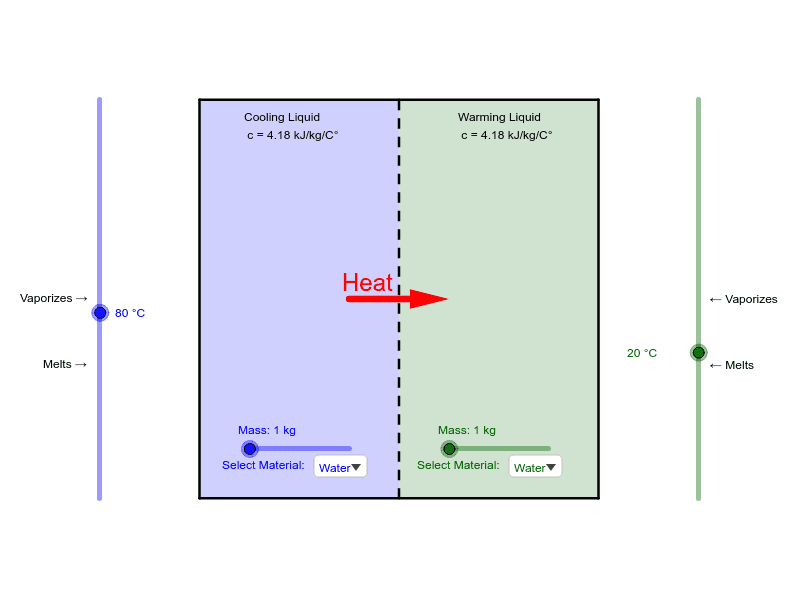
The energy involved in a phase change depends on two major factors. The number and strength of bonds or force pairs. The number of bonds is proportional to the number of molecules and thus to the mass of the sample.
The strength of forces depends on the type of molecules. The heat Q required to change the phase of a sample of mass m is given by. Is a measure of the heat energy Q per mass m released or absorbed during a phase change.
Is defined through the formula Q mL. Is often just called the latent heat of the material. When a phase change takes place the temperature on one side is CONSTANT but the presence of boilingcondensing fluids produces heat transfer.
Important in evaporation distillation LARGE h Its important to know in which regime you operate Each regime has different correlations Faith A. Morrison Michigan Tech U. 3 Newtons law of cooling vapor phase.
The melting of an unrestrained phase change material PCM around a horizontal tube arises in many applications such as ice storage for HVAC Heating Ventilating and Air Conditioning systems. The instantaneous heat transfer rate during the melting process must be known for optimal system design and operation of the application. A theoretical model was developed to analyze the heat transfer during.
Phase changes are always accompanied by a change in the energy of a system. For example converting a liquid in which the molecules are close together to a gas in which the molecules are on average far apart requires an input of energy heat to give the molecules enough kinetic energy to allow them to overcome the intermolecular attractive forces. The stronger the attractive forces the.
Phase changes introduce a discontinuity in the density and mass transfer between the two coexisting phases. This induces so-called production terms in the mass momentum and energy balance relations. To determine these terms the interface between the gaseous and the liquid phases is described by a separating immaterial smooth surface together with.
Heat n ΔHvap where n is the number of moles or heat m ΔHvap where m is the mass in grams Remember that a phase change depends on the direction of the heat transfer. If heat transfers in solids become liquids and liquids become solids at the melting and boiling points respectively. The energy involved in a phase change depends on two major factors.
The number and strength of bonds or force pairs. The number of bonds is proportional to the number of molecules and thus to the mass of the sample. The strength of forces depends on the type of molecules.
The heat required to change the phase of a sample of mass is given by. In the thermally fully-developed region mass transfer rate from the solid particles to liquid phase decreased because the rapid decrease of solid volume fraction near the wall impeded the phase change. Therefore the local heat transfer coefficient decreased along the flow direction due to the decreasing contribution of phase change to the heat exchange.
Moreover the solid temperature increased slowly corresponding to the increasing phase-change. The phase change in biological tissues during a freezing process is simulated by hyperbolic and parabolic heat equations with temperature-dependent enthalpy. It is observed that the experimental results are in a good agreement with that the calculated results by the enthalpy method.
The results shown that the Fourier model predicts tissues temperature lower than of the non-Fourier. Put a cup of water in the freezer and it will change to a solid. Put it out in the sun and eventually the liquid will disappear.
But in fact it hasnt really gone anywhere - it. A sample of ice is placed in a closed system container and allowed to melt. At the conclusion of the experiment it is observed that the mass remains constant.
Substance the first phase transitions discovered other thermodynamic phase changes occur in Nature as the change from normal electrical conductivity to superconductivity with or without magnetic field the change from paramagnetism to ferromagnetism the change from normal viscosity to superfluidity in. The second phase transition discovered was the ferromagneticparamagnetic transition at.