This cell line was derived from a 52-year-old male with DLBCL. Through whole genome and exome sequencing we characterized the genetic diversity of DLBCL.
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically challenged care for cancer patients especially those with active treatment that represent a vulnerable population for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Diffuse large b cell lymphoma cell lines. Several subsets of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma are distinguished by gene-expression profiling 6263. Chromosomal translocations involving BCL6 are characteristic for the germinal center B-cell GCB DLBCL subtype. Dysregulated BCL6 expression prevents the silencing and termination of the GC response and furthermore maintains the.
This approach identified a protein that is highly expressed in Diffuse Large B-cells Lymphomas DLBCL known as CYCLON whose encoding gene expression is associated with poor prognosis in lymphoma patients. The consideration of the tissue-of-origin of CYCLON gene expression showed that the encoding gene is in fact a testis-specific gene that is aberrantly active in lymphoma. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma worldwide.
We describe the establishment and molecular characteristics of the DLBCL cell line U-2946. This cell line was derived from a 52-year-old male with DLBCL. U-2946 cells carried the chromosomal translocation t814 and strongly expressed MYC but not the mature B-cell lymphoma.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma NHL in the United States and worldwide accounting for about 22 percent of newly diagnosed cases of B-cell NHL in the United States. More than 18000 people are diagnosed with DLBCL each year. DLBCL is an aggressive fast-growing NHL that affects B-lymphocytes.
Mediastinal B-cell lymphoma which often occurs in younger patients and grows rapidly in the chest mediastinum. Most cases do not fall into one of these categories and they are considered diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified or DLBCL-NOS. However these NOS cases can be grouped into subtypes of DLBCL that are diagnosed using.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common form of lymphoma in adults. The disease exhibits a striking heterogeneity in gene expression profiles and clinical outcomes but its genetic causes remain to be fully defined. Through whole genome and exome sequencing we characterized the genetic diversity of DLBCL.
Original Study BCL2 Expression in First-Line Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Identifies a Patient Population With Poor Prognosis Elizabeth Punnoose1 Franklin V. Peale1 Edith Szafer-Glusman1 Guiyuan Lei2 Richard Bourgon1 An D. Do1 Eugene Kim1 Liping Zhang3 Pedro Farinha45 Randy D.
Javier Munoz6 Maurizio Martelli7 Anja Mottok4 Gilles A. DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL LYMPHOMA AND HIGH-GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA. THERAPEUTIC RESPONSE - UNICENTRIC RETROSPECTIVE DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS.
Bianca Castro Bianca Castro. Serviço de Hematologia ClínicaCentro Hospitalar Universitário do PortoPortoPortugal. Claudia Pedrosa Claudia Pedrosa.
Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas DLBCLs represent the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma NHL. 1 Gene expression profiling classifies DLBCL into at least two molecular groups including. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common hematologic malignancy with an annual incidence of over 100000 cases worldwide.
Although more than half of these patients may achieve long-term remission the majority of the remaining patients succumb to DLBCL. Application of next-generation sequencing has revealed a striking degree of molecular and clinical heterogeneity. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL is a type of blood cancer.
Lymphomas are the most common type of blood cancers. There are two types of lymphoma. Managing the front-line treatment for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and high-grade B-cell lymphoma during the COVID-19 outbreak.
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically challenged care for cancer patients especially those with active treatment that represent a vulnerable population for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Aggressive lymphoid neoplasms such as. Diffuse large Bcell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common type of aggressive nonHodgkin lymphoma originating from the germinal center and it represents a heterogeneous group of diseases with variable outcomes that are differentially characterized by clinical features cell of origin COO molecular features and most recently frequently recurring mutations.
The phase 2 CAVALLI NCT02055820 study assessed efficacy and safety of venetoclax a selective B-cell lymphoma-2 Bcl-2 inhibitor with rituximab plus cyclophosphamide doxorubicin vincristine and prednisone R-CHOP in first-line 1L diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL including patients demonstrating Bcl-2 protein overexpression by immunohistochemistry Bcl-2 IHC. Newer more effective and non-cytotoxic therapies are an unmet need for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma DLBCL and other B-cell. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma DLBCL is the most common form of non-Hodgkins lymphoma in adults.
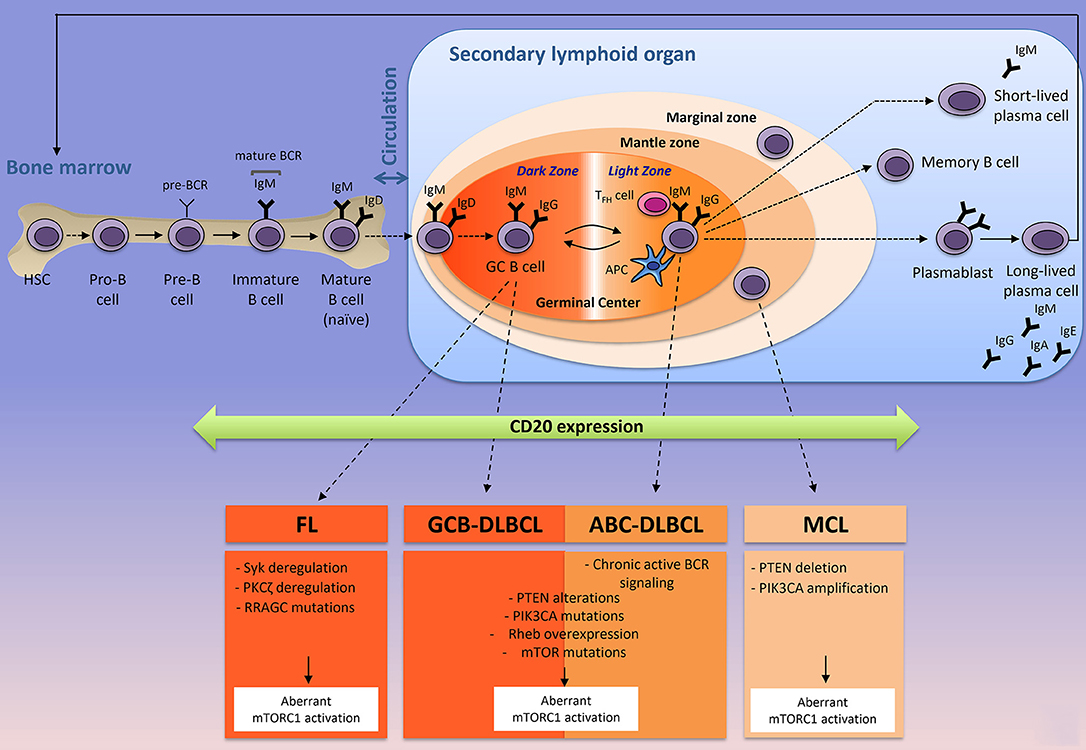
The majority of DLBCLs arise from antigen-exposed B cells during the germinal center GC reaction a process that optimizes the affinity of.