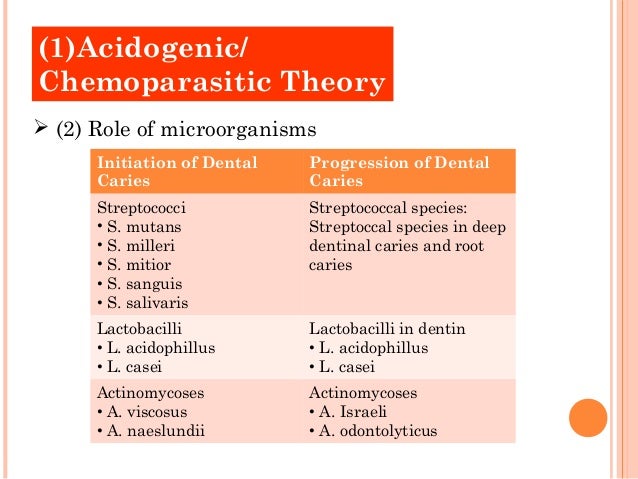
The Gram-positive and facultatively anaerobic mutans streptococci are aetiologically the most important bacteria in dental caries. A type of bacteria called the mutans streptococci are the most commonly implicated microbes in dental caries.
Unlike most infectious diseases where there is a single etiological agent dental caries is caused by a host of bacteria and therefore is termed a polymicrobial disease.
Dental caries bacteria species. Bacterial species other than S. Mutans eg species of the genera Veillonella Lactobacillus Bifidobacterium and Propionibacterium low-pH non-S. Mutans streptococci Actinomyces spp and Atopobium spp likely play important roles in caries progression.
The most frequent species found associated with dental caries were mutans streptococci and lactobacilli which shift the balance towards tooth tissue demineralisation. Oral biofilm Corresponding author. Mohammed Awadh Alshahrani Department of Dental Education.
The In-OvationR presented worse performance considering the levels of cariogenic bacterial species. Microbial species associated with dental caries found in saliva and in situ after use of self-ligating and conventional brackets J Appl Oral Sci. Epub 2019 Apr 11.
Authors Ana Zilda Nazar Bergamo 1 Mirian Aiko Nakane Matsumoto 1 Cássio. Dental caries is caused by acidogenic plaque microbiota formed on saliva-bathed tooth surfaces in which multiple organisms act collectively to initiate and expand a cavity. We explored bacterial species associated with the salivary microbiome of individuals with low susceptibility to dental caries.
The bacterial composition of saliva from 19 young adults was. Dental caries is a multifactorial polymicrobial disease with environmental behavioral and host risk factors. 1 The presence of cariogenic bacteria and fermentable carbohydrates are prerequisites for dental caries with bacterial metabolic activity resulting in the production of acid that can demineralize dental hard tissues.
Dental caries is caused by acidic metabolites of bacteria that usually live in the mouth where they nourish on carbohydrates. These prokaryotes especially Gram positive bacteria like Lactobacillus spp Streptococcus mutans and Actinomyces spp are available in oral biofilms which is the sticky slimy coating in the mouth that is most visible before brushing away that awful breath in the morning. The Gram-positive and facultatively anaerobic mutans streptococci are aetiologically the most important bacteria in dental caries.
Data have rapidly increased on the association of these bacteria with certain periodontal diseases or caries on phenotypic and genotypic characteristics pathogenic mechanisms antibiotic susceptibility patterns and transmission among family members. Dental caries is caused by acidogenic plaque microbiota formed on saliva-bathed tooth surfaces in which multiple organisms act collectively to initiate and expand a cavity. We explored bacterial species associated with the salivary microbiome of individuals with low susceptibility to dental caries.
The bacterial composition of saliva from 19 young adults was analyzed using barcoded. Types of Bacteria causing Dental Caries. 1 Pit fissure Caries.
2 Smooth surface Caries. 4 Deep dentinal caries. Most of these bacteria are present in the oral cavity even when there is no dental caries in.
Mutans Actinomyces spp and Lactobacillus spp. Were over-abundant in caries-active subjects whereas beneficial species associated with dental health included S. Taken together the number of species identified in.
Bacterial species other than S. Mutans eg species of the genera Veillonella Lactobacillus Bifidobacterium and Propionibacterium low-pH non- S. Mutans streptococci Actinomyces spp and Atopobium spp likely play important roles in caries progression.
These species included Streptococcus mutans 14 151617 and multiple Prevotella spp. 12 which have been reported to be associated with dental caries as well as Prevotella amnii. Bacterial species other thanS.
Mutans eg species of the generaVeillonella Lactobacillus Bifidobacterium and Propionibacterium low-pH non-S. Mutans streptococci Actinomyces spp and Atopobium spp likely play important roles in caries progression. Dental caries is one of the most common chronic infectious diseases in the world 2 39.
There are three major hypotheses. Dental caries can also be caused by other bacteria such as Enterococcus faecalis Actinomyces naeslundii A. Viscosus Rothia dentocariosa Propionibacterium Prevotella Veillonella.
The mouth contains a wide variety of oral bacteria but only a few specific species of bacteria are believed to cause dental caries. Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilli among them. Lactobacillus acidophilus Actinomyces viscosus Nocardia spp and Streptococcus mutans are most closely associated with caries in particular root caries.
Bacteria collect around the teeth and gums in a sticky creamy-colored mass. A type of bacteria called the mutans streptococci are the most commonly implicated microbes in dental caries. Their increase causes dental decay.
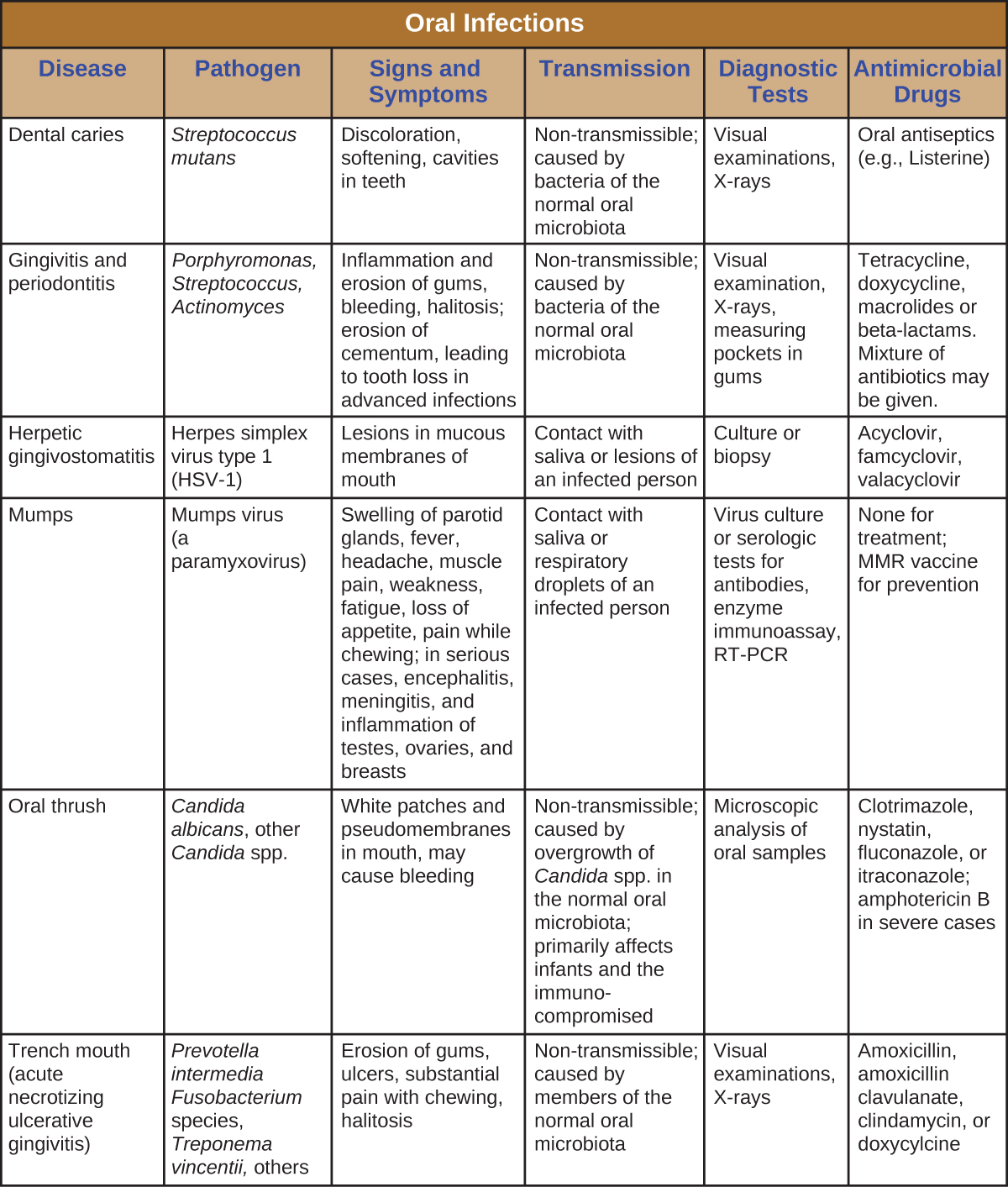
Dental caries more commonly known as tooth decay or cavities is the destruction of enamel dentin or the cementum caused by acid producing bacteria in a dental plaque. The result is a lesion in the crown or the root surface of the tooth. Unlike most infectious diseases where there is a single etiological agent dental caries is caused by a host of bacteria and therefore is termed a polymicrobial disease.
More than 800 species of bacteria colonize oral mucous 1300 species are found in the gingival crevice and nearly 1000 species comprise dental plaque. The mouth is a rich environment for hundreds of species of bacteria since saliva is mostly water and plenty of nutrients pass through the mouth each day. When kissing it takes only 10 seconds for no less than 80 million bacteria to be.