The antibiotics used in prophylaxis specifically target these bacteria. Patients were stratified by severity of periodontal disease and number of teeth extracted.

Additional Considerations About Infective Endocarditis Antibiotic Prophylaxis When Indicated Sometimes patients forget to premedicate before their appointments.
Dental antibiotic prophylaxis dosage. Additional Considerations About Infective Endocarditis Antibiotic Prophylaxis When Indicated Sometimes patients forget to premedicate before their appointments. The recommendation is that for patients with an indication for antibiotic prophylaxis the antibiotic be given before the procedure. This is important because it allows the antibiotic to reach adequate blood levels.
Prophylactic antibiotics are recommended when these patients undergo procedures that are at risk for producing bacteremia. This guideline is intended to help practitioners make decisions regarding antibiotic prophylaxis for dental patients at risk. Methods This guideline was originally developed by the Council on Clinical Affairs and adopted in 1990.
This document is a. The 2007 AHA guidelines state that an antibiotic for prophylaxis should be administered in a single dose before the procedure 34. However in the event that the dosage of antibiotic is inadvertently not administered before the procedure it may be administered up to two hours after the procedure.
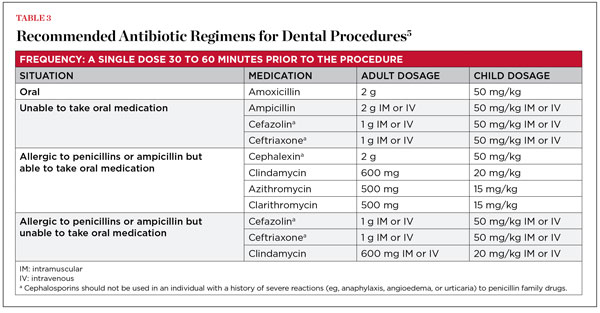
For patients already receiving an antibiotic that. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be taken in a single dose 30-60 minutes before dental treatment. This time period is recommended so that there will be high blood levels of antibiotic at the time bacteremia occurs.
2 grams orally 1 hour prior to the dental procedure Patients not allergic to penicillin and Cefazolin or ampicillin unable to take oral medications. Cefazolin 1 g or ampicillin 2 g intramuscularly or intravenously 1 hour prior to the dental procedure Patients allergic to penicillin. Clindamycin 600 mg orally 1 hour prior to the dental procedure.
And so the major change occurred in 1982 when the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy introduced a purely oral regime for antibiotic prophylaxis for dental procedures and that involved a 3 g oral dose of Amoxil one hour before dental procedures in patients who would be at risk of infective endocarditis to be followed up six hours later by 15 g dose and at the time that was thought to be a. Thirty-six outpatients in a dental clinic were randomized in a 322 ratio to experimental prophylaxis of topical amoxicillin 3 g per mouthwash rinse. 15 patients standard prophylaxis of oral amoxicillin 3 g in a single dose.
11 patients or no prophylaxis 10 patients respectively. Patients were stratified by severity of periodontal disease and number of teeth extracted. Data were analyzed for.
The use of antibiotics before an invasive dental procedure to prevent endocarditis as a consequence of the procedure is based on experimental research on animals. The efficacy of this measure has however not yet been demonstrated in humans. Starting in 2007 therefore fewer heart diseases have been indicated for endocarditis prophylaxis.
2 g antibiotic prophylaxis. Prophylaxis for dental patients at risk for infection. Operation Recommended Antibiotic Prophylaxis Re-dosing Schedule for Prolonged Surgery Hours Dental Oral Respiratory Tract or Esophageal Procedures Preferred.
Ampicillin OR Cefazolin Alternatives. Clindamycin 20 mgkg IVPO Max Dose 600 mg OR Ceftriaxone 4 4 8 16 Cardiothoracic Preferred. Those at greatest risk of an adverse outcome from infective endocarditis should receive single dose preventive antibiotics before all dental procedures that involve manipulation of gingival tissue or the periapical regions of teeth or that perforate the oral mucosa.
The following procedures and events do not need prophylaxis for high risk patients. Antibiotic prophylaxis should be given in one dose before the procedure. If the dose is not given before the procedure it can be given up to two hours afterward.
50 mgkg orally as a single dose 30 to 60 minutes prior to procedure. Maximum of 2 gdose Comments-Prophylaxis should be used for patients at high risk of adverse outcomes from endocarditis with underlying cardiac conditions who undergo any dental procedure that involves manipulation of gingival tissue or periapical region of a tooth and for those procedures that. The antibiotics used in prophylaxis specifically target these bacteria.
Following are the antibiotic prophylactic regimens for endocarditis administered as a single dose 30-60 minutes before the procedure. 50 mgkg not exceeding 2 g. Unable to take oral medication.
Adequate antibiotic prophylaxis was defined as having filled antibiotic prescriptions that would cover 300 days of the year. This definition of adequate antibiotic adherence has been endorsed by the National Quality Forum. 18 As such this quality assessment should be viewed as a best case assessment because some children still would not have prophylaxis for all days in a given year.
If your dental and medical professional determine antibiotic prophylaxis is a necessary preventive measure for you your dosage will depend on your age size and the antibiotic youre prescribed. Typically oral antibiotics should be taken one hour before your procedure and are best taken with a.