
The patient carried an unknown mutation on the other chromosome and was pancreatic sufficient. In normal cells the CFTR protein acts as a channel that.
The patient carried an unknown mutation on the other chromosome and was pancreatic sufficient.
Cystic fibrosis gene number. Each cell normally has 46 total chromosomes or 23 pairs of chromosomes. The seventh pair of chromosomes has a gene called the CFTR cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator gene. Changes mutations or errors in this gene are what cause CF.
This gene is very large and complex. More than 1800 different mutations in this gene have been found that cause CF. Each cell normally has 46 total chromosomes or 23 pairs of chromosomes.
The seventh pair of chromosomes has a gene called the CFTR cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator gene. Changes mutations or errors in this gene are what cause CF. This gene is very large and complex.
More than 1800 different mutations in this gene have been found that cause CF. 3 rows A number sign is used with this entry because cystic fibrosis is caused by homozygous or. Mutations in a gene called cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator CFTR cause CF.
More than 900 mutations in this gene have been found. This gene provides the instructions for the CFTR protein. In normal cells the CFTR protein acts as a channel that.
More than 1000 mutations in the CFTR gene have been identified in people with cystic fibrosis. Most of these mutations change single protein building blocks amino acids in the CFTR protein or delete a small amount of DNA from the CFTR gene. The most common mutation called delta F508 is a deletion of one amino acid at position 508 in the CFTR protein.
Cystic Fibrosis and COVID-19. People with cystic fibrosis CF are among those who might be at an increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19. In addition some people with CF are immunocompromised have a weakened immune system because they have had lung or other solid organ transplants and are at increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19.
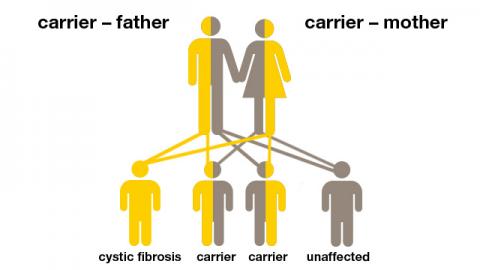
Every person has two copies of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator CFTR gene. A person must inherit two copies of the CFTR gene that contain mutations – one copy from each parent – to have cystic fibrosis. People who inherit one copy of the CFTR gene that contains a mutation and one normal copy are considered CF carriers.
Cystic fibrosis is most prevalent in Caucasian individuals and approximately 1 in every 29 individuals in the US is a carrier for the mutated CF gene. There are an estimated 30000 reported cystic fibrosis cases in the US and 70000 reported cases worldwide although the international number is undoubtedly low due to underreporting or early deaths. Cystic Fibrosis CF is a progressive genetic disease that causes respiratory infections and disabilities.
It is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator CFTR protein leading to the dysfunctionality of this protein. It effects mostly the lungs generating chronic infection inflammation respiratory failure and other complications. In the US one in every 31 carries a mutation of the CF gene.
5 Called the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator CFTR gene this mutation prevents the CFTR protein from working properly. There are more than 1700 known mutations of the disease. In an Italian patient with cystic fibrosis CF.
219700 known to be a genetic compound Ronchetto et al. 1992 found a C-to-T transition at nucleotide 3604 of the CFTR gene which changed an arginine residue at position 1158 to a stop codon R1158X. The patient carried an unknown mutation on the other chromosome and was pancreatic sufficient.
Two functional genes Two nonfunctional genes One functional gene one nonfunctional gene Cystic fibrosis 25 CF carriers 50 Unaffected 25 Parents CF carriers Potential children Who should consider carrier testing. An estimated 10 million people in the United States are carriers of cystic fibrosis. Individuals with a relative.
Around 85 of people with cystic fibrosis in Europe have this type of mutation which results in the CFTR protein not being transported to the surface of the cells in which it is required. The most common of this type of mutation is F508del.