
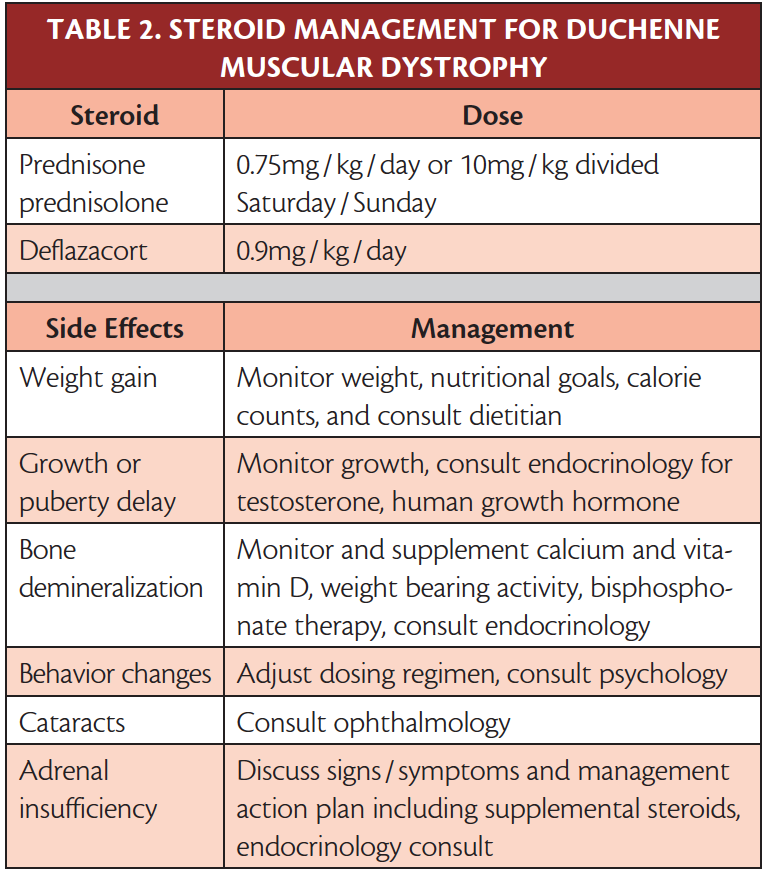
Untreated this incurable disease which has an X-linked recessive inheritance is characterised by muscle wasting and loss of walking ability leading to complete wheelchair dependence by 13 years of age. A 2005 American Academy of Neurology AAN guideline on the use of corticosteroids in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD recommended prednisone or deflazacort in the treatment of DMD for short-term benefit in muscle strength and function.
There are many types of corticosteroids that may be prescribed for muscular dystrophy.
Corticosteroids for the treatment of duchenne muscular dystrophy. Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Moderate quality evidence from RCTs indicates that corticosteroid therapy in DMD improves muscle strength and function in the short term twelve months and strength up to two years. Randomised controlled trials RCTs provide moderate quality evidence that treatment with corticosteroids in Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD compared with placebo improves muscle strength and function including respiratory muscle strength and function for six months. There is evidence of continuing benefit on muscle strength and function at one year.
On the basis of. Evidence from randomised controlled trials RCTs indicates that corticosteroids significantly improve muscle strength and function in boys with DMD in the short term six months and strength at two years two-year data on function are very limited. Corticosteroids now part of care recommendations for DMD are largely in routine use although questions remain over their ability to prolong walking when.
Prolongation of walking is a major aim of treatment. Evidence from randomised controlled trials RCTs indicates that corticosteroids significantly improve muscle strength and function in boys with DMD in the short term six months and strength at two years two-year data on function are very limited. Corticosteroids now part of care recommendations for DMD are largely in routine use although.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is the most common muscular dystrophy of childhood. Untreated this incurable disease which has an X-linked recessive inheritance is characterised by muscle wasting and loss of walking ability leading to complete wheelchair dependence by 13 years of age. Prolongation of walking is a major aim of treatment.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is the most common muscular dystrophy of childhood. Untreated this incurable disease which has an X-linked recessive inheritance is characterised by muscle wasting and loss of walking ability leading to complete wheelchair dependence by 13 years of age. Prolongation of walking is a major aim of treatment.
Request PDF Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Background. Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is the most common muscular dystrophy of. There is evidence from randomised controlled studies that glucocorticoid corticosteroid therapy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy improves muscle strength and function in the short-term six months to two years.
The most effective prednisolone regime appears to be 075 mgkgday given daily. In the short term adverse effects were significantly more common but not clinically severe. Long-term benefits and hazards of glucocorticoid.
Research funded in part by the NIHs National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases NIAMS has revealed insights into glucocorticoid steroid treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD. Scientists determined mechanisms of how glucocorticoid steroids improve muscle repair and function in mouse models of acute. Viltepso is an antisense oliogonucleotide indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is amenable to exon 53 skipping.
Vyondys 53 golodirsen Injection FDA Approved. A 2005 American Academy of Neurology AAN guideline on the use of corticosteroids in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD recommended prednisone or deflazacort in the treatment of DMD for short-term benefit in muscle strength and function. There are currently variations in practice in corticosteroid use.
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy 26 May 2016 Evidence from randomised controlled trials RCTs indicates that corticosteroids significantly improve muscle strength and function in boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD in the short term six months and strength at two years two-year data on function are very limited. Corticosteroids may preserve muscle tissue by reducing both inflammation and immune system attacks on those tissues. They also may speed up the processes that are involved in repairing cell membranes.
What corticosteroids are prescribed for muscular dystrophy. There are many types of corticosteroids that may be prescribed for muscular dystrophy. Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD is a genetic reces-sive X-linked disease affecting skeletal muscles and myo-cardium.
This is the most frequent muscular dystrophy in children affecting 1 out of 5000 male live births. Several studies have demonstrated the benefit of corticosteroids for DMD which are currently part of the care recommenda-tion. Corticosteroids slow the decline in muscle strength.
Pharmacological corticosteroid therapy is the standard of care in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy DMD that aims to control symptoms and slow disease progression through potent anti-inflammatory action. However a major concern is the significant. Steroid Therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Corticosteroids referred to as steroids for short are the main drug treatment for Duchenne.
In summary there is substantial evidence to recommend the use of corticosteroids to all DMD patients with the objective of preserving walking time as long as possible and reducing lung heart and orthopaedic complications 2. Naturally the adverse effects of. EMFLAZA is a corticosteroid indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy DMD in patients 2 years of age and older.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION Contraindication. Do not use if you are allergic to deflazacort or any of the inactive ingredients in EMFLAZA.