
As noted see Background respiratory acidosis may have a variety of different causes including the following. Respiratory acidosis is usually caused by a lung disease or condition that affects normal breathing or impairs the lungs ability to remove CO2.
Similarity clinical presentation of dyspnoea and cough productive of purulent sputum.
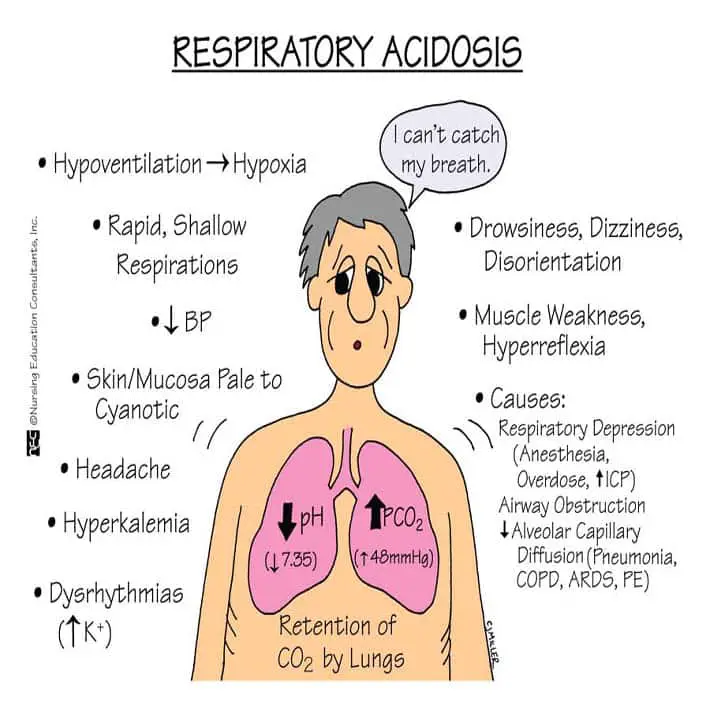
Copd causes respiratory acidosis. Causes Symptoms And Treatment. Respiratory acidosis develops when air exhaled out of the lungs does not adequately exchange the carbon dioxide formed in the body for the inhaled oxygen in air. There are many conditions or situations that may lead to this.
One of the conditions that can reduce the ability to adequately exhale carbon dioxide CO2 is chronic. Why does COPD cause respiratory acidosis. The kidneys also regulate your bloods concentration of bicarbonate a base.
Respiratory acidosis is usually caused by a lung disease or condition that affects normal breathing or impairs the lungs ability to remove CO2. Respiratory acidosis develops when air exhaled out of the lungs does not adequately exchange the carbon dioxide formed in the body for the inhaled oxygen. In this regard why does COPD cause respiratory acidosis.
Respiratory acidosis develops when air inhaled into and exhaled from the lungs does not get adequately exchanged between the carbon dioxide from the body for oxygen from the airChronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD is a common group of diseases that are particularly likely to cause respiratory acidosis. Hereof does COPD cause metabolic acidosis. The compensation can be predicted to some extent and is based on primary metabolic or respiratory disorder.
In COPD patients chronically elevated carbon dioxide shifts the normal acid-base balance toward acidic. This results in respiratory acidosis. Beside above what is a normal ABG For a COPD patient.
Persons with COPD are typically separated into. Acidosis occurs when the pH of the blood falls below 735 normal blood pH is between 735 and 745. Respiratory acidosis is typically caused by an.
Both metabolic acidosis and metabolic alkalosis can coexist with respiratory acidosis. This clinical setting may occur for example in patients with COPD who develop heart failure and are treated with high doses of diuretics or who have renal failure and vomiting. Acute respiratory acidosis occurs with acute Type II respiratory failure which can result from any sudden respiratory parenchymal eg pulmonary edema airways eg chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma pleural chest wall neuromuscular eg spinal cord injury or central nervous system event eg drug overdose.
Chronic respiratory acidosis can result from numerous processes and is. For non-infectious causes of Respiratory Acidosis there is usually a functional problem that makes the lungs less able to exhale CO 2. For example Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder COPD leads to scar tissue in the lungs which makes the lungs less pliable aka less able to.
Respiratory acidosis occurs when breathing becomes impaired to the degree that the ability to expel carbon dioxide is compromised. This hypoventilation increases the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood and decreases the bloods pH level. These changes may occur acutely in sudden illness or be due to chronic long-term diseases.
On the contrary chronic respiratory acidosis may be caused by COPD where there is a decreased responsiveness of the reflexes to states of hypoxia and hypercapnia. Other individuals who develop chronic respiratory acidosis may have fatigue of the diaphragm resulting from a muscular disorder. Chronic respiratory acidosis can also be seen in obesity hypoventilation syndrome also.
It has also been utilized to facilitate respiratory drive in nonmechanically ventilated patients with COPD. Although this is generally a forgiving intervention providers must carefully select patients for this medication as it can cause severe acidosis and deterioration of clinical status in severe COPD cases. The present report describes two cases of patients who developed worsening acidosis and hypercapnia after receiving acetazolamide.
As noted see Background respiratory acidosis may have a variety of different causes including the following. COPD Emphysema chronic bronchitis severe asthmaref5ref6 Neuromuscular d. Cardiac and respiratory causes of acute breathlessness should be considered when assessing a patient with a suspected exacerbation of COPD.
Similarity clinical presentation of dyspnoea and cough productive of purulent sputum. This can be difficult to distinguish from exacerbations of bacterial origin. Difference clinical and radiological findings of lung consolidation.