
The optimal technique should be used to minimize complications. Atrial tachyarrhythmias can occur following the irritation of the right atrium during right heart catheterization and is usually self-limiting.
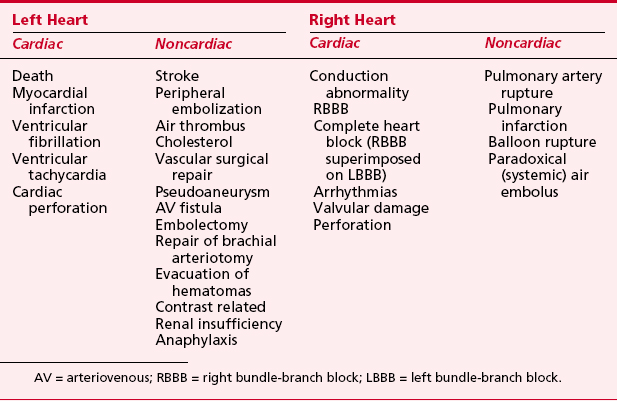
Possible complications of right heart catheterization are next to complications at the puncture site are rhytm disorders atrial extrasystole ventricular extrasystole ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation conduction disorders RBBB this can be exceptionally dangerous in case of a preexisting LBBB when a complete heart block develops damage to the pulmonic or tricuspid valve this can be prevented by pull back with a deflated balloon thrombo-emolism of.
Complications of right heart catheterization. 8 Zeilen Thrombotic thromboembolic and hemorrhagic complications of right heart catheterization occur. After evaluation of all reports complications were grouped categorically. We found that the most commonly reported access site-related issues were either carotid artery injury or arteriovenous fistula formation and injury to the tricuspid valve was the most.
The complications of this procedure. A variety of complications have been recognized clinically during prolonged catheterization including bacterial con taminationt catheter induced sepsisY venous thrombosisY and pulmonary emboli. 478 Case re ports of.
Complications of Right Heart Catheterization. A Prospective Autopsy Study Methods. Between August 2 1982 and October 20 1983 32 patients who died with a balloon-tipped flow-directed catheter.
Nineteen men and 13 women whose average age at death was 583 years range 19-80 were. Complications of right heart catheterization procedures in patients with pulmonary hypertension in experienced centers. When performed in experienced centers right heart catheter procedures in patients with pulmonary hypertension are associated with low morbidity and mortality rates.
We found that the most commonly reported access site-related issues were either carotid artery injury or arteriovenous fistula formation and injury to the tricuspid valve was the most commonly reported catheter-related complication. Our findings suggest that infrequent complications can occur with RHC and can be fatal. The optimal technique should be used to minimize complications.
Atrial tachyarrhythmias can occur following the irritation of the right atrium during right heart catheterization and is usually self-limiting. Transient brady arrhythmias are also a common occurrence in the cardiac cath lab. Prolonged episodes resulting in hypotension will need treatment with intravenous atropine or temporary transvenous pacing.
In people with preexisting right bundle branch block. As expected in any invasive procedure there are some patient related and procedure-related complications. With significant advances in the equipment used for cardiac catheterization the improved skill of the operators and newer techniques the rates of these complications have been reduced significantly.
The term cardiac catheterization can be used to refer to either right heart catheterization or left heart catheterization. Context Right heart catheterization RHC is commonly performed before high-risk noncardiac surgery but the benefit of this strategy remains unproven. Objective To evaluate the relationship between use of perioperative RHC and postoperative cardiac complication rates in patients undergoing major noncardiac surgery.
Possible complications of right heart catheterization are next to complications at the puncture site are rhytm disorders atrial extrasystole ventricular extrasystole ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation conduction disorders RBBB this can be exceptionally dangerous in case of a preexisting LBBB when a complete heart block develops damage to the pulmonic or tricuspid valve this can be prevented by pull back with a deflated balloon thrombo-emolism of. Overall complications directly related to right heart catheterization such as arrhythmias or hypotensive episodes were uncommon occurring in 22 of 7218 right heart catheterization procedures. Although the vast majority of these adverse events resolved with minimal or no intervention the potential for serious complications exists.
Certain adverse events may require aggressive intervention to. Potential Complications of a Right Heart Catheterization Anytime an arteryvein is punctured with a needle there is a risk for bleeding. Hematomas which is a collection of blood outside the vessel can develop.
Anytime a foreign object enters the human body there is a risk of infection. Possible risks of right-heart cath include. Bruising of the skin at the site where the catheter is inserted Excessive bleeding because of puncture of the vein during catheter insertion Partial collapse of your lung if your neck or chest veins are used to insert the catheter.
Cardiac catheterization is usually very safe though some people may feel discomfort having to lie down for the procedure. While risks depend on your circumstances and should be discussed with your doctor potential complications include. Bruising or bleeding where the doctor inserted the catheter.
Common complications of cardiac catheterization might include minor pain or bruising at the injection site. Other common complications of cardiac catheterization might occur if a patient is allergic to dye used in the procedure which might also cause kidney damage especially in diabetics. There are many different types of complications that can occur after cardiac catheterization.
Vascular complications are the most common because access is frequently obtained through the femoral artery. The high intravascular pressure makes sealing off the puncture site challenging. Overall the vast majority of complications were of mild-to-moderate severity and most commonly related to adverse events arising from venous access vagal reactions or pulmonary vasoreactivity testing table 2 34.
If left bundle branch block is present on the ECG the right heart catheterization procedure should be done with extreme caution in order to avoid iatrogenic right bundle branch block that could result in complete heart block. It is recommended to have a temporary pacemaker ready in case a prolonged episode of iatrogenic complete heart block develops. After all appropriate preprocedure.