Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms. Cilia Beat in concert forming the mucociliary escalator system which moves mucus containing particles and microorganisms toward the oropharynx.

The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage the epiglottis that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to.
Cilia in respiratory tract. Cilia play a major role throughout the body especially in the respiratory system. They can be described as hair-like structures that are found on the outside of cells lining the bronchus within. Respiratory cilia are the driving force of the mucociliary escalator working in conjunction with secreted airway mucus to clear inhaled debris and pathogens from the conducting airways.
Respiratory cilia are also one of the first. Motile or moving cilia are found in the lungs respiratory tract and middle ear. These cilia have a rhythmic waving or beating motion.
They work for instance to keep the airways clear of mucus and dirt allowing us to breathe easily and without irritation. They also help propel sperm. Ciliated cells of the respiratory epithelium play an essential role in the mechanisms of mucociliary clearance and ultrastructural alterations of cilia are known to be associated with respiratory disease.
May 30 2018. Most cilia in the respiratory system serve as a contamination filter or some component of a system thereof. The highest concentrations exist in your nose and trachea but they are in other parts of the system as well.
They work together with goblet cells which produce mucus to filter out dust and other particles that the vibrissae. Mean ciliary deviation in normal subjects was always less than 30 degrees. All patients with a mean ciliary deviation of greater than 30 degrees had recurrent respiratory tract disease.
Four of seven patients with primary ciliary dyskinesia had ciliary disorientation. In one this was the only defect. Typical examples are.
Cells with up to 200 cilia line parts of the respiratory system such as the trachea. The beating of cilia in the walls of the fallopian tubes propels the ovum down the tube into the uterus. Ciliated cells on the.
Cilia tiny muscular hair-like projections on the cells that line the airway are one of the respiratory systems defense mechanisms. Cilia propel a liquid layer of mucus that covers the airways. The mucus layer traps pathogens potentially infectious microorganisms and other particles preventing them from reaching the lungs.
The loss of cilia in the respiratory tract may result in which of the following. Reduced mucus production in the alveoli B. Inability of air to enter the alveolar space C.
Reduced red blood cell flow through the capillaries of the alveoli D. The cilia are short hairlike outgrowths of certain cells usually single cells capable of rhythmic beating. They can produce locomotion and feeding currents or the movement of fluids as in the respiratory ducts of animals and humans.
These outgrowths measure approximately 5-10 micrometers from the cell body. What is the function of cilia in the the respiratory tract. Cilia Beat in concert forming the mucociliary escalator system which moves mucus containing particles and microorganisms toward the oropharynx.
Cilia are tiny hair-like organelles that reside on the surface of cells. In the human body many are found on cells where they sweep debris away from the lungs and nasal cavities. They also line the Eustachian tubes and sinuses as well as the fallopian tubes in women.
Primary ciliary dyskinesia is a rare ciliopathic autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the respiratory tract fallopian tube and flagellum of sperm cells. The phrase immotile ciliary syndrome is no longer favored as the cilia do have movement but are merely inefficient or unsynchronized. Respiratory epithelial motile cilia which resemble microscopic hairs are.
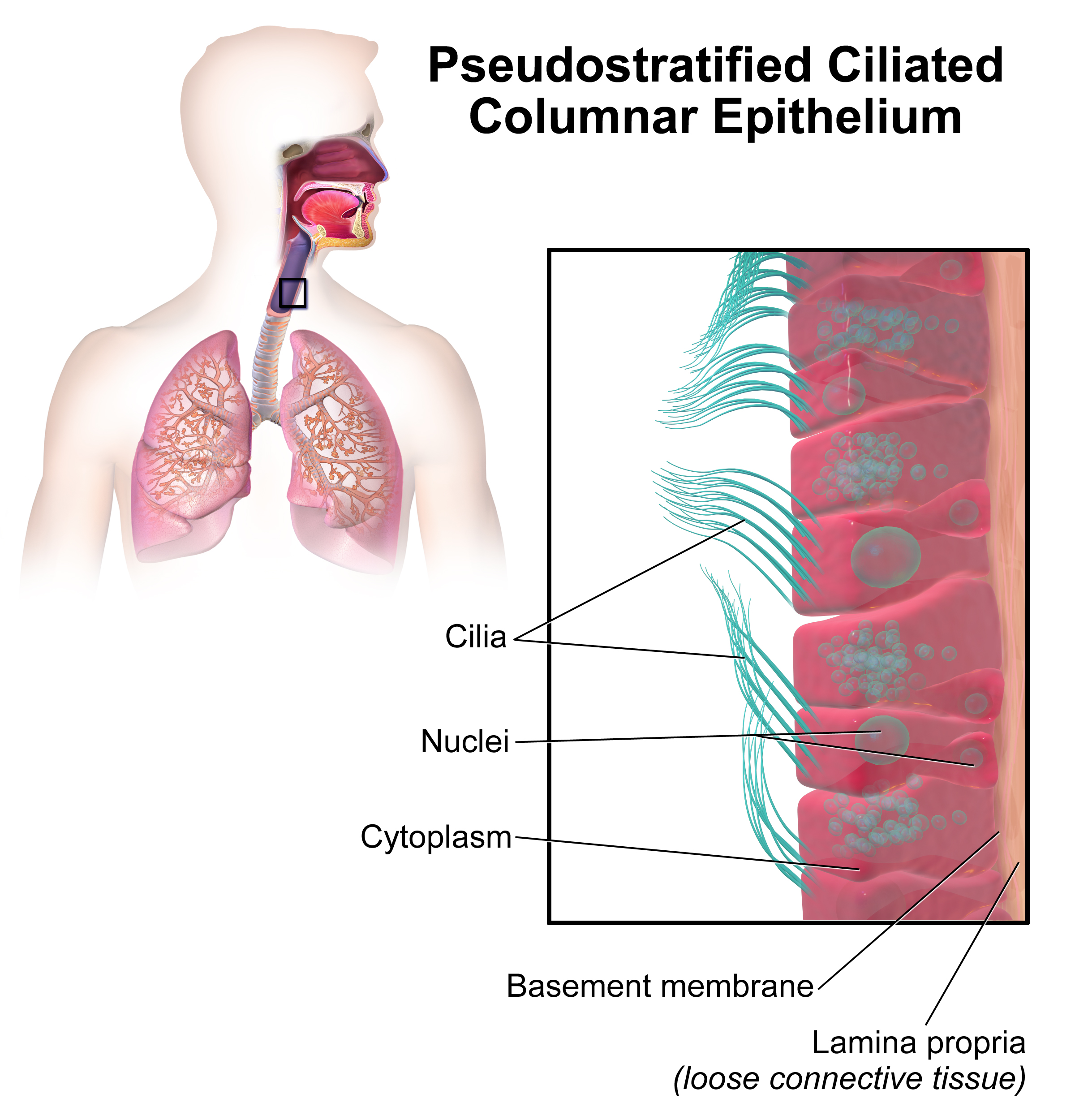
We report on ciliary aplasia of the respiratory tract a rare disorder of the mucociliary apparatus that is insufficiently recognized as a distinct entity. A culture method for ciliogenesis was developed by our laboratory and offers the advantage of studying cilia free of secondary changes associat. Wikipedia states that within the respiratory tract is a layer of cells known as the ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
The cells within this layer are of three types. Ciliated cells goblet cells and basal cells. As explained above ciliated epithelial cells move substances in a.
The bronchus in the lungs are lined with hair-like projections called cilia that move microbes and debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms. Was this page helpful.
Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next air moves into the pharynx a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage the epiglottis that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to.
What is the purpose of cilia and mucus in the respiratory tract. The bronchus in the lungs are lined with hair-like projections called cilia that move microbes and debris up and out of the airways. Scattered throughout the cilia are goblet cells that secrete mucus which helps protect the lining of the bronchus and trap microorganisms.