The activity of a microsomal cholesterol 7 hydroxylase determines the rate of formation of the primary bile acids and this enzyme is inhibited by bile acids. Cholesterol absorption was greater with cholic acid 79 than with chenodeoxycholic acid feeding 60 and the lowest levels were observed during ursodeoxycholic.

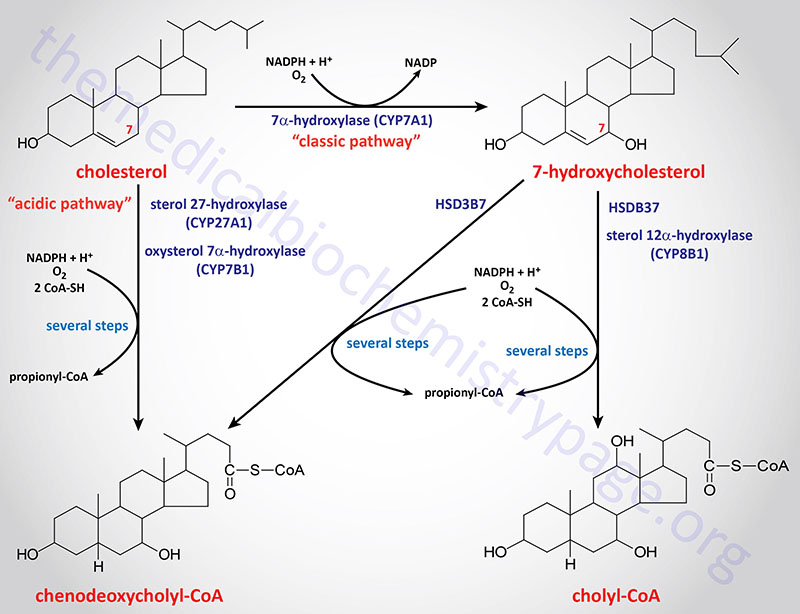
Primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are synthesized from cholesterol in hepatocytes.
Cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. The levels of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid remained high until the age of 6 months being about 5-fold higher than those in the sera of adults. Primary bile acid concentrations reached the adult level by the age of 1-2 years. These results indicate that developmental changes occur in the metabolism and excretion of bile acids in man.
Cholesterol absorption was greater with cholic acid 79 than with chenodeoxycholic acid feeding 60 and the lowest levels were observed during ursodeoxycholic. Cholesterol absorption was studied in mice receiving cholic chenodeoxycholic or ursodeoxycholic acids 02 of. Fasting and postprandial serum concentrations of conjugates of cholic CCA and chenodeoxycholic CCDA acid measured by radioimmunoassay were compared with morphological changes in percutaneous liver biopsies from 49 patients with alcohol abuse.
Sulfobromophthalein BSP and galactose elimination tests were. GC-MS revealed that B. Intestinalis AM-1 converts cholic acid CA and chenodeoxycholic acid into their 7-oxo derivatives 7-oxo-deoxycholic acid 7-oxo-DCA and 7-oxo-lithocholic acid respectively.
Intestinalis AM-1 possesses 7α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 7α-HSDH activity. Cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid for treating inborn errors of bile acid synthesis all ages NHS England will commission cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid for treating inborn errors of bile acid synthesis for all age groups in accordance with the criteria outlined in this document. A method has been developed for simultaneous determination of pool sizes and fractional turnover rates FTR of chenodeoxycholic acid CDCA and cholic acid CA in man by 13C12C isotope ratio measurements of bile acids in serum after oral administration of 20-50 mg of 24-13C-labeled bile acids.
13C12C isotope ratio measurements were performed by capillary gas. Chenodeoxycholic acid or Chenodiol is an epimer of ursodeoxycholic acid DB01586. Chenodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid naturally found in the body.
It works by dissolving the cholesterol that makes gallstones and inhibiting production of cholesterol in the liver and absorption in the intestines which helps to decrease the formation of gallstones. It can also reduce the amount of other bile acids. Jugated chenodeoxycholic acid02andconjugated deoxy-.
Cholic acidandchenodeoxycholic acidgreatlyexceededthevalues measured forhealthy controls. Cholic acid groups when they were compared with the combined ursodeoxycholic acid groups. The total bile acid pool expanded significantly in both the chenodeoxycholic acid and in the BOO-mg urso deoxycholic acid treatment groups.
The marked increases of biliary ursodeoxycholic acid and che nodeoxycholic acid respectively indicated compli. Cholic acid also known as 3α7α12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid is a primary bile acid that is insoluble in water it is a white crystalline substance. Salts of cholic acid are called cholates.
Cholic acid along with chenodeoxycholic acid is one of the two major bile acids produced by the liver where it is synthesized from cholesterol. These two major bile acids are roughly equal in concentration in. Primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are synthesized from cholesterol in hepatocytes.
The activity of a microsomal cholesterol 7 hydroxylase determines the rate of formation of the primary bile acids and this enzyme is inhibited by bile acids. Thus the synthesis of the bile acids is under negative feedback control. Ministration 500 mg ileal excretion of cholic acid increased to 517 f 96 pmol8 h and that of chenode- oxycholic acid increased to 337 f 42 pmol8 h indicating decreased absorption of these bile acids.
Following chenodeoxycholic acid administration 500 mg no significant increase of cholic acid. Both cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid was 65-70. Substrate saturation curves were observed for the 7a-dehydroxylation of cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid.
GCMS revealed that B. Intestinalis AM1 converts cholic acid CA and chenodeoxycholic acid into their 7oxo derivatives 7oxodeoxycholic acid 7oxoDCA and 7oxolithocholic acid respectively. Intestinalis AM1 possesses 7αhydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 7αHSDH activity.
Primary bile acids cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are sterile compounds synthesized from cholesterol in the liver where they are conjugated with glycine or taurine to form bile salts. Bile salts play an important role in cholesterol breakdown and may be released into the small intestine following a high-fat meal to solubilize dietary lipids thereby promoting their absorption. Chenodeoxycholic acid or cholic acid or a combination of the two.
About the new treatment. As described above treatment with chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid replaces the missing bile acids which can help stop symptoms appearing or prevent them from getting worse. Chenodeoxycholic acid is ineffective with stones of a high calcium or bile acid content.
Chenodiol suppresses hepatic synthesis of both cholesterol and cholic acid gradually replacing the latter and its metabolite deoxycholic acid in an expanded bile acid pool.