CCMs are benign vascular lesions that can occur anywhere in the brain parenchyma or leptomeninges but mainly occur in the supratentorial region. Conventional classification criterion is based on genetics and thus familial and sporadic forms can be distinguished.
Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs also known as cavernous angiomas have an incidence of 0105 and account for 510 of cerebral and spinal vascular malformations 1 3.
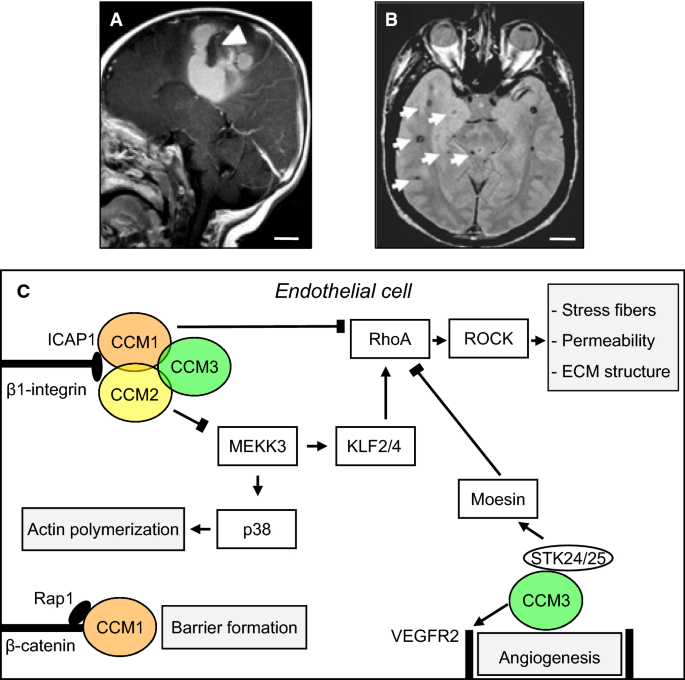
Cerebral cavernous malformation gene reviews. Excerpted from the GeneReview. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Familial Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are vascular malformations in the brain and spinal cord comprising closely clustered enlarged capillary channels caverns with a single layer of endothelium without mature vessel wall elements or normal intervening brain parenchyma. Cerebral cavernous malformation CCM of the familial type is caused by abnormalities in the CCM1 CCM2 and CCM3 genes.
These 3 proteins forming a complex associate with the maintenance of vascular endothelial cell-cell junctions. Excerpted from the GeneReview. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Familial Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are vascular malformations in the brain and spinal cord comprising closely clustered enlarged capillary channels caverns with a single layer of endothelium without mature vessel wall elements or normal intervening brain parenchyma.
Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are one of the most common types of vascular malformation which are featured enlarged and irregular small blood vessels. The cavernous cavities are merely composed of a single layer of endothelial cells and lack other support tissues such as elastic fibers and smooth muscle which make them elastic. Excerpted from the GeneReview.
Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Familial Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are vascular malformations in the brain and spinal cord comprising closely clustered enlarged capillary channels caverns with a single layer of endothelium without mature vessel wall elements or normal intervening brain parenchyma. Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are lesions affecting brain microvessels. The pathogenesis is not clearly understood.
Conventional classification criterion is based on genetics and thus familial and sporadic forms can be distinguished. However classification of sporadic cases with multiple lesions still remains uncertain. Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are collections of small blood vessels capillaries in the brain that are enlarged and irregular in structure.
These capillaries have abnormally thin walls that are prone to leak. They also lack other support tissues such as elastic fibers which normally make them stretchy. Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs also known as cavernous angiomas have an incidence of 0105 and account for 510 of cerebral and spinal vascular malformations 1 3.
CCMs are benign vascular lesions that can occur anywhere in the brain parenchyma or leptomeninges but mainly occur in the supratentorial region. Cerebral cavernous malformations are collections of small blood vessels capillaries in the brain that are enlarged and irregular in structure. These capillaries have abnormally thin walls and they lack other support tissues such as elastic fibers which normally make them stretchy.
Long-term antithrombotic therapy and risk of intracranial haemorrhage from cerebral cavernous malformations. A population-based cohort study systematic review and meta-analysis Lancet Neurol. Cerebral cavernous angiomas are relatively rare vascular malformations that may involve any part of the central nervous system.
Cerebral cavernous angiomas are to be distinguished from cerebral arteriovenous malformations 106070 108010. Epub 2018 Sep 25. The cerebral cavernous malformation disease causing gene KRIT1 participates in intestinal epithelial barrier maintenance and regulation.
Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are vascular lesions that can occur sporadically or as a consequence of inherited loss-of-function mutations predominantly in the genes CCM1 KRIT1 CCM2 MGC4607 OSM Malcavernin or CCM3 PDCD10 TFAR15. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Panel. Is a 4 gene panel that includes assessment of non-coding variants.
Is ideal for patients with a clinical suspicion of familial cerebral cavernous malformations. The genes on this panel are included in the Vascular Malformations. Cavernous hemangiomas located in the brain or spinal cord are referred to as cerebral cavernomas or more usually as cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs and can be found in the white matter but often abut the cerebral cortex.
When they contact the cortex they can represent a. Cerebral cavernous malformations CCMs are congenital vascular anomalies of the brain that can cause significant neurological disabilities including intractable seizures and hemorrhagic stroke. CCMs represent 5-15 of all cerebral vascular malformations and occur in 05 of the general population.