Vascular phase - changes in blood flow transient vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation - exudation of fluid into tissues 2. INFLAMMATION Cells or tissues of the body may be injured or killed by any of the agents physical chemical infectious described earlier.

The first part of acute inflammation is the Fluid Phase in which arteriole dilation and an increase in venule permeability allows fluid from the circulatory system to travel into the effected tissue.
Cellular phase of inflammation. The inflammatory phase starts to wane 23 days after injury at which point the proliferation phase begins. During the proliferation stage cells will migrate into the fibrin provisional matrix and begin to produce a new ECM. Acute swelling stage Phase 1 This is a fundamental type of response by the body to disease and injury.
It is characterized by the classical signs of pain heat redness and swelling. Inflammation is a key part of the bodys defense system an indispensable protective response by the bodys system of self-defense. Vascular phase - changes in blood flow transient vasoconstriction followed by vasodilation - exudation of fluid into tissues 2.
Cellular phase-infiltration of inflammatory cells. CELLULAR RESPONSE TO INJURY. INFLAMMATION Cells or tissues of the body may be injured or killed by any of the agents physical chemical infectious described earlier.
When this happens an inflammatory response or inflammation naturally occurs in the healthy tissues adjacent to the site of injury. During vessel spasm smooth muscle in blood vessels contract as a result of what in the cellular phase vasodilation and limits platelet aggregation in uninjured endothelium prostaglandins released by the injured endothelial cells start to initiate what process in the cellular phase. To the tissues initiating the third phase of the inflammatory reaction.
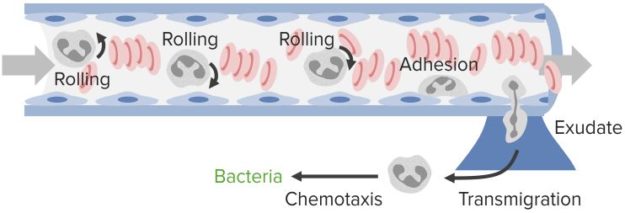
The cellular phase of the inflammatory reaction is characterized by the arrival to the site of inflammation of leukocytes circulating in the blood. In order to be recruited to the site of inflammation circulating. Cellular inflammation is an inflammatory process which occurs on a basic cellular level.
Inflammation is a normal process that occurs in the body and is designed in acute situations to aid in the healing of tissue. However its when this inflammation becomes a chronic every-day occurrence is when the damage and death of cells can occur which may lead to disease. Why does Cellular Inflammation.
Once offending agents are removed the mediators of inflammation are degraded quickly 2. Neutrophils have short lives and die via apoptosis within hours of leaving the blood 3. The inflammatory process inherently triggers stop processes anti-inflammatory cytokines from macrophages IL.
Chapter 7 Innate Immunity Inflammation Neal S. Huether and Kathryn L. McCance Chapter Outline Human Defense Mechanisms First Line of Defense.
Physical Mechanical and Biochemical Barriers Physical and Mechanical Barriers Biochemical Barriers Second Line of Defense. The Inflammatory Response Vascular Response Plasma Protein Systems Cellular Mediators of Inflammation. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
PDF On Mar 11 2019 Atyaf Altameemi and others published inflammation Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate. Inflammatory Response Healing of acute injuries begins with the acute vascular inflammatory response. The purpose of vascular changes is to increase blood flow to the local area mobilize and transport cells to the area to initiate healing.
The damaged cells are removed and the body begins to put new collagen in the area of injury. Acute inflammation can be broken down further into 3 different stages. The first part of acute inflammation is the Fluid Phase in which arteriole dilation and an increase in venule permeability allows fluid from the circulatory system to travel into the effected tissue.
In this short tutorial i have described the the basic concepts of inflammation and described cellular events in inflammation.