In this study breast cancer biopsies from. Although unlike melanoma breast cancer is not generally viewed as a highly immunogenic cancer recent studies have described a rich tumor immune microenvironment in a subset of breast cancers.

Using metastatic triple-negative breast cancer cells the most aggressive breast cancer for which there are few treatments and specialized modeling techniques the researchers cultivated tumor microenvironments.
Breast cancer tumor microenvironment. Triple negative breast cancer TNBC is the most aggressive and challenging form of breast cancers. Tumor microenvironment TME of TNBC is associated with induction of metastasis immune system suppression escaping immune detection and drug resistance. TME is highly complex and heterogeneous consists of tumor cells stromal cells and immune cells.
The rapid expansion of. 8 lignes The breast tumor microenvironment. Normal epithelium is composed of epithelial luminal and.
Different cells and mediators in the tumor microenvironment play important roles in the progression of breast cancer. The aim of this study was to determine the composition of the microenvironment during tumor progression in order to discover new related biomarkers and potentials for targeted therapy. In this study breast cancer biopsies from.
Breast cancer comprises a heterogeneous group of malignancies derived from the ductal epithelium. The microenvironment of these cancers is now recognized as a critical participant in tumor progression and therapeutic responses. Recent data demonstrate significant gene expression and epigenetic alterations in cells composing the microenvironment during disease.
Moreover breast cancer is characterized by a highly inflammatory microenvironment which is supported by the infiltrating immune cells cytokines and growth factors 5 6. In addition immune infiltration of breast tumors has been shown to be related to clinical outcome through the modulation of treatment response. Breast cancer microenvironment such as suppressive im- mune cells soluble factors and altered extracellular matrix act together to impede effective antitumor immunity and.
Triple negative breast cancer TNBC is most aggressive subtype of breast cancers with high probability of metastasis as well as lack of specific targets and targeted therapeutics. TNBC is characterized with unique tumor microenvironment TME which differs from other subtypes. TME is associated with induction of proliferation angiogenesis inhibition of apoptosis and immune system suppression and drug resistance.
Exosomes are promising nanovesicles which orchestrate the TME. Although unlike melanoma breast cancer is not generally viewed as a highly immunogenic cancer recent studies have described a rich tumor immune microenvironment in a subset of breast cancers. These immune infiltrates comprised cells from the innate and adaptive immune response can be detected and characterized in biopsy specimens and have prognostic value.
In this study of using two small but independent breast cancer cohorts we show that breast MRI-derived radiomics are associated with the tumors microenvironment in terms of the abundance of several cell types. While the reported findings warrant further evaluation on larger cohorts this study points to the potential value of quantitative radiomics as a non-invasive imaging. Tumor microenvironment inflammatory breast cancer.
It is well known that the cancerogenesis cancer cell proliferation survival invasion and metastasis are closely associated to the tumor microenvironment. This tumor environment is composed of tumor surrounding blood vessels inflammatory cells immune cells lymphocytes fibroblasts extracellular matrix and a. The tumor microenvironment plays an integral role in cancer development progression and treatment.
Understanding the intricate mechanisms that take place between solid difficult-to-treat tumors and the microenvironments they create is crucial to developing effective therapies and improving patient survival. Breast cancer for example though treatable is globally one of the most commonly. This image of a breast cancer tumor and its.
Immune checkpoint blockade ICB has revolutionized the treatment of cancer patients. The main focus of ICB has been on reinvigorating the adaptive immune response namely activating cytotoxic T cells. ICB has demonstrated only modest benefit against advanced breast cancer as breast tumors typically establish an immune suppressive tumor microenvironment TME.
The details of the approach were published in Advanced Biology. Using metastatic triple-negative breast cancer cells the most aggressive breast cancer for which there are few treatments and specialized modeling techniques the researchers cultivated tumor microenvironments. To explore if the tumor microenvironment contributes to the primary resistance of HER2-positive breast cancer cells to T-DM1 we examined whether Matrigel a basement membrane matrix that provides a three-dimensional 3D cell culture condition caused the primary resistance of HER2-positive T-DM1-sensitive breast cancer cells JIMT1 and SKBR-3 cells to T-DM1.
We evaluated the effect of thyroid status on breast cancer growth and dissemination in an immunocompetent mouse model. For this hyperthyroid and hypothyroid Balbc mice were orthotopically inoculated with triple negative breast cancer 4T1 cells. Tumors from hyperthyroid mice showed increased growth rate and an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment characterized by.
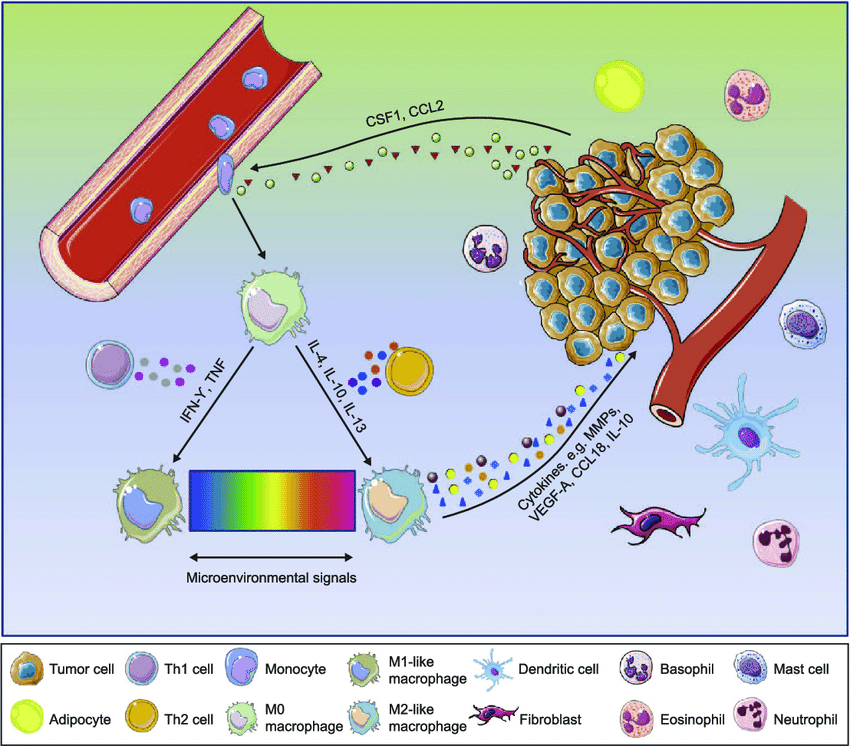
The tumor immune microenvironment TIME plays a key role in tumor progression and metastasis. Interactions between immune cells stromal cells and chemokines establish a pre-metastatic niche for circulating tumor cells 13. The cell types in TIME play different pro- and antitumor roles during tumor progression 4.
Studies in early-stage HER2 breast cancer showed that 16 of tumors had 50 lymphocytic infiltrate 10 and that a high level of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes TILs is associated with better clinical outcomes. 11 12 Also in patients with locally advanced HER2 breast cancer who received a single treatment of trastuzumab clinical response was associated with an increase in the.