
Less commonly breast cancer can begin in the stromal tissues which include the fatty and fibrous connective tissues of the breast. The diagram below shows how the different types of cells can develop from a single blood stem cell.
Of note is the finding that the claudin-low subtype seems to be over-represented in breast cancer cell.
Breast cancer cell diagram. 15 lignes Scientists study the behaviour of isolated cells grown in the laboratory for insights into how. Stage I Invasive Breast Cancer Tumor cells are confined to the breast and there is no lymph node involvement. Stage III Invasive Breast Cancer Tumor cells are usually present in the breast and lymph nodes.
Larger tumors can involve the chest wall. Inflammatory Breast Cancer The breast appears red and swollen and feels warm to the touch. Occasionally a lump may also be found in the breast.
Breast cancer is a disease in which cells in the breast grow out of control. There are different kinds of breast cancer. The kind of breast cancer depends on which cells in the breast turn into cancer.
Breast cancer can begin in different parts of the breast. A breast is made up of three main parts. Lobules ducts and connective tissue.
The lobules are the glands that produce milk. The ducts are tubes that carry. Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast such as cells lining the ducts and lobules begin to grow abnormally.
These cells have the potential to grow out of control and invade the surrounding tissue. When this occurs this is called invasive breast cancer. If the cancer cells continue to grow they may spread beyond the breast to other parts of body which could become life-threatening.
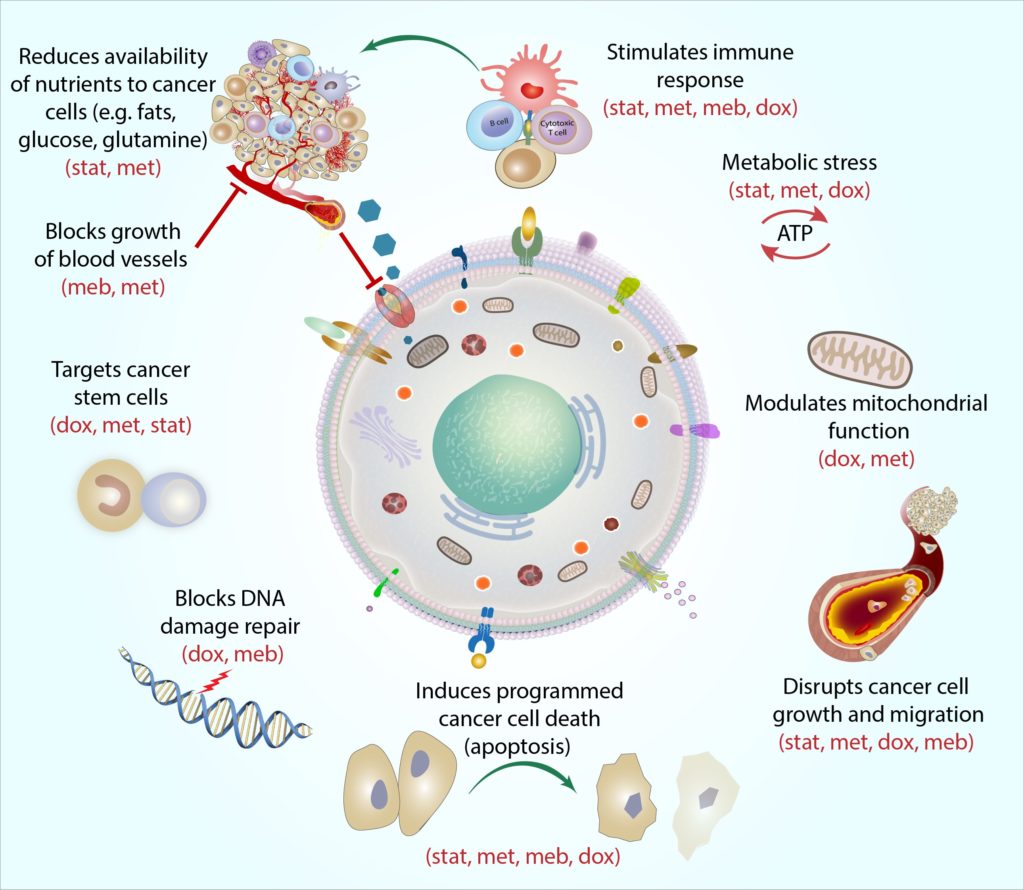
Diagram shows changes in cell structure and cellular activity. So what are we looking at here. This diagram was provided to me by one of my surgical partners to describe what is going on in the breast tissue.
You also need to remember that most breast cancers take 10 to 12 years to grow to a point where they can be felt as a dime size mass. As in most diseases there is a tipping point. The human breast cancer resistance protein BCRPABCG2 is the second member of the G subfamily of the large ATP-binding cassette ABC transporter superfamily.
BCRP was initially discovered in multidrug resistant breast cancer cell lines where it confers resistance to chemotherapeutic agents such as mitoxantrone topotecan and methotrexate by extruding these compounds out of the cell. In the diagram shown in Figure 1 we have represented 19 KEGG metabolic and signaling pathways and cell processes altered by mutations in their components in the 602 breast cancer samples of the NGS studies for which the molecular subtype had been assigned 1-4. All pathways and processes are altered although to different extents.
Breast cancer is the leading type of malignant tumor observed in women and the effective treatment depends on its early diagnosis. Diagnosis from histopathological images remains the gold standard for breast cancer. The complexity of breast cell histopathology BCH images makes reliable segmentation and classification hard.
In this paper an automatic quantitative image analysis. No figure vi 15 curin attacks triple negative breast cancer cells tiny capsule effectively kills cancer cells. Leer esta página en español.
Grade is a score that tells you how different the cancer cells appearance and growth patterns are from those of normal healthy breast cells. Your pathology report will rate the cancer on a scale from 1 to 3. Grade 1 or low grade sometimes also called well differentiated.
Grade 1 cancer cells look a little bit. The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes under the arm. Stage I Early stage of invasive breast cancer.
The tumor is no more than 2 centimeters three-quarters of an inch across. Cancer cells have not spread beyond the breast. Stage 0 Carcinoma in situ.
A group of abnormal cells that remain in the tissue in which they first formed. These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby. The term breast cancer refers to a malignant tumor that has developed from cells in the breast.
Usually breast cancer either begins in the cells of the lobules which are the milk-producing glands or the ducts the passages that drain milk from the lobules to the nipple. Less commonly breast cancer can begin in the stromal tissues which include the fatty and fibrous connective tissues of the breast. These cells develop and mature differentiate as they grow into white cells red cells or platelets.
The diagram below shows how the different types of cells can develop from a single blood stem cell. BC Cancer Agency BREAST STAGING DIAGRAM For CLINICIAN USE Right Breast Left Breast Note. Central area as shown by solid circle around the areola is defined as a 3 cm.
Radius from edge of the nipple 2. Indicate scars on Staging Diagram 3. 3D bioprinting has recently been used to form multicellular structures consisting first of a breast cancer cell core surrounded by human mammary fibroblasts and umbilical vein endothelial cells HUVECs.
Then primary human subcutaneous preadipocytes and MSCs were incorporated which led to the formation of a more reactive desmoplastic TME. The same model was then tested for pancreatic. Application of sophisticated transcriptional profiling to breast cancer cell lines using various platforms has gone some way to address these issues.
In general these studies have shown that the luminal basal HER2 and claudin-low clusters identified in breast tumours can easily be distinguished in breast cancer cell lines Table 1 13 2226. Of note is the finding that the claudin-low subtype seems to be over-represented in breast cancer cell.