
Direct Brain Temperature Monitoring Methods Brain temperature can be measured directly using probes placed into cerebral tissue or the lateral ventricles. In intensive care clinical practice the continuous monitoring of core temperature in patients with brain injury is currently highly recommended.
The regulation of brain temperature is largely dependent on the metabolic activity of brain tissue and remains complex.
Brain injury and temperature regulation. Temperature instability following brain injury likely involves hypothalamic injury pathologic changes in cerebral blood flow metabolic derangement and a neurogenic inflammatory response. Although targeted temperature management TTM exerts pleiotropic effects the heterogeneity of brain injury has hindered identification of patient subsets most likely to benefit from TTM. Early optimism about TTMs.
These interactions have a great impact during brain injury and their regulation is the basis for targeted temperature management TTM in the neurocritical care unit NCCU. The first challenge becomes determining how to measure the brains temperature as most patients are not good candidates for invasive direct brain temperature monitoring. Central fever is a known complication of traumatic brain injury TBI particularly in association with brain stem involvement.
Chronic deficits in thermoregulation after TBI have not been reported. We describe a patient who had central fevers acutely after injury but developed intermittent temperature elevations during thermal stress in the post-acute phase. A prospective evaluation of the patients.
The regulation of brain temperature is largely dependent on the metabolic activity of brain tissue and remains complex. In intensive care clinical practice the continuous monitoring of core temperature in patients with brain injury is currently highly recommended. After major brain injury brain temperature is often higher than and can vary independently of systemic temperature.
It has been shown that in. Targeted temperature management TTM has been recognized to protect tissue function and positively influence neurological outcomes after brain injury. While shivering during hypothermia nullifies the beneficial effect of TTM traditionally antishivering drugs or paralyzing agents have been used to reduce the shivering.
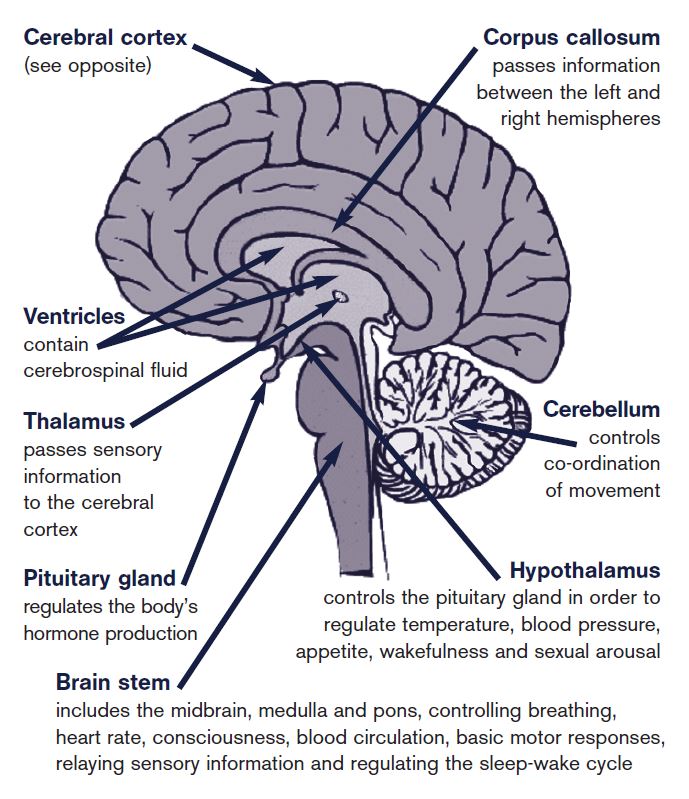
The hypothalamic area of the brain helps in controlling. When the hypothalamus activates these glands they bring that water to the surface of the skin. The water then evaporates from the skin and cools the body.
If the hypothalamus becomes damaged after a brain injury the body may have trouble regulating its temperature. As a result heat sensitivity can occur. To mitigate the secondary brain injury in TBI patients many basic and clinical researches have been performed for the innovation of pharmacological treatments and temperature managements 3 5 7.
We need to keep our body temperature around 37 C or 99 F. A part of the brain called the hypothalamus sends instructions to the skin via the nervous system to keep things in order. If it thinks we are cold the hairs on our skin stand up.
This traps air next to our bodies offering some extra insulation. Signals between the brain and areas innervated below the level of injury may not be able to get past the site of injury. As a result individuals may lose sensation below their level of injury which can make it difficult for your brain to understand when the body is too cold or warm.
Your bodys ability to regulate temperate is known as thermoregulation. A brain injury can sometimes cause problems with temperature regulation making it harder for survivors to control their body temperature. They may feel too hot or too cold or fluctuate between the two.
Other symptoms such as fatigue and cognitive problems may be exacerbated in hot weather. Temperature Regulation After TBI Fever is the most commonly observed temperature disturbance after brain injury especially if brainstem structures are involved. Many fevers are the result of infection related to the injury since the bloodbrain barrier has been disrupted.
Object moved to here. It is an exhausting amazing treatment for the cognitive aspects of a brain injury things such as concentration memory writing reading persistence stamina emotional stability open awareness etc. They started doing HRV heart rate variability work at the beginning of my treatment sessions.
The idea was to relax the body and mind get the heart rate rising and falling in sync with. Direct Brain Temperature Monitoring Methods Brain temperature can be measured directly using probes placed into cerebral tissue or the lateral ventricles. The first thermal recording from the brain of an awake animal dates back to 1860 when the relationship between.
Problems with temperature regulation happen in people with cervical and high thoracic spinal cord injuries. Body temperature may change somewhat with the air temperature. If you are in a cold place body temperature will drop.
If you are in a very warm place body temperature will rise. The regulation of brain temperature is largely dependent on the metabolic activity of brain tissue and remains complex. In intensive care clinical practice the continuous monitoring of core.
Audit of temperature regulation in intensive care patients with traumatic brain injury and stroke in Australia and New Zealand CLARITY Traumatic Brain Injury TBI and Stroke ischaemic and haemorrhagic including aneurysmal and non-aneurysmal haemorrhage are globally the most common forms of neurologically-related disability in adults.