Soft tissue swelling is caused by injury or inflammation of tissue ligaments or tendons that surround bones. Hello Thanks for your query.

Deep soft tissue swelling joint effusion or early periosteal changes may be seen within days after onset of infection.
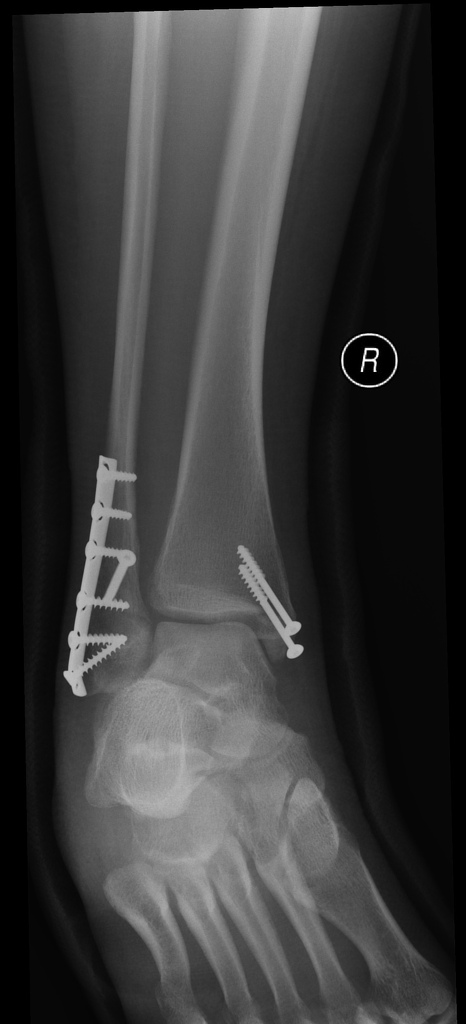
Bimalleolar soft tissue swelling. What does bimalleolar soft tissue thickening mean Diffuse soft tissue swelling Soft tissue swelling above clavicle and allergy. Unstable Weber B fracture of the right distal fibular and fracture of the medial malleolus bimalleolar ankle fracture. Associated soft tissue swelling.
Associated soft tissue swelling. Hello Thanks for your query. Soft tissue swelling is not better seen in x-rays.
If the swelling and pain persists you might required MRI to see soft tissue swelling better. I do hope that you have found something helpful and I will be glad to answer any further query. A 15-year-old male figure skater presented with a painful soft-tissue swelling of the bilateral bimalleolar region.
The pain had been present for two months and there was no. Soft tissue swelling is caused by injury or inflammation of tissue ligaments or tendons that surround bones. It can range from a minor bruise or bump to a fracture or dislocated joint.
Treatment for soft tissue injuries depends on the severity of the situation and how it occurred. Mild cases of bruising generally heal without intervention but severe strains or sprains may require a doctors. Radiography not shown shows diffuse soft-tissue swelling of the volar aspect of the middle finger but no underlying bone abnormality.
MRI of the middle finger is per-formed Figs. 1A1E approximately 8 hours after presentation. MRI MRI of the hand reveals an elongated soft-tissue mass in the volar soft tissue of the middle finger extending from the level of the metacarpophalangeal joint.
Deep soft tissue swelling joint effusion or early periosteal changes may be seen within days after onset of infection. Furthermore conven-tional radiography helps to exclude fracture or tumor. Destructive bone changes do not occur until 710 days after the onset of infection.
During the first 23 days of symptoms radionuclide bone imaging may be particularly useful in showing a well. Prepatellar soft tissue swelling. Clumps of calcifications in the prepatellar soft tissues in chronic cases 3.
Hypoechoic fluid sometimes containing debris is noted anteriorly to the patellar surface 2. Oval shaped fluid-filled sac is seen anterior to the patella and displays low T1 and bright T2STIR signal intensity. When hemorrhage occurs T1 signal increases and T2 GRE.
Standard PRICE Protection Rest Ice Compression Elevation therapy should be started upon acute presentation to reduce swelling and attenuate pain. Patients may be made non-weightbearing and placed in a lower extremity splint with the ankle in a neutral position for 3-5 days if symptoms dictate. The assistance of a compression dressing may also be warranted depending on the severity of the swelling.
The history often reveals an accident fall or sports injury as the complaints begin soon following the injury. Examination of the ankle joint reveals pain tenderness and swelling which is evaluated to understand if it is a soft tissue injury or a fracture. As the symptoms are similar it is difficult to differentiate between an ankle sprain and an ankle fracture.
More so the diagnosis of bimalleolar ankle. The anatomi- cally reduced bi- and trimalleolar fractures showed resolution of soft-tissue swelling maximally over the first 3-month period following which the swelling con- tinued to decrease over the following 12 months. Soft-tissue swelling was most severe and most pro- longed in those fractures not reduced anatomically and was worse in those treated by operative methods com- pared.
Right-sided heart failure can cause pitting edema a swelling in the tissue under the skin of the lower legs and feet. Pressing this tissue with a finger tip leads to a noticeable momentary indentation. The decrease in sodium and water excretion can result in fluid retention and overload.
Thyroid or liver disease. These conditions can change the concentration of protein in the blood. We performed single screw fixation after assessing the soft tissue condition and employed a technique of using continuous longitudinal force to bring together fracture fragments ankle ligamentotaxis during surgery.
Open reduction with a mini-hook plate and tension band wire was used for bimalleolar fracture repair using the combined anteromedial and anterolateral approach with. A bimalleolar fracture is a fracture of the ankle that involves the lateral malleolus and the medial malleolus. Studies have shown that bimalleolar fractures are more common in women people over 60 years of age and patients with existing comorbidities.
Surgical treatment will often be required usually an Open Reduction Internal Fixation ORIF. This involves the surgical reduction or realignment of the. Soft tissue swellings in the foot are common and in general thought to be benign.
Preoperatively most are thought to be ganglia and surgery is often performed by inexperienced surgeons frequently under local anaesthetic. Because of this recurrence rates of excision of ganglia have been reported as high as 50. Kirby et all have recently highlighted the incidence of malignant.