
Serotonin 5HT or 5-hydroxytryptamine norepinephrine NE and dopamine DA. Role of postsynaptic 5ht-2 and 5ht-3 receptors.
They work by increasing the level of serotonin in the brain.
Antidepressants mechanism of action. Mechanism of action of antidepressants A wide range of effective drugs is available for the treatment of major depression. The discovery of these agents has not always been the result of rational drug design. Tricyclic antidepressants formed the mainstay of treatment until the 1990s and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs ha.
The mechanisms of actions of different antidepressants such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIs phenelzine Nardil and tranylcypromine Parnate associate with the inhibition of. 10 rows A common mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs has not been found. This stems partly.
Indirect activation of neurotransmitter receptors by antidepressants may also lead via increases in endogenous levels of serotonin in synapses in specific brain regions to activation of various G proteins coupled to a receptor signal of transduction transcription factors and neurotrophic factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor BDNF. 22 rows A possible common mechanism of action of antidepressant treatments. Reduction in the.
Antidepressant32 However no drug appears to work more rapidly than another and the time course is generally prolonged. Nonetheless some data3334 suggest that drugs that have actions on both serotonergic and noradrenergic systems dual-action compounds have a quicker onset of action than that of other available antidepressants. Mirtazapine is primarily used for major depressive disorder and other mood disorders.
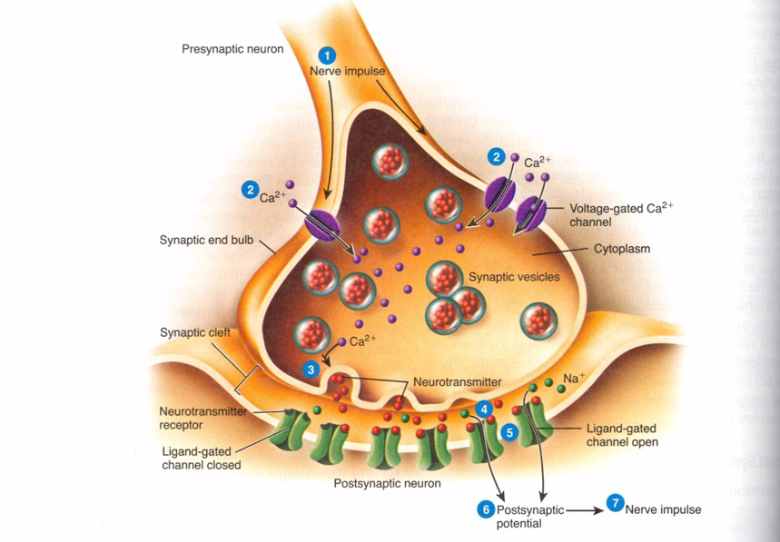
Onset of action appears faster than some selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRI and similar to tricyclic antidepressants. In 2010 NICE recommended generic SSRIs as first line choices as they are equally effective as other antidepressants and have a favourable risk. The termination of action of biogenic amines norepinephrine NE and serotonin 5-HT is determined by reuptake into the presynaptic terminal.
Drugs that block reuptake such as tricyclic antidepressants increase the efficacy of those transmitters by allowing them to remain in the synaptic cleft and activate the receptors longer Figure I-51. Antidepressants work by controlling the balance of the neurochemistry in the brain. There are three chemicals referred to as neurotransmitters.
Serotonin 5HT or 5-hydroxytryptamine norepinephrine NE and dopamine DA. Each class of antidepressant has a mechanism that works to increase the levels of these neurotransmitters. Early antidepressant medicationstricyclic antidepressants TCAs and monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIswere discovered through astute clinical observations.
These first-generation medications were effective because they enhanced serotonergic or noradrenergic mechanisms or both. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or SSRIs are the most widely used class of antidepressants. They work by increasing the level of serotonin in the brain.
Unlike MAOIs and TCAs SSRIs do not significantly affect norepinephrine levels in the brain. Clomipramine Imipramine Amitriptyline 30 31 45 60 61. They act by inhibiting both transporters for serotonin and norepinephrine thereby preventing their.
How is vortioxetine different than other serotonin modulators. Difference between trazodones antidepressant vs hypnotic action. Role of postsynaptic 5ht-2 and 5ht-3 receptors.
Role of presynaptic alpha 2 receptor. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF ANTIDEPRESSANTS AND MOOD STABILIZERS. Bipolardisorder BPDtheprovinceof moodstabilizers has long been considered a recurrent disorder.
For more than50yearslithiumtheprototypalmoodstabilizerhas been known to be effective not only in acute mania but alsointheprophylaxisofrecurrentepisodesofmaniaand. Cyclic antidepressants ease depression by affecting chemical messengers neurotransmitters used to communicate between brain cells. Like most antidepressants cyclic antidepressants work by ultimately effecting changes in brain chemistry and communication in brain nerve cell circuitry known to regulate mood to help relieve depression.