Now in eLife Célia Souque José A. But the efficiency of antibiotics is compromised by a growing number of antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
This is the first of two articles about the antibiotic resistance crisis.
Antibiotic resistance articles 2015. The antibiotic resistance crisis. Causes and threats P T. Author C Lee Ventola.
PMC4378521 Abstract Decades after the first patients were treated with antibiotics bacterial infections have again become a threat because of the rapid emergence of resistant bacteria-a crisis attributed to abuse. This is the first of two articles about the antibiotic resistance crisis. Part 2 will discuss strategies to manage the crisis and new agents for the treatment of bacterial infections.
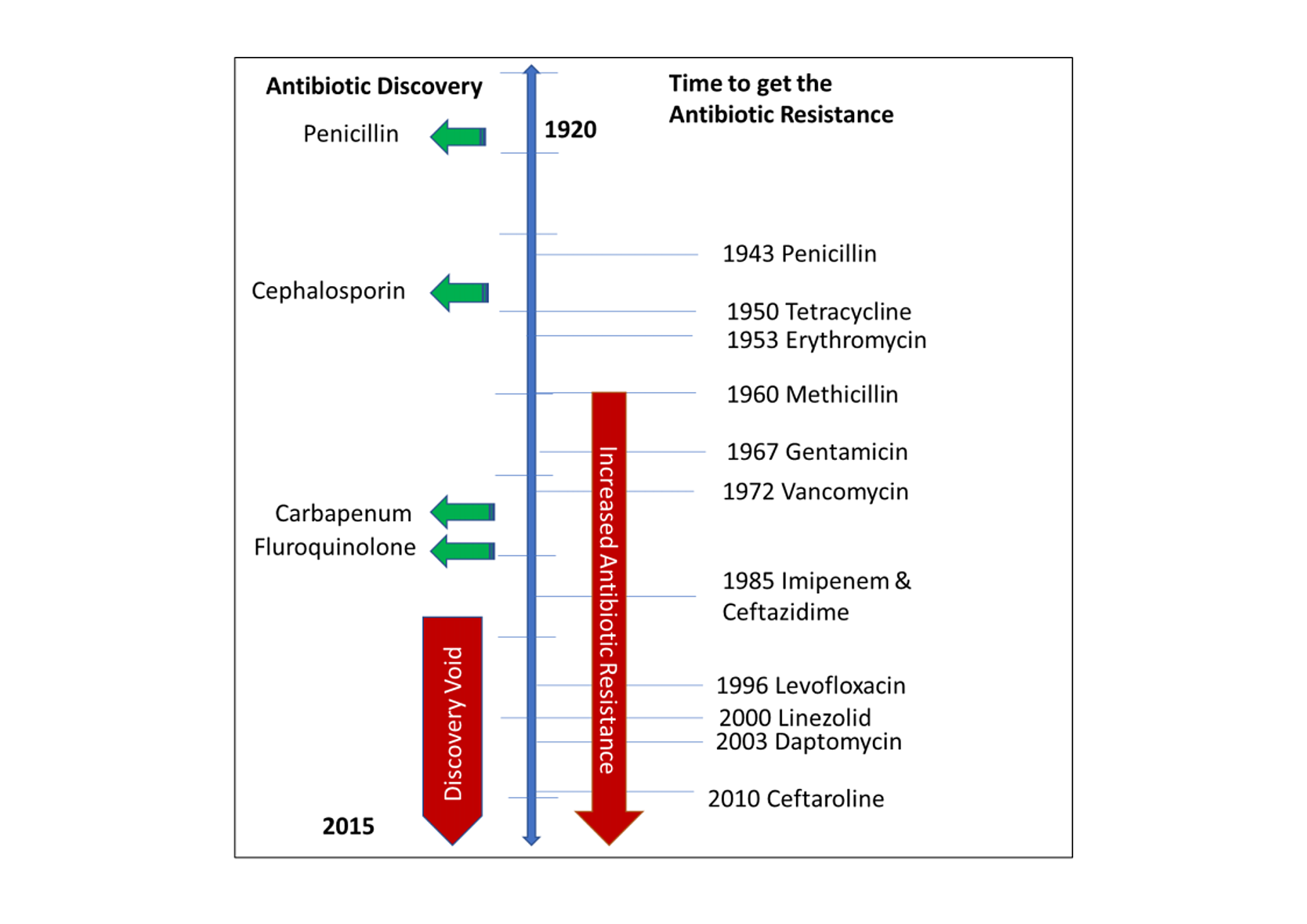
The rapid emergence of resistant bacteria is occurring worldwide endangering the efficacy of antibiotics which have transformed medicine and saved millions of lives16Many decades after the first patients were treated with antibiotics. Antibiotic resistance happens when bacteria change and become resistant to the antibiotics used to treat the infections they cause. Over-use and misuse of antibiotics increase the development of resistant bacteria and this survey points out some of the practices gaps in understanding and misconceptions which contribute to this phenomenon.
Antibiotic resistance is ancient and the resistome is a dynamic and mounting problem. Causes of the global resistome are overpopulation enhanced global migration increased use of antibiotics in clinics and animal production selection pressure poor sanitation wildlife spread and poor sewerage disposal system12 Antibiotic treatment is one of the main approaches of. Antimicrobial resistance AMR became in the last two decades a global threat to public health systems in the world.
Since the antibiotic era with the discovery of the first antibiotics that provided consistent health benefits to human medicine the misuse and abuse of antimicrobials in veterinary and human medicine have accelerated the growing worldwide phenomenon of AMR. Responsible for intrinsic antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Antibiotic resistance can be acquired by bacteria through chromosomal mutations or via horizontal gene transfer from other bacteria.
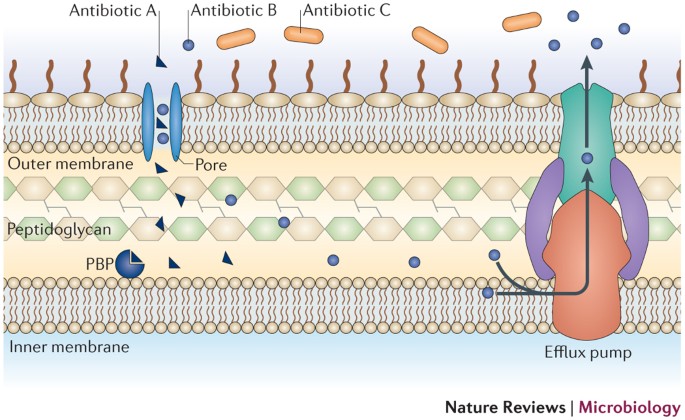
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria can develop mainly due to three mechanisms Figure 2. I Decreased influx or increased efflux of antibiotics. Antibiotic entry into the cell is mainly through porins.
The multivariate regression model used for explaining antibiotic resistance is where the dependent variable ABRAntibiotic Resistance Rate is the rate of resistance to antibiotics measured in bacteria causing bloodstream infections i 1 2 N is the subscript representing country and t 1 2 T represents the time unit in years. 13 rows On CDCs website antibiotic resistance is also referred to as antimicrobial. Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest public health challenges of our time.
Each year in the US at least 28 million people get an antibiotic-resistant infection and more than 35000 people die. Fighting this threat is a public health priority that requires a collaborative global approach across sectors. CDC is working to combat this.
Antibiotic resistance is considered one of the greatest threats to public health in the UK and worldwide. Primary care is responsible for over 75 of all antibiotics prescribed and therefore an important contributor to antibiotic resistance in the community2 3 Oral antibiotics profoundly affect bacteria in the lower gastro-intestinal tract which are thought to be the. 09212015 0308 PM.
Im very concerned about the consequences of antibiotic resistance. Weve been thinking as a society that antibiotics are basically free that we can take them. Antibiotic resistance is a worldwide problem threatening our ability to treat infections Infections caused by multi-resistant bacteria are increasing among the elderly living in nursing homes NH 24The elderly are the age group with the highest prevalence of antibiotic use in Norway Anatomical and physiologic changes caused by aging 6 7 usage of urinary catheters nasogastric.
The Scientists articles tagged with. Bacteria-infecting viruses affect the composition and behavior of microbes in the. If you ask where were having the most trouble in the world of antibiotic resistance it is with Gram-negative bacteria said Stephen Trent corresponding author of the study and a UGA.
Now in eLife Célia Souque José A. Escudero and Craig MacLean of the University of Oxford and the Universidade Complutense de Madrid report new insights into how bacteria evolve on demand when exposed to antibiotic treatment Souque et al 2021Souque et al. Used two strains of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa differing only by the presence or absence of a functional integrase.
Antibiotics represent one of the most successful forms of therapy in medicine. But the efficiency of antibiotics is compromised by a growing number of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Antibiotic resistance which is implicated in elevated morbidity and mortality rates as well as in the increased treatment costs is considered to be one of the major global public health threats.
As predicted almost 70 years ago by the man who discovered the first antibiotic drug resistance is upon us. A 2013 report from the Centers for. Devoted to overcoming the global spread of antimicrobial resistance and healthcare-associated infections Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Control.