
During the eighteen months following delivery the mean serum alkaline phosphatase activities were significantly raised. Alkaline phosphatase ALP is an enzyme found in most tissues in the human body.
The normal range of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is 20 to 140UL although this can vary from lab to lab.
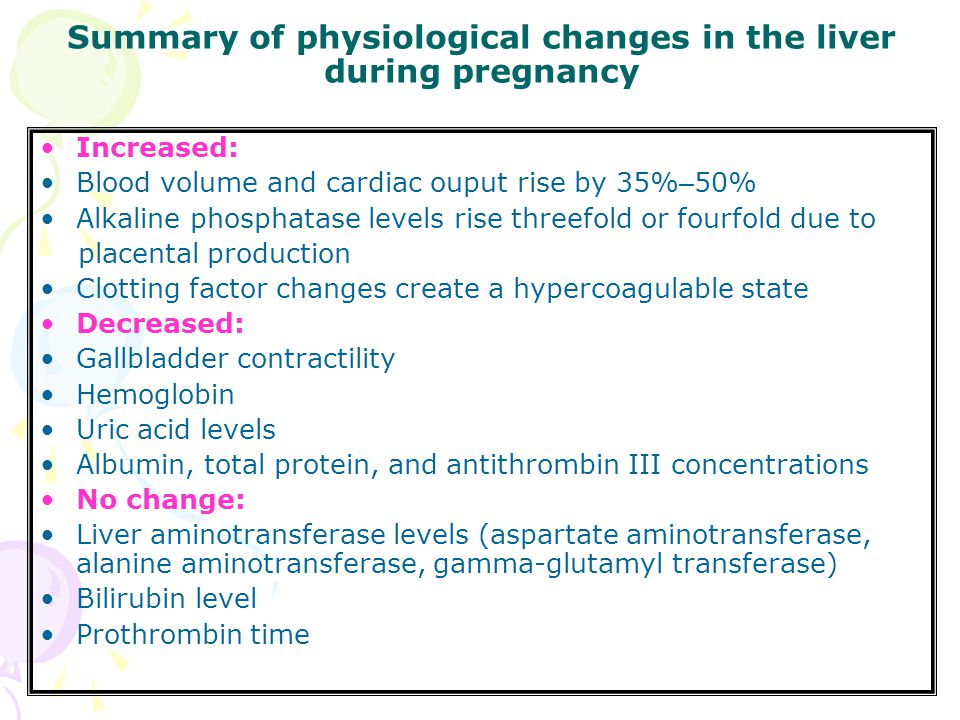
Alkaline phosphatase elevated in pregnancy. Elevation of alkaline phosphatase level according to the gestational age. ALP is an enzyme produced by liver bones kidneys small intestine and placenta. In a pregnant patient elevation of ALP may be related to HELLP syndrome intrahepatic cholestasis malignancy and liver or bone diseases.
Although obstetricians have observed elevations in serum alkaline phosphatase ALP during pregnancy these typically are not much more than twice the pre-pregnancy upper limit of normal. There is currently a paucity of cases in which exaggerated increases are observed. Seeing an atypically elevated value can be distressing to both the clinician and the patient especially when it is.
Alkaline phosphatase ALP is an enzyme found in most tissues in the human body. Alkaline phosphatase is increased during pregnancy and this is the norm since it is contained in large quantities in the placenta. This enzyme is also used in diagnostics.
Early elevated alkaline phosphatase increases the risk of large-for-gestational-age birth weight in pregnant women with normal glucose tolerance A significantly increased risk of LGA was associated with higher serum concentrations of ALP in pregnant women with NGT even it is in normal reference range. Some causes of elevated alkaline phosphatase include Paget disease healing fractures acromegaly osteogenic sarcoma liver or bone metastases leukemia myelofibrosis rickets osteomalacia hypervitaminosis D cholestasis of pregnancy biliary obstruction hyperthyroidism infiltrative liver diseases eg sarcoid TB amyloidosis abscess. During pregnancy alkaline phosphatase may reach three times the upper normal limit.
An abnormally elevated or rising alkaline phosphatase may be a marker of placental dysfunction. In cases with an abnormally elevated alkaline phosphatase more frequent monitoring may be indicated. During the eighteen months following delivery the mean serum alkaline phosphatase activities were significantly raised.
Increase in plasma volume which occurs during pregnancy is suggested as the cause of the fall in serum enzyme activity in the second trimester whereas the rise in enzyme activity in the third trimester is attributed to the well-known increase in serum alkaline phosphatase of. Children with elevated serum alkaline phosphatase for age eg 500 international unitsL in neonates or 1000 international unitsL in children up to nine years of age. What Does High Alkaline Phosphatase Mean.
The normal range of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is 20 to 140UL although this can vary from lab to lab. Children and pregnant women can have significantly higher levels of the enzyme in their blood. Values above 130 UL are.
Thus although the neutrophil alkaline phosphatase has diagnostic value in certain other disease states the above findings suggest that it is of little or no value in pregnancy. The possibility of hormonal control of the elevated level of neutrophil alkaline phosphatase seen in pregnancy and simulated pregnancy is discussed as is the possible relationship to increases in serum alkaline phosphatase in pregnancy. What Is Alkaline Phosphatase.
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme. An enzyme is a type of protein that catalyzes causes or accelerates chemical reactions in the body. ALP is produced mainly by the liver and bones but is also synthesized in smaller quantities by the intestines and kidneys.
ALP is also secreted from the placenta during pregnancy. Elevated alkaline phosphatase levels lead to the inconsistent intracellular fat depots which release itself into the bloodstream. Cancer- Cancer causes elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase in the bodies of the patients.
Mostly its found in the liver and the bones. A recent study compared healthy women and women with breast cancer. Undifferentiated pluripotent stem cells have elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase on their cell membrane therefore alkaline phosphatase staining is used to detect these cells and to test pluripotency ie embryonic stem cells or embryonal carcinoma cells.
If alkaline phosphatase is higher than normal values the patient may have healing fractures Paget disease acromegaly liver metastases bone metastases osteogenic sarcoma leukemia rickets myelofibrosis osteomalacia biliary obstruction pregnancy cholestasis hypervitaminosis D hyperthyroidism cirrhosis liver diseases infiltrative or myeloma. Bacterial toxin lipopolysaccharide LPS long recognized as a potent proinflammatory mediator has been identified as a risk factor for pregnancy complications. Alkaline phosphatase AP isozymes have been shown to detoxify LPS by dephosphorylation.