When the body fights bacterial or viral infections it can become immune to. Remarkably the bacterial adaptive immune system known as CRISPR dont worry about what it stands for is based on a similar principle.

Innate immune responses are activated directly by pathogens and defend all multicellular organisms against infection.
Adaptive immune response to bacteria. Innate and adaptive immunity in bacteria. Mechanisms of programmed genetic variation to fight bacteriophages Bacteria are constantly challenged by bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria the most abundant microorganism on earth. Bacteria have evolved a variety of immunity mechanisms to resist bacteriophage infection.
Adaptive Immunity to Bacteria Overview. The adaptive and innate responses work together to destroy bacteria. The adaptive response ensures the innate.
The response to extracellular infection involves complement and phagocytosis. B cell and T H 2. Innate immune responses are activated directly by pathogens and defend all multicellular organisms against infection.
In vertebrates pathogens together with the innate immune responses they activate stimulate adaptive more The function of adaptive immune responses is to destroy invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. It is also linked to the adaptive immune response. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5.
Nature 410 10991103 2001. Th17 cells are induced early in the adaptive response to extracellular bacteria and help to recruit the neutrophil response that eliminates these pathogens. They also direct the destructive inflammatory responses that are part of many autoimmune diseases.
Innate and adaptive immune responses against Staphylococcus aureus skin infections Staphylococcus aureus is an important human pathogen that is responsible for the vast majority of bacterial skin and soft tissue infections in humans. Overall these data suggest that both cell-mediated immunity and innate immunity may play important roles in the protection against intracellular bacterial infection as they do in mammals. Our study would also contribute toward the understanding of immune responses that provide protection against other intracellular pathogens.
In this case there is no learned response no matter how many times the body is exposed to the same organism. The second line of defense is called adaptive immunity. When the body fights bacterial or viral infections it can become immune to.
Innate and adaptive host immune responses are fundamental for defense against streptococcal pharyngitis and are central to the clinical manifestation of disease. Streptococcus pyogenes the Group A Streptococcus GAS is the most common cause of. The adaptive immune system takes over if the innate immune system is not able to destroy the germs.
It specifically targets the type of germ that is causing the infection. But to do that it first needs to identify the germ. This means that it is slower to respond than the innate immune system but when it does it is more accurate.
Bacteria arent nearly as complex as humans yet they too have an adaptive immune system. How does it work. Remarkably the bacterial adaptive immune system known as CRISPR dont worry about what it stands for is based on a similar principle.
Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses during Listeria monocytogenes Infection. It could be argued that we understand the immune response to infection with Listeria monocytogenes better than the immunity elicited by any other bacteria. Monocytogenes are Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically tractable and easy to cultivate in.
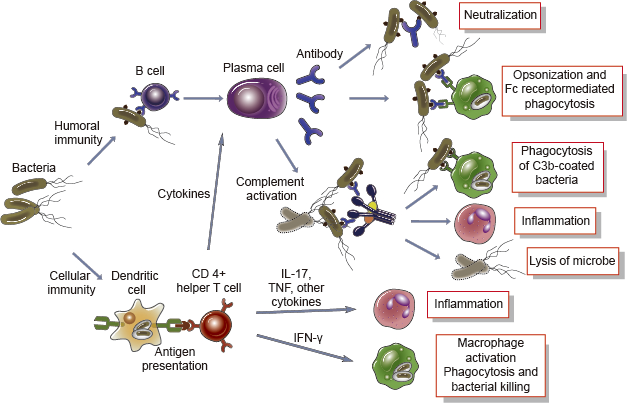
The adaptive immune response which includes both B cell-based humoral immunity and T cell-based cellular immunity reacts much more specifically and powerfully to invading pathogens. B cells produce antibodies that help to control microbial invasion in a variety of ways as described in this interactive. Overview of Adaptive Immune Defenses One of the major defenses against bacteria is the immune defenses production of antibody molecules against the organism.
The tips of the antibody called the Fab portion Figure 56. 1 have shapes that are complementary to portions of bacterial proteins and polysaccharides called epitopes. 27 Adaptive Immunity Antigens and the Adaptive Immune Response.
Adaptive immunity occurs after exposure to an antigen either from a pathogen or a vaccination. The adaptive or acquired immune response takes days or even weeks to become establishedmuch longer than the innate response. However adaptive immunity is more specific to an invading pathogen.